Air and Atmosphere Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5, Air and Atmosphere Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-5. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -5 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Air and Atmosphere Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 6th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-5 | Air and Atmosphere |
| Unit-1 | Air and Atmosphere |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Air and Atmosphere Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
Question: 1. State what do you understand by the term ‘air’. Explain its importance to mankind.
Answer: Air is a mixture whose composition varies at different intervals of time and different places of the world. Man cannot survive without air and water and hence the air is very essential for survival.
Question: 2. Give a brief account of the discovery of air & the scientists involved.
Answer: John Mayow (1674) proved air has two components – active and inactive components. Other scientists (1800s) discovered noble gases, CO2, water vapours.
Question: 3. What is meant by the term ‘atmosphere’. State the role played by the atmosphere for the survival of mankind.
Answer: A blanket of air around earth is called the atmosphere. Without an atmosphere, life would not be possible as the atmosphere protects us from harmful gases. We could not live without the air present in the atmosphere. In the absence of the atmosphere, the earth would get so cold at night that we would not be able to survive. No CO2 and N2 for plants without atmosphere.
Question: 4. Explain in brief the different layers of the atmosphere & the basic functions of the main layers.
Answer:
| Layers of atmosphere | Distance from earth (approximate) | Basic Function |
| (i) Troposphere | 0 to 10 kilometers | The troposphere contains most of the air and oxygen in the atmosphere. This air is fit for respiration and survival of living organisms. Weather conditions are formed in the troposphere. |
| (ii) Stratosphere | 10 to 50 kilometers | The stratosphere contains the ozone layer which prevents the harmful effects of the sun (U. V. rays) from reaching the earth. |
| (iii) Mesosphere | 50 to 80 kilometers | The mesosphere is a very cold layer and most meteors burn up in this layer and hence are prevented from entering the earth’s atmosphere |
| Thermosphere | 80 to 320 kilometers | – |
Question: 5. Describe a simple experiment with the help of a diagram to show that –
a] Air occupies space
b] Air has mass
c] Air exerts pressure
d] Air is highly compressible
Answer: (a) Air occupies space —
![a] Air occupies space](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/a-Air-occupies-space-300x153.png)
1. Press an inverted glass
2. Tilt the tumbler to one side, tumbler over the water.
Observation : On tilting the tumbler, bubbles of air are seen coming out. Water slowly enters the tumbler to take place of the trapped air in the tumbler.
Conclusion : Air occupies space (the space in the tumbler was occupied by air).
(b) Air has mass —
![b] Air has mass](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/b-Air-has-mass-300x167.png)
1. An inflated balloon is placed on one side of the scale.
Observation : It is seen that the scale moves towards one side. It moves on the side on which the inflated balloon was placed.
Conclusion : Air has mass.
(c) Air exerts pressure —
![c] Air exerts pressure](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/c-Air-exerts-pressure.png)
1. Take an open can, fill it with water and heat it. On formation of steam, place the cap on tightly and keep the can aside.
Observation : On condensation of the steam the pressure inside the can reduces. The air outside, exerts pressure on the can which crumples slowly.
Conclusion : Air exerts pressure.
(d) Air is highly compressible —
![d] Air is highly compressible](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/d-Air-is-highly-compressible-300x165.png)
1. A leak proof syringe filled completely with air only (i.e. empty) is taken.
Observation : On pressing the piston of the syringe, the piston moves inwards. Air (gas) inside the syringe has maximum inter-molecular space and is highly compressible.
Conclusion : Air is highly compressible.
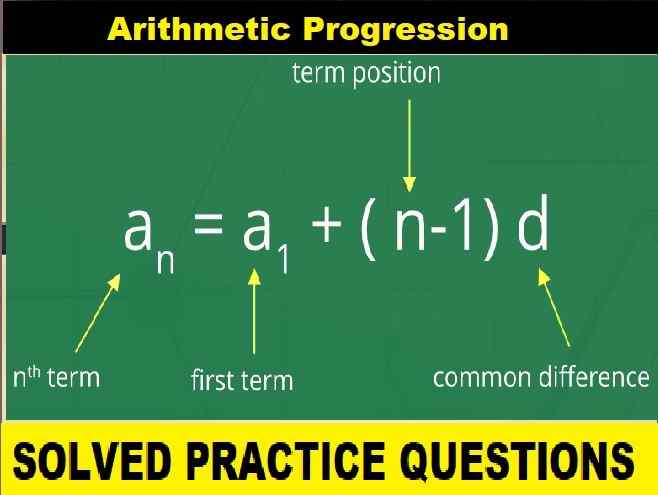
Question: 6. Name the components of air with their approximate percentage by volume in air. Does the percentage by volume of each component remain the same, in the atmosphere of different parts of the world.
Answer: The main components of the air are :
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
Composition of air by volume:
Nitrogen: 78% or 4/5 th
Oxygen: 21% or 1/5 th
Carbon dioxide: 0.03 – 0.04%
Inert gases: 0.9%
[Water vapours, dust particles, other impurities]: variable
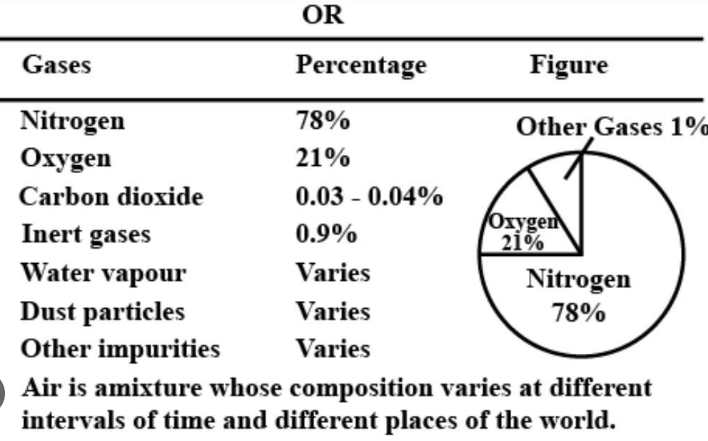
Air is a mixture whose composition varies at different intervals of time and different places of the world.
Question: 7. With the help of a labeled diagram, describe a simple experiment to show the presence of oxygen & nitrogen in air using a piece of white phosphorus.
Answer: Activity to show the presence of oxygen and nitrogen in air using a piece of white phosphorous.

1. A trough is taken and filled with water.
2. Over it is placed a bell-jar marked with five equal parts.
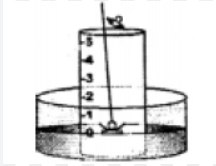
3. A crucible containing white phosphorus is placed on a cork.
4. The cork is made to float on the water.

5. A heated iron rod is them taken.
6. The phosphorus is ignited with the heated rod.
Observation : Dense white fumes of phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) are formed when the phosphorus (P) burns in the active component of air (oxygen).
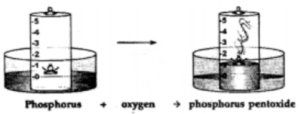
The rise in the level of water in the bell-jar is by – 1/5

Conclusion: Oxygen 1/ 5 Supports Used up in Active (approx. vol.) combustion buring compound
Nitrogen 4 / 5 Does not Remains In Active (approx . vol.) support behind in the component combustion bell-jar
The active component of air i.e. oxygen (1/5 of air) is used up in burning. The remaining inactive component of air i.e. nitrogen (4/ 5 of air) is not used up in burning.
Question: 8. You are given a test tube with two outlets and a bottle of lime water. Using the same, how would you demonstrate experimentally the presence of carbon dioxide in air.
Answer: Procedure:
1. Take lime water in a test tube with two outlets ‘A’ and ‘B’ as shown above.
2. Air is sucked slowly through the outlet ‘B’.
3. Air moves in through end ‘A’ and passes through the lime water.
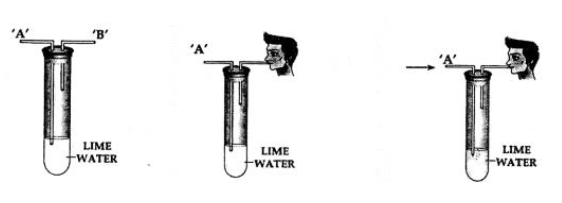
Observation: The line water in the test tube turns milky.
Conclusion: Air which is sucked in from and ‘A’ contains carbon dioxide which turns the lime water milky. Hence, air contains – carbon dioxide.
Question: 9. Give a reason why water droplets appear on the outer surface of a tumbler containing ice.
Answer: Water vapour present in air, condenses on the cooler surface of the tumbler. Hence they condenses into tiny water droplets.
Question: 10. Explain the importance of nitrogen of the air for plant growth.
Answer: Nitrogen of air is converted to soluble nitrogenous compounds in the soil in the presence of air and moisture. These are absorbed by plants and converted to plant proteins.
Question: 11. Give a reason why nitrogen is filled in food packets & not oxygen.
Answer: Give a reason why nitrogen is filled in food packets & not oxygen:
- Food material containing fat or oil when left for a long time becomes rancid i.e., smell and taste changes. This is because they get oxidized when they come in contact with atmospheric oxygen.
- Nitrogen gas is filled in the food packets to prevent oxidation as the Nitrogen is nonreactive in nature.
- It keeps the food fresh and preserved by reducing the bacterial growth in the food packages.
Question: 12. State what would happen, if the air above the earth contained mainly oxygen & no nitrogen.
Answer: Nitrogen is utilised by plants for their growth and development. Free nitrogen of the air is converted to nitrogen compounds which are absorbed by the plants and converted to plant proteins. In the absence of nitrogen no plants will be survived on the earth.
Question: 13. State the utility of oxygen for respiration in –
a] living organisms
b] plants
Answer: (a) Respiration in living organisms :
Respiration— It is a process whereby living things
1. Use oxygen from their air to oxidize food substances mainly glucose, in their body cells.
2. Release energy in the form of heat.
3. Carbon dioxide and water vapour are also produced and released in the exhaled.
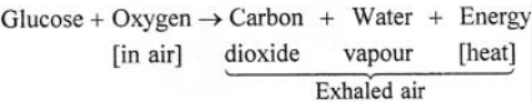

Process—
1. Inhaled air— Oxygen from inhaled air dissolves in the blood stream in the lungs. It is carried to the cells where the food materials i.e. glucose is oxidized by the oxygen.
2. Exhaled air— Carbon dioxide, water vapour and heat energy diffuse out of the lungs as exhaled air.
3. Energy liberated— The energy liberated is utilized for metabolic activities and maintains the body temperature
(b) Respiration in plants :
1. Plants respire during the day and night.
2. Plants— Respire through tiny pores on the surface of the leaves called ‘stomata’.
3. The stomata help in taking in oxygen of the air and giving out carbon dioxide. Thus, they function as respiratory organs.
4. Plants do not perform bodily activities and hence need less energy than animals. The rate of respiration in plants is thereby slower than in animals.
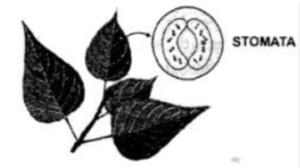
Photosynthesis in plants:
Photosynthesis in plants: is a process by which green plants prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
1. In the leaf of a green plant are present leaf cells which contain chloroplasts in which is present a green pigment called chlorophyll.
2. During photosynthesis which occurs during daytime, carbon dioxide and water in the presence sunlight and chlorophyll is changed into glucose and oxygen is released out.

3. Hence oxygen in the air is renewed by photosynthesis and therefore the amount of oxygen in air does not get depleted or removed from air.
Question: 14. Compare respiration and combustion – both involving oxygen of the air.
Answer: Respiration is a process whereby living organisms:
1. Use oxygen from the air to oxidize food substances mainly glucose, in their body cells.
2. Release energy in the form of heat.
3. Carbon dioxide and water vapour are also produced and released in the exhaled air.

Combustion or burning, involves oxidation i.e. combination of substances like fuels with oxygen or air generally resulting in production of heat and light.
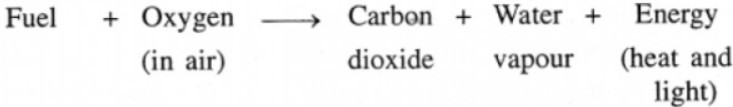
Carbon dioxide is released into the air as a result of all burning.
Question: 15. Explain the importance of carbon dioxide for –
a] photosynthesis
b] warming the earth’s environment.
State what would happen if excess carbon dioxide as a pollutant is released into the atmosphere.
Answer: (a) During photosynthesis which occurs during daytime, carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll is changed into carbohydrates and oxygen is released out.

Hence oxygen in the air is renewed by photosynthesis and therefore the amount of oxygen in air does not get depleted or removed from air.
(b) Infrared (I.R.), visible rays and ultra violet (U.V.) rays are present in the earth’s surface.
The reflected U.V. rays from the earth’s surface pass through the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, but the I. R. rays are prevented by the carbon dioxide from being radiated out of the earth’s surface. This results in the earth’s environment staying warm. The thick CO2 layer prevents the heat radiations from being radiated out which results in a rise in global temperature.
Reason: It results in a rise in global temperature.
Question: 16. State in brief how water vapour in the atmosphere determines the climatic conditions.
Answer: Water vapour in the atmosphere in excess :
(a) Minimizes the rate of evaporation.
(b) Produces rain, mist etc. thereby determining climatic conditions. The rain serves as a natural source of water for plants and animals.
Question: 17. Give a reason why two different rare [inert] gases find application in advertisement sings and fluorescent bulbs.
Answer: 1. Neon – In neon sign advertisements A brilliant red glow is seen on passage of an electric current through neon gas at low pressure. The colour can be changed by mixing mercury vapour and argon with neon.
2. Xenon – In fluorescent bulbs flash bulbs and lasers. It emits intense white light in discharge tubes.
Question: 18. A mixture has a variable composition. Give three other reasons why air is considered a mixture and not a compound.
Answer: Air is a mixture because :
1. Air has no formula, a mixture has no formula whereas compound has a formula.
2. No energy changes are involved to form air from various gases.
3. When air is formed out of its constituents no change in mass nor change in volume takes place.
4. Properties of air vary from place to place and time to time. i.e. there is more CO2 in towns as compared to villages where more oxygen prevales as compared to towns.
5. Components of air can be separated by simple physical methods.
Question: 19. State a reason why there is a balance in the amount of carbon dioxide in the air, even though carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere by various processes.
Answer: By the way of photosynthesis in plants which which occurs during daytime, carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll is changed into carbohydrates and oxygen is released out.

Hence, oxygen in the air is renewed by photosynthesis and therefore the amount of oxygen in air does not get depleted or removed from air.
Question: 20. Name three different appliances where air is utilized.
Answer:
1. Vehicles – Run on tyres which are inflated with air.
2. Brake mechanisms – Of trains and other machines, work on compressed air.
3. Pumps and siphons – Work on air pressure.
—: End of Air and Atmosphere Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5 :—
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.