Atmospheric Pollution Exe-8D Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-8. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-8 Atmospheric Pollution with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Atmospheric Pollution Exe-8D Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-8 | Atmospheric Pollution |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 8D Structured/Application/Skill Answer Type (Ozone) |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
D. Exercise – 8D Structured/Application/Skill Answer Type
Atmospheric Pollution Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-145
Question 1.
Study the following figure and answer the questions that follow :
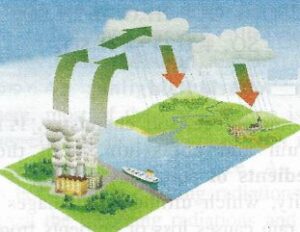
(a) What phenomenon is depicted in this figure ?
(b) Mention the cause of it and give the reactions involved.
(c) State any two consequences of the above phenomenon.
(d) List the ways by which you can reduce and/or prevent it from happening.
Answer:
(a) Acid rain
(b) Fossil fuels contain compounds of nitrogen and sulphur in addition to carbon. Due to combustion of these fuels, large amounts of sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen and carbon dioxide get discharged into the atmosphere. These oxides dissolve in rainwater to form mineral acids causing acid rain.
Formation of sulphuric acid : Sulphur dioxide is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen into sulphur trioxide which combines with water to form sulphuric acid.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⟶ 2SO3 (g)
SO3 (g) + H2O (l) ⟶ H2SO4 (aq)
Formation of nitric acid : Oxides of nitrogen are produced naturally during thunder and lightning. They are also produced by internal combustion engines.
N2 + O2 high temperature → (3000°C) 2NO
Nitrogen oxide then gets oxidized in the atmosphere to nitrogen dioxide.
2NO + O2 ⟶ 2NO2
Nitrogen dioxide combines with water to form a mixture of nitrous acid and nitric acid which causes acid rain.
2NO2 + H2O ⟶ HNO2 + HNO3
(c) Two consequences of acid rain are :
- Acid rain affects soil chemistry. It removes calcium and potassium, both the basic ingredients of soil, thus making it lose its fertility, which ultimately damages forests. Acid rain causes nutrient loss from plants thus damaging their leaves.
- The water of lakes and rivers is gradually becoming acidic due to acid rain, which is affecting aquatic life.
(d) The ways to reduce and/or prevent acid rain are :
- Use coal or oil with low sulphur content to reduce the emission of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen.
- Use of scrubber (a device which absorbs gaseous pollutants) for removing sulphur dioxide from a smoke stack.
— : End of Atmospheric Pollution Exe-8D Structured Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends