Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-4. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 4C |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
C. Exercise – 4C
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-69
Question 1. Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment led to the discovery of :
(i) Electron
(ii) Proton
(iii) Atomic nucleus
(iv) Neutron
Answer:
(iii) Atomic nucleus
(b) The number of valence electrons in O2- is :
(i) 6
(ii) 8
(iii) 10
(iv) 4
Answer:
(ii) 8
(c) Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of potassium ?
(i) 2, 8, 9
(ii) 8, 2, 9
(iii) 2, 8, 8, 1
(iv) 1, 2, 8, 8
Answer:
(iii) 2, 8, 8, 1
(d) The mass number of an atom whose unipositive ion has 10 electrons and 12 neutrons is :
(i) 23
(ii) 22
(iii) 20
(iv) 21
Answer:
(i) 23
(e) The number of valence electrons in Cl- ion is:
(i) 16
(ii) 8
(iii) 17
(iv) 18
Answer:
(ii) 8
(f) The correct electronic configuration of Fluorine is:
(i) 2, 8
(ii) 8, 2, 1
(ii) 7, 2
(iv) 2, 7
Answer:
(iv) 2, 7
(g) An element ‘A’ has 15 electrons and 16 neutrons. The correct representation of this element is:
(i) 1615A
(ii) 3116A
(iii) 3115A
(iv) 1516A
Answer:
(iii) 3115A
(h) An atom having 3 protons and 4 neutrons will have a valency of :
(i) 3
(ii) 7
(iii) 1
(iv) 4
Answer:
(iii) 1
(i) Elements with valency 2 are:
(i) Always metals
(ii) Always non-metals
(iii) Can be metals or non-metals
(iv) Metalloids (semi metals)
Answer:
(iii) Can be metals or non-metals
(j) Nucleus of an atom is composed of :
(i) Electrons and neutrons
(ii) Protons and neutrons
(iii) Protons, neutrons and electrons
(iv) Electrons and protons
Answer:
(ii) Protons and neutrons
(k) There are 3 electrons in M shell of an atom. Its atomic number is:
(i) 11
(ii) 13
(iii) 15
(iv) 3
Answer:
(ii) 13
(l) The maximum number of electrons that M shell can occupy is:
(i) 18
(ii) 8
(iii) 2
(iv) 10
Answer:
(i) 18
(m) Which orbit is nearest to the nucleus of an atom?
(i) K
(ii) L
(iii) M
(iv) N
Answer:
(i) K
C. Exercise – 4C
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-70
(n) Atoms combine to attain an electronic configuration similar to their nearest :
(i) Metals
(ii) Noble gas
(iii) Non-metals
(iv) Semi metals
Answer:
(ii) Noble gas
(o) Isotopes differ in the number of their:
(i) Electrons
(ii) Protons
(iii) Neutrons
(iv) Electrons and protons
Answer:
(iii) Neutrons
Question 2.
Name the following:
(a) The element which does not contain any neutron in its nucleus.
(b) An element having valency ‘zero’.
(c) Metal with valency 2
(d) Two atoms having the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.
(e) The shell closest to the nucleus of an atom.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Helium
(c) Magnesium
(d) Isotopes
(e) K shell
Question 3.
Match the atomic numbers 4,14,8,15 and 19 with each of the following:
(a) A solid non-metal of valency 3.
(b) A gas of valency 2.
(c) A metal of valency 1.
(d) A non-metal of valency 4.
Answer:
| Atomic Number | Name with valency |
| (a) 15 | A solid non-metal of valency 3 |
| (b) 8 | A gas of valency 2 |
| (c) 19 | A metal of valency 1 |
| (d) 14 | A non-metal of valency 4 |
Question 4.
(a) What are inert elements?
(b) Why do they exist as monoatoms in molecules?
(c)What are valence electrons?
Answer:
(a) The elements have a complete outermost shell, i.e. 2 or 8 electrons. They ordinarily do not enter intoany reaction.
(b) These exist as monoatoms because molecules of these elements contain only one atom.
(c) Valence electrons: The number of electrons present in the valence shell is known as valence electrons.
Question 5.
In what respects do the three isotopes of hydrogen differ? Give their structures.
Answer:
The three isotopes differ only due to their mass number which is respectively 1,![]() 2 and 3 and named protium, deuterium and tritium.
2 and 3 and named protium, deuterium and tritium.

(Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Chemistry Class-9 ICSE)
Question 6.
What is the significance of the number of protons found in the atoms of different elements?
Answer:
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines the element type of the atom.
Question 7.
Element X has electronic configuration 2,8,18,8,1. Without identifying X,
(a) Predict the sign and charge on a simple ion of X.
(b) Write if X will be an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent. Why?
Answer:
(a) X1+
(b) Oxidising agent, because it has the ability to donate electrons.
Question 8.
Define the terms:
(a) Mass number
(b) Ion
(c) Cation
(d) Anion
(e) Element
(f) orbit
Answer:
(a) Mass number is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
(b) Ion is an atom or molecule which carries a positive or negative charge because of loss or gain of electrons.
(c) Cation is a positively charged ion which is formed when an atom loses one or more electrons; for example, Na+, Hg2+ and Ca2+.
(d) Anion is a negatively charged ion which is formed when an atom gains one or more electrons; for example, Cl– and I–.
(e) Element is a substance which cannot be split up into two or more simple substances by usual chemical methods of applying heat, light or electric energy; for example, hydrogen, oxygen and chlorine.
(f) Orbit is a circular path around the nucleus in which electrons of the atom revolve.
Question 9.
From the symbol 2He4 for the element helium, write down the mass number and the atomic number of the element.
Answer:
Atomic number = 2
Mass number = 4
Question 10.
An atom of an element has two electrons in the M shell.
What is the (a) atomic number (b) number of protons in this element?
Answer:
Number of electrons in the M shell = 2
So, the number of electrons in the K and L shells will be = 2, 8
Hence, atomic number = 2 + 8 + 2 = 12
Number of protons = 12
Question 11.
Five atoms are labeled A to E
| Atoms | Mass No | Atomic No. |
| A | 40 | 20 |
| B | 19 | 9 |
| C | 7 | 3 |
| D | 16 | 8 |
| E | 14 | 7 |
(a) Which one of these atoms:
(i) contains 7 protons
(ii) has electronic configuration 2,7
(b) Write down the formula in the compound formed between C and D
(c) Predict : (i) metals (ii) non-metals
Answer:
(a)
(i) Atom E contains 7 protons.
(ii) Atom B has an electronic configuration 2, 7.
(b)
Atom C stands for 7Li3, Atom D stands for 8O16.
Hence, compound formula is Li2O.
(c)
Metals: A and C, Non-metals: B, D, E
Question 12.
12Mg24 and 12Mg26 are symbol of two isotope of magnesium.
(a) Compare the atom of these isotope with respect to:
(i) Composition of their Nuclei.
(i) Their electronic configuration.
(b) Give reason why two isotopes of magnesium have different mass numbers.
Answer:
(a)
(i)
| 12Mg24 | 12Mg26 | |
| No. of electrons | 12 | 12 |
| No. of protons | 12 | 12 |
| No. of neutrons | 24 – 12 = 12 | 26 – 12 = 14 |
Hence, composition of nuclei
12Mg24 →

(ii) Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
(b) Mass numbers of two isotopes of magnesium are different because of different number of neutrons, i.e. 12 and 14, respectively.
Question 13.
What are nucleons? How many nucleons are present in phosphorus? Draw its structure.
Answer:
Nucleons: Particles which constitute the nucleus are called nucleons.
Protons and neutrons are the nucleons.
Atomic mass of phosphorus = 31
Atomic number = 15
Question 14.
What are isotopes? With reference to which fundamental particle do isotopes differ? Give two uses of isotopes.
Answer:
Isotopes: Atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Isotopes differ with reference to neutrons.
Uses of isotopes:
Some isotopes are radioactive, i.e. isotopes of cobalt are used for treating cancer and other diseases.
An isotope of 235U is used as a fuel in a nuclear reactor.
(Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Chemistry Class-9 ICSE)
Question 15.
Why do 3517Cl and 3717Cl have the same chemical properties? In what respect do these atoms differ?
Answer:
Isotopes have the same atomic number i.e., the same number of electrons and protons and hence the same electronic configuration. Chemical properties are determined by the electronic configuration of an atom. Thus, the isotopes of an element are chemically alike.
Isotopes have different mass numbers [A] due to different number of neutrons. 3517Cl has 18 neutrons whereas 3717Cl has 20 neutrons. Due to different atomic masses these atoms differ in their physical properties like density, melting point, boiling point, etc.
Question 16.
Explain fractional atomic mass. What is the fractional mass of chlorine?
Answer:
Atomic masses of the isotopes of chlorine are 35 and 37. However, in any given sample of chlorine gas, the isotopes occur in the approximate ratio 3:1, 75% of Cl35 and 25% of Cl37. So, the relative atomic mass or atomic weight of chlorine is 35.5.
Fractional atomic mass of chlorine
At. Mass = 3(35) + 1(37) = 105 + 37
2 2
Question 17.
(a) What is meant by ‘atomic number of an element”?
(b) Complete the table given below
| No. of protons | No. of electrons | No. of Neutrons | Atomic Number | Mass number | |
| 17Cl35 | |||||
| 17Cl37 |
(c) Write down the electronic configuration of (i) chlorine atom (ii) chlorine ion
Answer:
(a) Atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
(b)
| No. of protons | No. of electrons | No. of neutrons | Atomic number | Mass number | |
| 17Cl35 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 17 | 35 |
| 17Cl37 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 17 | 37 |
(c)
(i) Electronic configuration of chlorine = 2, 8, 7
(ii) Electronic configuration of chlorine ion = 2, 8, 8
Question 18.
Draw diagrams representing the atomic structures of the following:
(a) Sodium atom
(b) Chlorine ion
(c) Carbon atom
(d) Oxygen ion
Answer:
(a) atomic structures of Sodium atom

(b) atomic structures of Chlorine ion
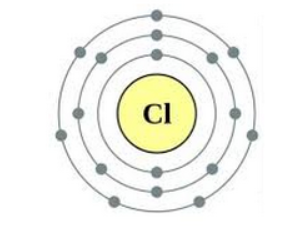
(c) atomic structures of Carbon atom

(d) atomic structures of Oxygen ion

Question 19.
Complete the following table relating to the atomic structure of some elements.
| Element Symbol | Atomic
Number |
Mass
Number |
Numbers of neutrons | Number of Electrons | Number of Protons |
| Li | 3 | 6 | |||
| Cl | 17 | 20 | |||
| Na | 12 | 11 | |||
| Al | 27 | 13 | |||
| S | 32 | 16 |
Answer:
| Element Symbol | Atomic
Number |
Mass
Number |
Numbers of Neutrons | Number of Electrons | Number of Protons |
| Li | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Cl | 17 | 37 | 20 | 17 | 17 |
| Na | 11 | 23 | 12 | 11 | 11 |
| Al | 13 | 27 | 14 | 13 | 13 |
| S | 16 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
C. Exercise – 4C
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-71
Question 20.
Give reasons
(a) Physical properties of isotopes are different.
(b) Argon does not react.
(c) Actual atomic mass is greater than mass number.
(d) 17Cl35 and 17Cl37 do not defer in their chemical reaction
Answer:
(a) Physical properties depend on atomic mass, and isotopes have different mass number, i.e. they have different number of neutrons. So, isotopes have different physical properties.
(b) Argon does not react as it has the outermost orbit complete, i.e. 8 electrons in the outermost shell.
(c) Actual atomic mass is greater than the mass number because the mass number is a whole number approximation of atomic mass unit. In fact, neutrons are slightly heavier than protons, and an atom has over 200 sub-atomic particles.
(d) are isotopes of chlorine element which differ in the number of neutrons, whereas chemical properties are determined by the electronic configuration of an atom. Isotopes of an element are chemically alike.
Question 21.
Give the use of the following isotopes:
(a) Radioactive isotopes
(b) 235U
(c) 60Co
(d) 131I
(e) 14C
Answer:
(a) Radioactive isotopes — Used in industry to detect the leakage in underground oil pipelines, gas pipelines and water pipelines.
(b) 235U — Used as fuel in nuclear reactors.
(c) 60Co — used in radiotherapy for treating cancer and other diseases.
(d) 131I — Used in treatment of goitre.
(e) 14C — Used for determining the age of historical and geological material.
Question 22.
How does the Modern atomic theory contradict and correlate with Dalton’s atomic theory?
Answer:
The latest research on the atom has proved that most of the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory contradict. However, Dalton was right that atoms take part in chemical reactions.
Comparisons of Dalton’s atomic theory with the modern atomic theory.
Dalton’s atomic theory:
(i) Atoms are indivisible.
(ii) Atoms of the same element are similar in every respect.
(iii) Atoms combine in a simple whole number ratio to form molecules.
(iv) Atoms of different elements are different.
(v) Atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Modern atomic theory:
(i) Atoms are no longer indivisible and consist of electrons, protons, neutrons and even more sub-particles.
(ii) Atoms of the same element may differ from one another called isotopes.
(iii) Atoms of different elements may be similar called isobars.
(iv) Atoms combine in a ratio which is not a simple whole number ratio; e.g. in sugar, the C12H22O11 ratio is not a whole number ratio.
Question 23.
Explain:
(a) Octet rule for formation of sodium chloride
(b) Duplet rule for formation of hydrogen
Answer:
Elements tend to combine with one another to attain the stable electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas.
(a) Octet rule for formation of Sodium chloride
Sodium atom has 1 electron in the valence shell which it donates to the chlorine atom with 7 electrons in the valence shell to attain the stable electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas, i.e. 8 electrons in the valence shell. This is known as the octet rule. These elements combine to form sodium chloride.
(b) Duplet rule for formation of Hydrogen
Hydrogen atom has one electron in the valence shell which it shares with another hydrogen atom having one electron to complete its duplet state, i.e. two electrons in the valence shell and resulting in the formation of hydrogen.
Question 24.
An element:
A atomic number 7 mass numbers 14
B electronic configuration 2,8,8
C electrons 13, neutrons 14
D Protons 18 neutrons 22
E Electronic configuration 2,8,8,1
State (i) Valency of each element (ii) which one is a metal (iii) which is non-metal (iv) which is an inert gas
Answer:
(i)
Element A
Atomic number = 7 = Number of electrons = 2, 5
Valency of A = 8 – 5 = 3
Element B
Electronic configuration 2, 8, 8
Valency of B = Zero
Element C has 13 electrons
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 3
Valency of C = 3
Element D
Protons = 18 = Electrons = 2, 8, 8
Valency of D = Zero
Element E
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 8, 1
Valency of E = 1
(ii) C and E are metals.
(iii) A is a non-metal.
(iv) A, C and E are not inert gases.
(Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Chemistry Class-9 ICSE)
Question 25.
Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 6,9 and 12 respectively. Which one:
(a) Forms an anion
(b) Forms a cation
(c) Has four electrons in its valence shell?
Answer:
Atomic numbers of X Y Z
6 9 12
(2, 4) (2, 7) (2, 8, 2)
(a) Y(2, 7) forms an anion.
(b) Z(2, 8, 2) forms a cation.
(c) X(2, 4) has four electrons in the valence shell
— : End of Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4C Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends