Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4D Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-4. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4D Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 4D |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
D. Exercise – 4D
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-74
Question 1.
How do atoms attain noble gas configurations?
Answer:
Combining atoms attain the noble gas configuration by transferring or sharing electrons.
Question 2.
Define electrovalent bond.
Answer:
The chemical bond formed due to the electrostatic force of attraction between a cation and an anion is called an electrovalent bond.
Question 3.
Elements are classified as metals, non-metal, metalloids and inert gases. Which of them form electrovalent bond?
Answer:
Metals have a tendency to lose their valence electrons (1, 2 or 3). So, they combine with non-metals which have 7, 6 or 5 electrons in their valence shell to form an electrovalent bond.
Question 4.
(a) An atom X has three electrons more than the noble gas configuration. What type of ion will it form?
(b) Write the formula of its (X)
(i) sulphate
(ii) nitrate
(iii). phosphate
(iv) carbonate
(v) hydroxide.
Answer:
(a) An atom X will lose its three electrons to acquire the noble gas configuration and form a positive ion (a cation).
(b) The formulae are
(i) X(SO4)3
(ii) X(NO3)3
(iii). XPO4
(iv) X2(CO3)3
(v) X(OH)3
Question 5.
Mention the basic tendency of an atom which makes it to combine with other atoms
Answer:
Besides chaos, everything in this world wants stability. The same is the case with atoms. For atoms, stability means having the electron arrangement of an inert gas, i.e. octet in the outermost shell. Helium has two electrons (duplet), while all other inert gases, i.e. neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon have eight electrons (octet) in the outermost shell.
Question 6.
What type of compounds are usually formed between metals and non-metals and why?
Answer:
Electrovalent compounds are usually formed between metals and non-metals.
Atoms of metallic elements which have 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons can lose electron(s) to atoms of non-metallic elements which have 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons and thereby form an electrovalent bond.
Question 7.
(a) In the formation of the compound XY2, an atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. What is the nature of bond in XY2?
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of this compound.
Answer:
(a) Nature of bond in XY2 is an ionic bond.
(b) Electron dot structure of XY2:
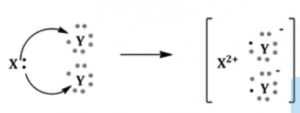
Question 8.
An atom X has 2, 8, 7 electrons in its shell. It combines with Y having 1 electron in its outermost shell.
(a) What type of bond will be formed between X and Y?
(b) Write the formula of the compound formed.
Answer:
(a) Ionic bond
(b) XY
Question 9.
Draw orbit structure diagram of
(a) sodium chloride (NaCl) and
(b) calcium oxide (CaO).
Answer:
(a) orbit structure diagram of NaCl

(b) orbit structure diagram of CaO

Question 10.
Compare :
(a) Sodium atom and sodium ion
(b) Chlorine atom and chloride ion, with respect to
(i) Atomic structure
(ii) Electrical state
Answer:
(a) Comparison of Sodium atom and sodium ion
| Sodium atom | Sodium ion |
| Sodium atom is electrically neutral. | Sodium ion is positively charged. |
| In sodium atom, there are 11 protons and 11 electrons, i.e. equal number of protons and electrons. | In sodium ion, there are 11 protons but 10 electrons, i.e. sodium ion contains lesser number of electrons. |
| Sodium atom has only one electron in its valence shell. | Sodium ion has 8 electrons in its valence shell. |
| Size of a sodium atom is larger than a sodium ion. | Size of a sodium ion is smaller than a sodium atom. |
(b)
In chlorine atom, the number of protons (17) is equal to the number of electrons (17).
In chloride ion, there are 17 protons but 18 electrons.
(i) Chlorine atom is electrically neutral. Chloride ion is negatively charged.
(ii) Chlorine ion is reactive. It reacts with sodium vigorously forming sodium chloride. Chloride ion is unreactive. It does not react with sodium.
Chlorine (Cl2) is a poisonous, toxic, corrosive gas which is used in the manufacture of bleaching agents and disinfectants. It is non-toxic and readily adsorbed by plants.
Question 11.
The electronic configuration of fluoride ion is the same as that of neon atom. What is the difference between the two?
Answer:
Fluoride ion is a negatively charged ion with 9 protons and 10 electrons.
Neon atom is electrically neutral with 10 protons and 10 electrons.
Question 12.
(a) What do you understand by redox reactions?
(b) Explain oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons.
Answer:
(a) Transfer of electron(s) is involved in the formation of an electrovalent bond. The electropositive atom undergoes oxidation, while the electronegative atom undergoes reduction. This is known as a redox reaction.
(b) Oxidation: In the electronic concept, oxidation is a process in which an atom or ion loses electron(s).
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–
Reduction: In the electronic concept, reduction is a process in which an atom or ion accepts electron(s).
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Question 13.
Potassium (At No. 19) and chlorine (At No. 17) form a compound. Explain the formation of the compound on the basis of:
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
(c) Oxidizing agent
(d) Reducing agent
Answer:
2K + Cl2 → 2KCl
(a) Oxidation: In the electronic concept, oxidation is a process in which an atom or ion loses electron(s).
K → K+ + e–
(b) Reduction: In the electronic concept, reduction is a process in which an atom or ion accepts electron(s).
Cl2 + 2e–→ 2Cl–
.(c) Oxidising agent
An oxidising agent oxidises other substances either by accepting electrons or by providing oxygen or an electronegative ion, or by removing hydrogen or an electropositive ion.
Cl2 + 2e–→ 2Cl–
(d) Reducing agent
A reducing agent reduces other substances either by providing electrons or by providing hydrogen or an electropositive ion, or by removing oxygen or an electronegative ion.
K → K+ + e–
— : End of Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4D Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends


