Atomic Structure Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4, Atomic Structure Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-4. We Provide Step by Step Solutions to Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
Atomic Structure Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure |
| Unit-1 | Atomic Structure |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Atomic Structure Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4
Question: 1. State the main postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory. How does the modern atomic theory contradict and correlate with Dalton’s atomic theory.
Answer: Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory:
- Matter consist of small indivisible particles called atoms.
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed.
- Atoms of the same element are alike in every aspect and differ from atoms of all other elements.
- Atoms combine with other atoms in simple whole number ratio’s forming compound atoms or molecules.
- An atom is the smallest unit of matter which takes part in a chemical reaction and all chemical changes result from separation or combination of atoms.
Contradictions with Modern atomic theory:
| Dalton’s atomic theory | Modern atomic theory |
|---|---|
| Atoms are indivisible and indestructible. | Atoms are divisible and destructible. |
| An atom is the smallest indivisible particle of an element | Atoms are divisible – consisting of subatomic particles like electrons, protons and neutrons. |
| Atoms of the same element are alike in all respects and differ from atoms of other elements. | Atoms of the same element may not be alike in all respects as seen in the case of isotopes which are atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass numbers. |
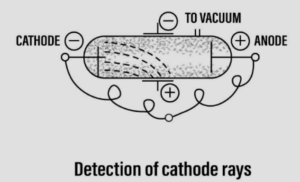
Question: 2. With reference to the discovery of the structure of an atom, explain in brief – William Crookes experiment for the discovery of cathode rays, followed by – J.J. Thomson’s experiment pertaining to the constituents of the cathode rays. State which sub-atomic particle was discovered from his experiment.
Answer: Discovery of the three subatomic particles – electrons, protons and neutrons:
Atom is built up of three sub-atomic particles –electrons, protons, and neutrons.
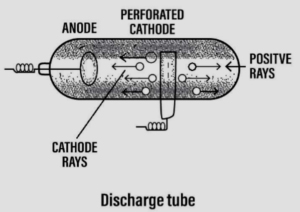
Discovery of cathode rays leading to the discovery of ‘electrons’
- Scientist – William Crookes [1878]
- Discovery – The cathode rays
Experiment:
Question: 3. Explain in brief -the Goldstein experiment which led to the discovery of the proton and Rutherford’s experiment which led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus.
Answer: Discovery of – Protons
- Discovery – Constituent of positive rays i.e. particles that contain – protons.
Experiment:

- Goldstein used a modified cathode ray tube with a perforated cathode.
- He observed a new type of rays produced from the anode passing through the holes of the perforated cathode. These rays were called anode rays.
Conclusion:
- Anode rays or positive rays consist of positively charged particles now called – protons.
- The positive rays were affected by electric & magnetic fields but – in a direction opposite to that of cathode rays.
- Thus with the discovery of the positive particles – proton was initiated.
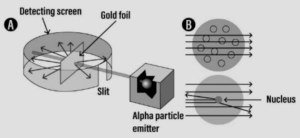
Discovery of – Atomic nucleus:
- Discovery – Study of the atomic model leading to the discovery of – atomic nucleus.
Experiment:
Question: 4. ‘Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed orbits or shells called energy levels’. State how these energy levels are represented.
Answer: (a) Electrons revolve around the nucleus in – fixed ‘orbits’ called energy levels
(b) The energy levels 1, 2, 3… are represented by – integer ‘n’ or as K, L, M, N…
(c) Electrons rotate around the nucleus, in one or more of the energy levels.
Question: 5. Draw a neat labelled diagram representing an atom. Name the three sub-atomic particles in the atom and represent them symbolically showing the mass and charge of each. State where the sub-atomic particles are present in the atom.
Answer:
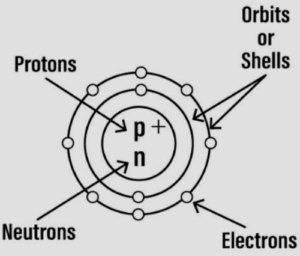
The three sub-atomic particles in the atom are:
| S. No. |
Sub-atomic particle |
Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Proton | +1p1 |
| 2. | Neutron | 0n1 |
| 3. | Electron | -1e0 |
Question: 6. Define the term – ‘atomic number’ of an atom. If an atom ‘A’ has an atomic number of eleven, state the number of protons and electrons it contains.
Answer: Atomic number is the number of protons in the atom of an element. Since the atom is electrically neutral i.e. is charge less, therefore
number of electrons = number of protons.
∴ It has 11 P and 11 electrons.
Atomic number z = p = e
Question: 7. Define the term – ‘mass number ’ of an atom. If an atom t ‘B’ has mass number 35 & atomic number 17, state the number of protons, electrons & neutrons it contains.
Answer: Mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of electrons
In the atom ‘B’, mass number = 35 and atomic number = 17
Number of protons = Atomic Number = 17 = p
Mass number = 17 + Number of neutrons
35 = 17 + n
n = 18
Number of neutrons = 18
Number of electrons = number of protons = 17
Question: 8. State why the atomic weight of an element is also termed – relative atomic mass.
Answer: As atomic weight is the number of times, one atom of an element is heavier than the mass of an atom of hydrogen or 1⁄12 the mass of an atom of carbon, hence, it is also termed as Relative Atomic Mass.
Question: 9. State how electrons are distributed in an atom. Explain in brief the rules which govern their distribution.
Answer: Electrons revolve around the nucleus in imaginary paths called orbits or shells. Different Orbits are K shell [first shell, n=1], L shell [second shell, n=2] M, N…… etc.
Rules governing the distribution of electrons are summarized below:
The maximum number of electrons in each shell or orbit is determined by the formula 2n2, where n is the number of shell.
K shell, n=1, no. of electrons = 2 x 12 = 2
L shell, n=2, no. of electrons = 2 x 22 = 8
M shell, n=3, no. of electrons = 2 x 32 = 18
The outermost shell cannot have more than 18 electrons. A new shell cannot be started until the previous one has reached its maximum limit.
Question: 10. If an atom ‘A’ has atomic number 19 & mass number 39, state –
(i) Its electronic configuration.
(ii) The number of valence electrons it possesses.
Answer: Atomic number = 19
Number of protons = Number of electrons = 19
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
39 = 19 + N
N = 20
Electronic configuration
19 = (2, 8, 8, 1)
Electrons in K shell (1st) = 2, L shell (2nd) = 8, M shell (3rd) = 8, N shell (4th) = 1
Valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, i.e. 1 in this atom.
Question: 11. Draw the atomic diagrams of the following elements showing the distribution of – protons, neutrons & the electrons in the various shells of the atoms.
a] Carbon – 126C
b] Oxygen – 168O
c] Phosphorus – 3115P
d] Argon – 4018Ar
e] Calcium – 4020Ca
[The upper number represents the – mass number & the lower number the – atomic number e.g. calcium – mass number = 40, atomic number = 20]
Answer:
a] Carbon – 126C

Atomic number = 6
Mass Number = 12
No. of p = 6, e = 6, n = 12 – 6 = 6
Electronic configuration – (K, L) = (2, 4)
b] Oxygen – 168O
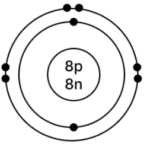
Atomic number = 8
Mass Number = 16
No. of p = 8, e = 8, n = 16 – 8 = 8
Electronic configuration – (K, L) = (2, 6)
c] Phosphorus – 3115P
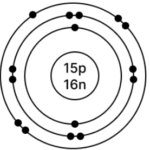
Atomic number = 15
Mass Number = 31
No. of p = 15, e = 15, n = 31 – 15 = 16
Electronic configuration – (K, L, M) = (2, 8, 5)
d] Argon – 4018Ar

Atomic number = 18
Mass Number = 40
No. of p = 18, e = 18, n = 40 – 18 = 12
Electronic configuration – (K, L, M) = (2, 8, 8)
e] Calcium – 4020Ca
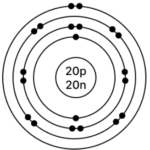
Atomic number = 20
Mass Number = 40
No. of p = 20, e = 20, n = 40 – 20 = 20
Electronic configuration – (K, L, M, N) = (2, 8, 8, 2)
Question: 12. ‘ Valency is the number of hydrogen atoms which can combine with [or displace] one atom of the element [or radical] forming a compound’. With reference to the above definition of valency, state the valency of chlorine in hydrogen chloride, giving reasons.
Answer: Hydrogen chloride [HCl], one atom of chlorine has combined with one atom of hydrogen, and also 1 atom of hydrogen can be replaced by metals like potassium, sodium. Hence valency of chlorine in one.
Question: 13. ‘ Valency is also the number of electrons – donated or accepted by an atom so as to achieve stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas’. With reference to this definition –
(a) State what is meant by ‘stable electronic configuration’.
(b) State why the valency of –
(i) Sodium, magnesium & aluminum is : +1, +2 & +3 respectively.
(ii) Chlorine, oxygen & nitrogen is : -1, -2 & -3 respectively.
Answer: (a) Stable electronic configuration — The atom’s outermost shell needs 2 electrons for stability (duplet rule) if it has only one shell. If it has multiple shells, it requires 8 electrons (octet rule) in the outermost shell for stability.
(b) (i) The atoms of sodium, magnesium and aluminum donate 1, 2 and 3 electrons, respectively, in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration of 8 electrons (octet rule) in the outermost shell. Hence, their valences are +1, +2 & +3.
(ii) The atoms of chlorine, oxygen and nitrogen accept 1, 2 and 3 electrons, respectively, in order to achieve a stable electronic configuration of 8 electrons (octet rule) in the outermost shell. Hence, their valences are -1, -2 & -3.
Question: 14. With reference to formation of compounds from atoms by electron transfer – electro valency, state the basic steps in the conversion of sodium & chlorine atoms to sodium & chloride ions leading to the formation of the compound – sodium chloride. [electronic configuration of : Na = 2, 8, 1 & Cl = 2, 8, 7]
Answer: Electronic configuration:
Na Cl
11 = 2, 8, 1 17 = 2, 8, 7
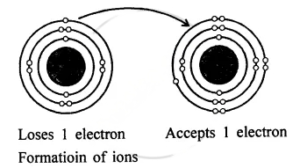
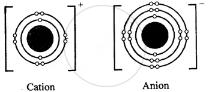
Na+ + Cl–
⇒ NaCl compound
– : End of Atomic Structure Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4 :–
Return to – Dalal New Simplified Chemistry ICSE Class-8 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.


