Atomic Structure Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4 Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-4. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -4 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-7.
Atomic Structure Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 7th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure |
| Unit-1 | Atomic Structure |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise – 1
Atomic Structure Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-4
Question 1. State the meaning of the term – (a) atom (b) molecule (c) radical – with a suitable example.
Answer 1: Atom – The basic/smallest unit of matter which cannot be broken into more simpler particles.
Molecule – The smallest particle of a substance which can exist independently and retain properties of the substance.
Radical – An atom/ group of atoms which has charge
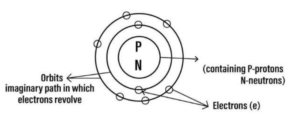
Question 2. Draw the basic structure of an atom representing its –
(a) Subatomic particles
(b) Nucleus
(c) Orbits or shells.
Answer- 2: Diagram showing basic structure of atom
Question -3. In the Modern Periodic Table – atoms of all elements are arranged according to the their increasing order of – atomic numbers. An atom of nitrogen has seven protons and seven electrons. State what would be its atomic number.
Answer 3: Atomic number [Z]
Z = No. of protons [p]
Z = No. of electrons [e]
Z = 7 = 7 (No of Proton=7 given)
Hence Atomic number = 7
Question 4. State the main points of contradiction of Dalton’s atomic theory by the Modern Atomic Theory.
Answer 4: The main postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory are:
- The matter is made up of indivisible particles known as atoms.
- The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same including mass. This can also be stated as all the atoms of an element have identical mass while the atoms of different elements have different masses.( 11H, 21 H,31H ) Isotopes
- Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. This implies that during chemical reactions, no atoms are created nor destroyed.
- The formation of new products (compounds) results from the rearrangement of existing atoms (reactants).
- Atoms of an element are identical in mass, size and many other chemical or physical properties, but atoms of two-different elements differ in mass, size, and many other chemical or physical properties.
The modern atomic theory contradicts dalton’s atomic theory :
- Atoms are divisible into protons, neutrons, electrons.
- Atoms of the same element have different properties, such atoms are isotopes.
- Atoms of different elements have the same properties, such atoms are isobars.
- Atoms can combine in any ratio and not just whole numbers.
Question 5. ‘Atoms of the same element or different of Dalton’s atomic theory by the Modern Atomic Theory. Give two examples each of –
(a) Atoms of the same element
(b) Atoms of different elements combining to form a molecule.
Answer 5: (a) Atoms of the same element or different elements combine to form a molecule.
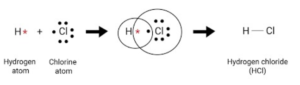
(b) A molecule is the smallest particle of a pure substance – element or compound
- which can exist independently and
- retain the physical & chemical properties of the substance.
Question 6. Explain the term – ‘atomicity’. Give a reason why –
(a) Helium is considered monoatomic, but hydrogen a diatomic molecule.
(b) Ozone is considered triatomic, but phosphorus a tetratomic molecule.
Answer 6: Atomicity —Atomicity is the number of atoms that make a molecule of an element.
(a) Helium is considered mono-atomic because it has 1 atom in its molecule, hydrogen is considered diatomic because it has 2 atoms of hydrogen in its molecule.
(b) Ozone is considered triatomic because it has 3 atoms of oxygen, phosphorus is considered tetratomic because it has 4 atoms in its molecule.
Question 7. State the atomicity of the following:
(a) Neon
Answer: (a) Mono-atomic
(b) Oxygen
Answer: (b) Di-atomic
(c) Chlorine
Answer: (c) Di-atomic
(d) Argon
Answer: (d) Mono-atomic
(e) Sulphur
Answer: (e) Poly-atomic
Question 8. ‘A radical takes part – unsplit in a chemical reaction and retains its identity in reactions’. With reference to the radical – (a) ammonium (b) bisulphate (c) carbonate – state the group of atoms present in each radical.
Answer 8:
| Radical | Representattion | Group of atoms present in a radical |
| a. Ammonium | NH4+ | 1 atom of nitrogen; 4 atom of hydrogen |
| b. Bisulphate | HSO41− | 1 atom of hydrogen and sulphur; 4 atoms of oxygen |
| c. Carbonate | CO3− − | 1 atom of carbon; 3 atoms of oxygen |
Question 9. Differentiate between the following with suitable examples- A basic radical and a acid radical
Answer 9: The positive part of a radical is called basic radical and the negative part of a radical is called acid radical. Basic radical can be a metal while acid radical can be Non- Metal.
Example –
In Sodium Chloride Compound
Basic radical – Sodium
Acid radical – Chloride
In Ammonium Hydroxide – Compound
Basic radical – Ammonium
Acid radical – Hydroxide
Question 10. Name the cation and the anion in the salt – calcium sulphate.
Answer 10: In a salt of calcium sulphate the positive and negative parts exist as ions.
- The positively charged ions are called – cations. Ca1+
- The negative charged ions are called – anions. S041-
| Name of compound | Formula | Anion | Cation |
| Calcium sulphate | CaSO4 | Ca+ | SO4− |
Question: 11. Explain the term – ‘valency’. State giving reasons the valency of –
(a) Chlorine in hydrogen chloride
(b) Sulphate in sulphuric acid
(c) Nitrogen in ammonia
(d) Magnesium in magnesium oxide
Answer 11: Valency is the number of hydrogen atoms that combine or displace with another atom to form a compound.
- One atom of hydrogen combines with one atom of chlorine to form HCl, Hence the valency of chlorine in this case is 1.
- Two atoms of hydrogen combine with one radical of sulphate to form H2SO4, the valency of sulphate is 2.
- Three atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of nitrogen to form NH3, the valency of nitrogen in this case is 3.
- Valency of magnesium in MgO is 2, as it needs 2 oxygen atoms to form magnesium oxide.
Question 12. Give the symbol and valency of the following elements and radicals.
-
Potassium
-
Sodium
-
Hydrogen
-
Calcium
-
Aluminium
-
Magnesium
-
Zinc
-
Chlorine
-
Sulphur
-
Nitrogen
-
Oxygen
-
Ammonium
-
Bicarbonate
-
Nitrate
-
Bisulphate
-
Bisulphite
-
Hydroxide
-
Carbonate
-
Sulphate
-
Sulphite
Answer 12:
| Elements/Radicals | Symbol | Valency |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Potassium | K | 1 |
| 2. Sodium | Na | 1 |
| 3. Hydrogen | H | 1 |
| 4. Calcium | Ca | 2 |
| 5. Aluminium | Al | 3 |
| 6. Magnesium | Mg | 2 |
| 7. Zinc | Zn | 2 |
| 8. Chlorine | Cl | 1 |
| 9. Sulphur | S | 2 |
| 10. Nitrogen | N | 3 |
| 11. Oxygen | O | 2 |
| 12. Ammonium | NH4+ | 1 |
| 13. Bicarbonate | HCO3- | 1 |
| 14. Nitrate | NO3- | 1 |
| 15. Bisulphate | 1 | |
| 16. Bisulphite | 1 | |
| 17. hydroxide | OH- | 1 |
| 18. carbonate | CO3- | 2 |
| 19. Sulphate | SO3-2 | 2 |
| 20. sulphite | S- | 2 |
Question 13. Give an example of three elements exhibiting variable valency.
Answer 13: Three examples of elements exhibiting variable valency:
- Tin (Sn) has valency 2 or 4
- Iron (Fe) can show a valency of 2 and 3.
- Copper (Cu) can show a valency of 1 and 2.
Question 14. State what is meant by the term – ‘chemical formula. Give the chemical formula of –
(a) sodium hydroxide
(b) sodium nitrate
(c) sodium bicarbonate
(d) sodium sulphite
(e) magnesium nitrate
(f) ammonium sulphate
(g) carbonic acid
(h) calcium phosphate
Answer 14: The Symbolic representation of a substance by means of symbols is called Chemical formula
(writing Radicle with charge and inter change the value by cris cross)
(a) Sodium hydroxide

(b) Sodium nitrate
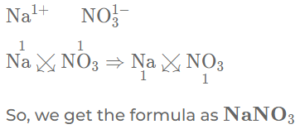
(c) Sodium bicarbonate
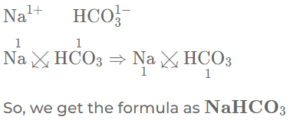
(d) Sodium sulphite

(e) Magnesium nitrate
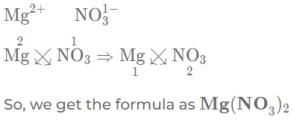
(f) Ammonium sulphate
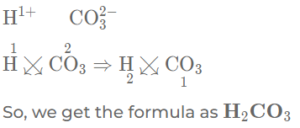
(g) Carbonic acid
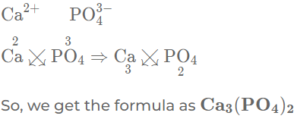
(h) Calcium phosphate
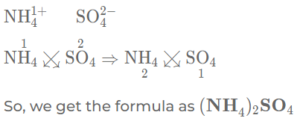
Question 15. ‘Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide’. Give a word equation and a molecular equation of the same. Is the equation written, a balanced equation. Give reasons.
Answer 15: Word equation of statement : – ‘Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide’
Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid -> sodium chloride + water
Molecular equation of statement : – ‘Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide’
NaOH + HCl —–> NaCl + H20
No. of atoms of each element of reactant/s = No. of atoms of each element of product/s.
Therefore, the above equation is said to be balanced equation.
Question 16. State what the group number in the Modern Periodic Table signifies. Give a reason why elements in the same group, have similar valency & similar chemical properties.
Answer 16: Group number signifies the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom of the element.
- Number of electrons in the outer shell of all elements in a group is the same.
- Hence all elements in the same group of the periodic table have same ‘Valency’ and similar ‘Chemical properties’.
– : End of Atomic Structure Class-7 Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-7 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.



please workbook ka bhi solutions