Circle Circumference and Area Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-17B ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17. We Provide Step by Step Solutions / Answer of Area of Trapezium for OP Malhotra Maths. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics.

Circle Circumference and Area Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-17B ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-17 | Circle Circumference and Area |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-17B | Solved Questions on Area of Circle |
| Edition | 2025-2026 |
Solved Questions on Area of Circle
Circle Circumference and Area Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-17B ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17
Que-1: Find the area of the circle whose :
(i) diameter = 7 cm.
(ii) radius = 14 cm.
(iii) diameter = 2.8 cm
Sol: (i) Diameter = 7 cm
∴ Radius (r) = 7/2 cm
∴ Area of the circle = πr² = (22/7) × (7/2) × (7/2) cm²
= 77/2 = 38.5 cm²
(ii) Radius (r) = 14 cm
∴ Area = πr² = (22/7) × 14 × 14 cm² = 616 cm²
(iii) Diameter = 2.8 cm
∴ Radius (r) = 2.8/2 = 1.4 cm
∴ Area = πr² = (22/7) × 1.4 × 1.4 cm²
= 6.16 cm²
Que-2: A horse is tied to a pole with 28 m long string. Find out the area which the horse can graze.
Sol: Length of string = 28 m
∴ Radius (r) = 28 m
Area which the horse can graze = πr²
= (22/7) × 28 × 28 m² = 2464 m²
Que-3: Find the radius of a circular field whose area is
(i) 154 cm2
(ii) 1386 cm²
Sol: (i) Area of a circular field = 154 cm²
Let r be the radius, then
πr² = 154
⇒ (22/7) r² = 154 ⇒ r² = 154×(7/22) = 49
⇒ r² = (7)² ⇒ r = 7
∴Radius = 7 cm
(ii) Area of the circular field = 1386 cm²
Let r be the radius of the field, then
⇒ πr² = 1386 ⇒ (22/7) r² = 1386
⇒ r² = 1386×(7/22) = 63 × 7 = 441 = (21)²
⇒ r = 21
∴Radius = 21 cm
Que-4: The area of a circle is 24.64 cm2. Find its circumference.
Sol: Area of a circle = 24.64 cm²
Let r be the radius then
πr² = 24.64 ⇒ (22/7) r² = 24.64
⇒ r² = 24.64×(7/22) = 1.12 × 7 = 7.84
⇒ r² = (2.8)² ⇒ r = 2.8
Now circumference = 2πr
= 2 × (22/7) × 2.8 cm = 17.6 cm
Que-5: A copper wire, when bent in the form of a square, encloses an area of 121 cm2. If the same wire is bent into the form of a circle, find the area of the circle
Sol: Area of a square = 121 cm²
∴ Side of the square (a) = √Area = √121 = 11 cm
∴ Perimeter of the wire = 4a = 4 × 11 = 44 cm
Then perimeter of circular wire which is bent down = 44 cm
∴ Radius = circumference 2π
= (44×7)/(2×22) = 7 cm
Then area of the circle = πr²
= (22/7) × 7 × 7 = 154 cm²
Que-6: The circumference of a circle is equal to the perimeter of a square. The area of the square is 484 sq m. Find the area of the circle.
Sol: The area of the square = 484 sq. m
∴ Side of the square (a) = √Area
= √484 m = 22 m
and perimeter of square = 4a = 4 × 22 m = 88 m
∴ Circumference of the circle = perimeter of the square = 88 m
∴ Radius (r) = circumference 2π = (88×7)/(2×22) m = 14 m
and area of the circle = πr² = 227 × 14 × 14sq. m = 616 sq. m
Que-7: A wire is in the form of a circle of radius 42 cm. It is bent into a square. Determine the side of the square and compare the areas of the regions enclosed in the two cases.
Sol: Radius of circular wire (r) = 42 cm
∴ Its circumference = 2πr
= 2 × (22/7) × 42 = 264 cm
(i) Now perimeter of square formed by the circular wire = 264 cm
∴ Side of the square = 264/4 = 66 cm
(ii) Now area of circle = πr²
= (22/7) × 42 × 42 cm² = 5544 cm²
and area of square = (side)²
= (66)² = 4356 cm²
Ratio in the two areas = 5544 : 4356
= 56 : 44 = 14 : 11
Que-8: From a copper plate, which is a square of side 12.5 cm, a circular disc of diameter 7 cm is cut off. Find the weight of the remaining part, if 1 sq. cm of the plate weighs 0.8 gm.
Sol: Side of a square = 12.5 cm
Diameter of disc = 7 cm
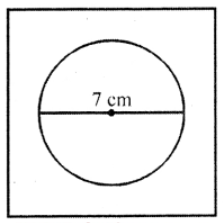
Radius (r) = 7/2 cm
∴ Area of square = a² = (12.5)² cm² = 156.25 cm²
Area of circular disc = πr²
= (22/7) × (7/2) × (7/2) cm²
= 77/2 = 38.5 cm²
∴ Area of remaining part = 156.25 – 38.50 = 117.75 cm²
Weight of one sq. cm = 0.8 gm
∴ Total weight of the remaining portion = 117.75 × 0.8 gm = 94.2 gm
Que-9: The circumference of two circles are in the ratio 2 : 3. Find the ratio of their areas.
Sol: Ratio in the circumferences of two circles = 2 : 3
Let circumference of the first circle = 2x
and of the second circle = 3x
∴ Radius (r1) of first circle
= circumference / 2π = 2x/2π = x/π
and radius (r2) of second circle = 3x/2π
Now area of the first circle = πr²
= π × (3x/2π)² = (π×9x²)/4π² = 9x²/4π
∴ Ratio = x²/π : (9x²/4π)
= 1 : (9/4) = 4 : 9
Que-10: A square park has each side of 100 m. At each corner of the park, there is a flower bed in the form of a quadrant of radius 14 m as shown in the figure. Find the area of the remaining part of the park. (Take π = 22/7)
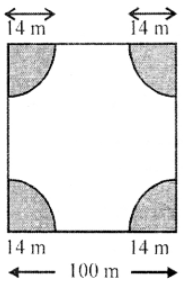
Sol: Side of the square park = 100 m
∴ Area = (side)² = (100)² = 10000 m²
Radius of each quadrant at the corner of the park = 14 m
∴ Area of one quadrant = (1/4)πr²
(1/4) × (22/7) × (14) × (14) m² = 154 m²
and area of 4 quadrants = 154 × 4 = 616 m²
∴ Area of the remaining portion of the park
= 10000 – 616 = 9384 m²
Que-11: The radius of a circular field is 20 m. Inside it runs a path 5 m wide all around. Find the area of the path.
Sol: Radius of circular field (R) = 20 m
Width of inside path = 5 m
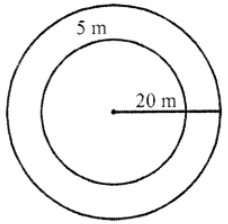
Inner radius (r) = 20 – 5 = 15 m
∴ Area of path = outer area – inner area = πR² – πr²
= π [R² – r²] = (22/7) [(20)² – (15)²] m²
= π (20 + 15) (20 – 15) m²
= (22/7) × 35 × 5 = 550 m²
Que-12: A road 3.5 m wide surrounds a circular plot whose circumference is 44 m. Find the cost of paving the road of Rs. 10 per m2.
Sol: Width of road = 3.5 m
Circumference of a circular plot = 44 m
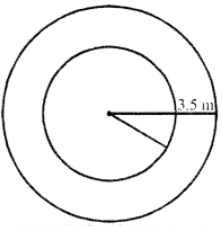
Radius of the plot = circumference 2π
= (44×7)/(2×22) = 7 m
∴ Outer radius (R) = 7 + 3.5 = 10.5 m
∴ Area of the outer road = outer area – inner area =πR² – πr²
= π(R² – r²) = π[(10.5)² – (7)²]
= (22/7) (10.5 + 7) (10.5 – 7) m²
= (22/7) × 17.5 × 3.5 m² = 192.5 m²
Cost of paving the road = Rs. 10 per m²
∴ Total cost = 192.5 × 10 = Rs. 1925
Que-13: A lawn is in the shape of a semi-circle of diameter 35 dm. The lawn is surrounded by a flower bed of width 3.5 dm all round. Find the area of the flower bed in dm2.
Sol: Inner diameter of semicircular lawn = 35 dm
∴ Radius (r) = 35/2 = 17.5 dm
Width of the flower bed = 3.5 dm
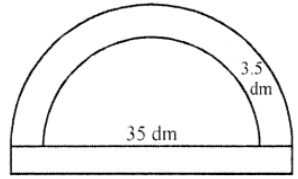
∴ Outer radius (R) = 17.5 + 3.5 = 21 dm Now area of the flower bed = outer area inner area
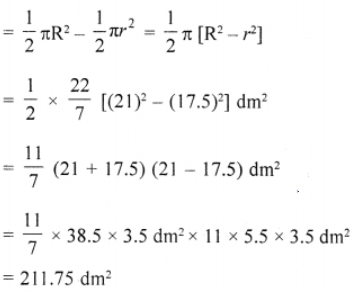
Que-14: A road which is 7 m wide surrounds a circular park whose circumference is 352 m. Find the surface area of the road.
Sol: Width of road = 7 m
Circumference of park = 352 m
∴ Radius of the park (r) = circumference 2π
= (352×7)/(2×22) = 56 m
∴ Outer radius (R) = 56 m + 7 m = 63 m
∴ Area of the road = πR² – πr² = π (R² – r²)
= π [(63)² – (56)²] m²
= (22/7) (63 + 56) (63 – 56) m²
= (22/7) × 119 × 7 m² = 2618 m²
Que-15: The shaded area in the figure between the circumferences of two concentric circles is 346.5 cm2. The circumference of the inner circle is 88 cm. Calculate the radius of the outer circle.
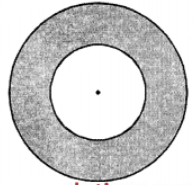
Sol: Area of shaded portion = 346.5 cm²
Circumference of the inner circle = 88 cm
∴ Inner radius (r) = circumference 2π
= (88×7)/(2×22) = 14 cm
Let outer radius = R, then
Area of shaded portion = πR² – πr²
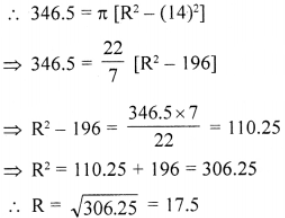
Radius of outer circle = 17.5 cm.
Que-16: Find the area enclosed between two concentric circles of radii 3.5 cm and 7 cm. A third concentric circle is drawn outside the 7 cm circle so that the area enclosed between it and the 7 cm circle is the same as that between the two inner circles. Find the radius of the third circle, correct to one decimal place.
Sol: Radius of first inner circle (r1) = 3.5 cm
and radius of second circle (r2) = 7 cm
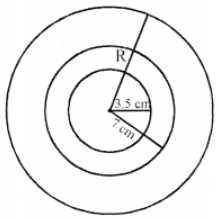
Area between these two circles
= π[r2)² – (r1)²] = (22/7) [(7)² – (3.5)²]
= (22/7) (7 + 3.5) (7 – 3.5) cm²
= (22/7) × 10.5 × 3.5 cm² = 115.5 cm²
Let the radius of third circle = R
Area between the last two circles = 115.5 cm
∴ π[R² – (7)²] = 115.5
⇒ (22/7) [R² – 49] = 115.5
⇒ R² – 49 = (115.5×7)/22 = 36.75
⇒ R² = 36.75 + 49 = 85.75 cm²
∴ R = √85.75 = 9.26
∴ Radius of third circle = 9.26 = 9.3 cm
Que-17: A circular field has a perimeter of 650 m. A plot, in the shape of a square having its vertices on the circumference of the field, is marked in the field. Calculate the area of the square plot.
Sol: Perimeter of a circular field = 650 m
∴ Diameter of the field = circumference π
= 650π = 650×(7/22) m
∵ The square plot has its vertices on the circumference of the circle
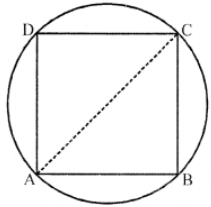
∴ Diagonal of square = diameter of the circle
= (650×7)/22 m
∴ Area of square plot = ( Diagonal )² / 2
= (1/2) [(650×7)/22]² = (1/2) [4550/22]²
= (1/2) (206.818)²
= (1/2) (42773.76) m²
= 21386.88 m² = 21387 m²
Que-18: The inside perimeter of a practice running track with semicircular ends and straight parallel sides is 312 m. The length of the straight portions of the track is 90 m. If the track has uniform width of 2 m throughout, find its area.
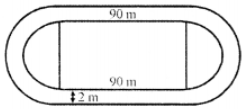
Sol: Inside perimeter of the running track with hemispheres ends and straight parallel sides = 312 m
Length of straight portion = 90 m
∴ Perimeter of hemisphere end of one side
= (312−180)/2 = 132/2 = 66 m
∴ Radius = (Perimeter × 2)/2π = (66×2×7)/(2×22) = 21 m
Width of track = 2 m
∴ Outer radius = 21 + 2 = 23 m
∴ Area of the track = Area of semicircular ends + area of rectangular portions
= 2π [(23)² – (21)²] + 90 × 2 × 2
= 2π (23 + 21) (23 – 21) + 360
= 2π × 44 × 2 + 360 = 2 × 88π + 360
= (176π + 360) m²
Que-19: The boundary of the shaded region in the figure consists of three semi-circular arcs, the smaller ones being equal. If the diameter of the larger arc is 10 cm. Calculate
(i) the length of the boundary
(ii) the area of the shaded region.
(Take π to be 3.14)
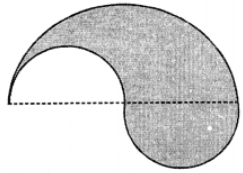
Sol: Diameter of larger semicircle = 10 cm
∴ Radius (R) = 10/2 =5 cm
Diameter of each of the smaller semicircles = 5 cm
∴ Radius of each semicircle (r) = 5/2 cm
(i) Perimeter of the shaded portion
= (1/2) × 2πR + 2 × (1/2) × 2πr = πR + 2πr
= π[R + 2r] = 3.14 (5 + 2 × (5/2))
= 3.14 × 10 cm = 3.14 cm
(ii) Area of shaded portion
= (1/2)πR² – (1/2)πr² + (1/2)πr²
= (1/2)πR² = (1/2) × 3.14 × 5 × 5 cm²
= 39.25 cm² = 39.3 cm²
Que-20: A bed of roses is like in the figure. In the centre is a square and on each side there is semi-circle. Side of the square is 21 m. If each rose-plant needs 6 m2 of space, find out the number of plants which can be planted in the whole figure.
Sol: Side of square ABCD = 21 m
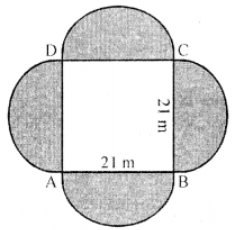
Area of square portion = (side)²
=(21)² m² = 441 m²
Radius of each semicircular portion (r) = 212 m
∴ Area of 4 semicircular portion = 4 × (1/2)πr²
= 2 × (22/7) × (21/2) × (21/2) m² = 693 m²
Total area of the figure = 441 + 693 = 1134 m²
∴ Area required for one rose plant = 6 m²
∴ Number of plants = 1134/6 = 189
Que-21: Find the area of the region between two concentric circles given in figure, if the length of the chord of the outer circle touching the inner circle is 14 cm.
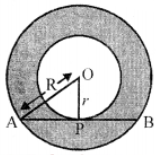
Sol: Length of chord AB = 14 cm
∵ OP ⊥ AB
∴ AP = PB = 14/2 = 7 cm
Let OA = R and OP = r
In right △OAP
OA2 = OP2 + AP2
⇒ R2 = r2 + (7)2
⇒ R2 – r2 = 49 …(i)
Now area of shaded portion
= πR2 – πr2
= π(R2 – r2) =(22/7) × 49 [From (i)]
= 154 cm²
Que-22: The figure shows a circle with centre at O and ∠AOB = 90°. If the radius of the circle is 40 cm, calculate the area of the shaded portion of the circle. (Take π = 3.14)
Sol: Radius of the circle (r) = 40 cm
∠AOB = 90°
Area of quadrant OAB = (1/4) πr²
= (1/4) × 3.14 × 40 × 40 cm² = 1256 cm²
Area of △AOB = (1/2) OA × OB (∵ ∠AOB = 90°)
= (1/2) × 40 × 40 = 800 cm²
∴ Area of shaded portion
= 1256 cm² – 800 cm² = 456 cm²
Que-23: ABCD is a flower bed. If OA = 21 m and OC = 14 m, find the area of the bed.
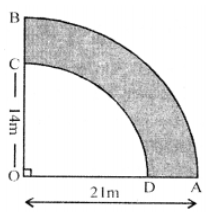
Sol: In the figure OAB is a quadrant whose radius
OA = 21 cm
and radius of quadrant
OCD = OC = 14 cm
∴ Area of bed (shaded portion)
= (1/4)πR² – (1/4)πr²
= (1/4)π [R² – r²] = (1/4) × (22/7) (21² – 14²)
= (11/14) [441 – 196] = (11/14) × 245 m²
= (11×35)/2 = 385/2 = 192.5 m²
Que-24: In the figure, A, B, C and D are centres of equal circles which touch externally in pairs and ABCD is a square of side 14 cm. Find the area of the shaded region.
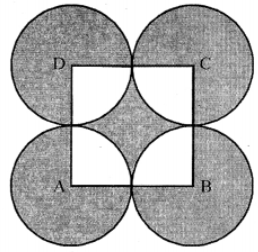
Sol: Side of square ABCD = 14 cm
AB = BC = CD = DA = 14 cm
∴Radius of each circles = 14/2cm = 7cm
∴ Area of shaded portions = area of 4 circles + area of square – area of 4 quadrant
= Area of 4 circles – area of one circle + area of square
= Area of 3 circles + area of square
= 3 × (22/7) × 7 × 7 + 14 × 14 cm²
= 462 + 196 = 658 cm²
= 658 cm²
–; End of Circle Circumference and Area Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-17B ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17 :–
Return to :– OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends


