Chemistry Specimen Paper Sec-D 2023 Solved for ISC Class-12. Step by step solutions as council prescribe guideline of model sample question paper. During solutions of Chemistry specimen paper we explain with figure , graph, table whenever necessary.
Student can achieve their goal in next upcoming exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12.
ISC Class-12 Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Solved sec-D
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12th (xii) |
| Subject | Chemistry (Section-D) |
| Topic | ISC Specimen Paper Solved |
| Syllabus | on Revised syllabus |
| Session | 2022-23 |
ISC Class-12 Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Solved sec-D
Warning :- before viewing solution view Question Paper
SECTION D – 15 MARKS
ISC Class-12 Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Solved sec-D
Question 19:
(i) Starting with methyl magnesium bromide, how will the following compounds be synthesised?
(a) Acetaldehyde
Ans:- Methyl magnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. Acetaldehyde is prepared by methyl magnesium bromide by reacting it with HCN followed by hydrolysis. The Grignard reagent gets added to HCN and after the hydrolysis of the addition compound acetaldehyde is formed
(b) Acetone
Ans: Acetone can be prepared by reacting methyl magnesium bromide with methyl nitrile. The Grignard reagent is important to make Carbon-Carbon bonds. Hydrolysis is a chemical breakdown of compounds when treated with water.
(c) Acetic acid
Ans: A carboxylic acid is produced with one more carbon than the original Grignard reagent. In this case, acetic acid is formed as the product. So, when Methyl magnesium bromide is treated with carbon dioxide and hydrolysed, the product is Acetic acid
(ii) Explain the following:
(a) Chloroacetic acid is stronger acid than acetic acid.
(b) Formic acid reduces Tollen’s reagent but acetic acid does not.
Ans :
(a) Due to the inductive effect of the chlorine atom the electron density is reduced over the already weakened O-H bond in the carboxylic moiety (due to the presence of alpha carbonyl group) which in turn make it a stronger acid than acetic acid as the ease of releasing the hydrogen to the base is increased.
(b) Formic acid is unique because it contains both an aldehyde group and carboxyl group also. Hence it can act as a reducing agent. It reduces Tollens reagent. But acetic acid has no aldehydic group hence it does not reduces Tollens reagent.
Question 20:
(i) Name the type of isomerism shown by the following pairs of coordination compounds.
(a) [Pt(H2O)4Cl2]Cl2.H2O and [Pt(H2O)3Cl3]Cl.2H2O
Ans: Hydrate isomerism
(b) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Co(NH3)4Br2]Cl2
Ans: geometrical isomerism
(c) [Cr(H2O)5(SCN)]Cl2 and [Cr(H2O)5(NCS)]Cl2
Ans: : Linkage isomerism
(ii) Consider the complex ion [Co(CN)6]³- and answer the following questions: (atomic number of Co = 27)
(a) Type of hybridisation of central metal atom— d² sp²
(b) Magnetic nature— Paramagnetic
(c) Geometry of the complex ion–octahedral geometry
(d) Low spin complex or high spin complex–Low spin complex
Question 21:
(i) A 0·06 molar CH3COOH solution offers a resistance of 55 ohms to a conductivity cell at 25oC. If the cell constant is 0·45cm-1 and the molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 398·5 ohm-¹ cm²mol-¹. Calculate:
(a) Specific conductance
(b) Molar conductance
(c) Degree of dissociation
Ans :
(a) Molarity = 0·06
Resistance R = 55 ohms
Cell constant, l / a = 0·45cm-1
A∞ = 398·5 ohm-¹ cm²mol-¹.
C = 1/R = 1/55 = 0.018 ohm-¹
Specific conductance k = conductance × cell constant
(b) Molar conductance = k x 100 / molarity
0.018 x 100 / 0·06 = 30
(c) Degree of dissociation= 30/ 398·5 = 0.075
(ii) Calculate the number of coulombs of charge required to deposit 24·35g of aluminum from a solution containing Al³+ ions. (Atomic weight of Al = 27)
Ans:
or
(i) Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction given below and calculate the emf of the cell at 298K.
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+ (0.1M) → 2Cr3+ (0.01M) + 3 Fe(s)
Given: E°(Cr3+ | Cr) = – 0.74 VE° (Fe2+ | Fe) = – 0.44 V
Ans :
The balanced chemical reaction can be written as follows:
2 Cr(s) + 3 Fe2+(0.1 M) → 2 Cr3+(0.01 M) + 3 Fe(s)
E°(Cr3+ | Cr) = – 0.74 VE°
(Fe2+ | Fe) = – 0.44 V
The cell can be represented as follows:
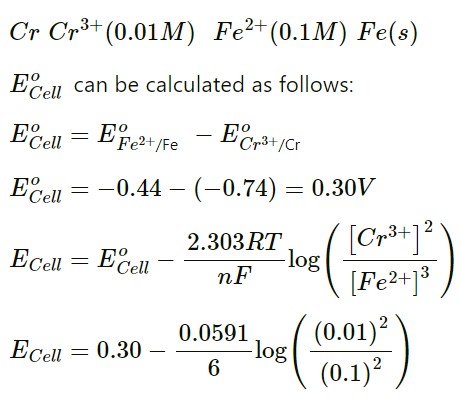
ECell = 0.30 + 0.01
ECell = 0.31 V
(ii) Calculate the molar conductance at infinite dilution for NH4OH given that ![]()
, 240 , 129 ohm cm mole
Ans
λ∞m for Ba(OH)2=λ°Ba2++2λ° OH−....(i)
λ∞m for (BaCl2)=λ°Ba2++2λ° Cl−....(ii)
λ∞m for (NH4Cl)=λ°NH+4+λ° Cl−....(iii)
∵λ∞mf(NH4OH)=λ°NH+4+λ° OH−
= 1/2 eq.(i) + eq.(iii)-1/2 eq.(ii)
=(1 x 457 /2)+129− (1 x 240 /2)
=237.5 ohm−1cm2mol−1
–: End of Chemistry Specimen Paper Sec-D 2023 Solved for ISC Class-12 :–
–: Visit also :–
Return to : ICSE Specimen Paper 2023 Solved
Thanks