Language of Chemistry Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5 Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-5. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -5 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-7.
Language of Chemistry Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 7th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-5 | Language of Chemistry |
| Unit-1 | Language of Chemistry |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise – 1
Language of Chemistry Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
Question 1. Explain the term ‘chemical reaction’ with special reference to – ‘reactants’ and ‘products’.
Answer 1: A reaction between matter that react together and form new products. The substances that undergo reaction are reactants while the new substances formed are called products.
Question 2. Represent the addition of dilute sulphuric acid to zinc by means of a chemical equation. State the function of the arrow between the reactants and products.
Answer 2:
- Reactants
Left hand side write the reactants (substances which take part in a reaction).
- Products
Right hand side write the products (substances formed as a result of the reaction).
Chemical equation formed is
Zn [dil.] + H2SO4→ ZnSO4 +H2[g]
The function of the arrow (→) between the reactants and products is that it represents the chemical reaction taken place between two reactants.
Question 3. A chemical reaction is generally accompanied by certain external indications or characteristics. These include – change of –
(a) colour
(b) state
(c) smell
(d) evolution of gas
(e) formation of precipitate
(f) evolution or absorption of heat.
With reference to change of colour – state the change in colour seen when the following arc.heated – (1) copper carbonate (2) zinc carbonate (3) mercury [II]oxide (4) lead [IV] oxide.
Answer 3: Change of colour — In certain chemical reactions a change of colour is seen to be observed. Heat on substances to observe change in colour of reactants and products.
On heating product formed:
- CuCO3 → CuO + CO2[g]
- ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 [g]
- 2HgO → 2Hg + O2 [g]
- 2PbO2→2PbO + O2 [g]
Change in colour:
- Copper carbonate is green coloured, when heated it gives out a black solid copper oxide.
- Zinc carbonate is white coloured, when heated it gives a yellow solid – zinc oxide
- Mercury [II] oxide is red, when heated it turns silvery
- Lead [IV] oxide is brown, when heated it turns yellow.
Question 4. Give a balanced equation for addition of iron to copper [II] sulphate solution. State the change in colour seen.
Answer 4: Copper [II] sulphate + Iron → Iron [II] sulphate + Copper
![]()
The colour changes from blue(CuS04) to light green(FeS04)
Question 5. In certain reactions a change of state is observed i.e. solid to liquid, liquid to gas etc. – State the change of state of the products – to give the respective reactants in each case.
(a) C + 2S → CS2
(b) NH3 + HCl ⇌ NH4Cl
(c) 2H2 + O3 → 2H2O
(d) 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Answer 5: (a) Carbon with sulphur
C[s] + 2S[s] → CS2[s] (carbon di sulphide)
The solid changes to a liquid state
(b) Ammonia with hydrogen chloride
NH3[g] + HCl[g] → NH4Cl[s] (ammonium chloride)
The gas changes to solid-state
(c) Hydrogen with oxygen
2H2[g] + O2[g] + 2H2O[l]
The gas changes to liquid state.
(d) Decomposition of water, water decomposes to hydrogen gas and oxygen gas
2H2O[l] → 2H2[g] + O2[g]
The liquid changes to gaseous state.
Question 6. In certain reactions a change of smell is observed. Give two examples from daily life of the same.
Answer 6: In certain chemical reactions – a change of smell is seen to be observed.
- A fresh egg gets spoiled and turns into a rotten egg, or fresh food on keeping for a long time gets spoiled. Thus a chemical change may have undergone, which many result in a change in odour [foul smell maybe Evolved].
- A piece of fresh bread is kept in the open for a few days. A foul smell maybe observed along with growth of fungus, after keeping the bread for a prolonged time.
Question 7. In certain reactions an insoluble solid called precipitate is formed. State the colour and name of the precipitate formed in each of the following reactions involving addition of:
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate.
(b) Iron [II] sulphate to sodium hydroxide.
(c) Iron [III] chloride to ammonium hydroxide.
(d) Copper [II] sulphate to sodium hydroxide.
(e) Lead nitrate to ammonium hydroxide.?
Answer 7: (a) Dilute hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate.
In the reaction of Silver nitrate and dil. hydrochloric acid
AgNO3 + HCl → HNO3 + AGCl↓ (silver chloride)
The precipitate formed is Silver Chloride which is milky white in colour.
(b) Iron [II] sulphate to sodium hydroxide.
Iron [II] sulphate and sodium hydroxide
FeSO3 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + Fe(OH)2↓ (Iron [II] hydroxide)
The precipitate formed is Iron [II] hydroxide which is dirty green in colour.
Iron [III] chloride and ammonium hydroxide
FeCl3 + 3NH4OH → 3NH4Cl + Fe(OH)2↓ (Iron [III] hydroxide)
The precipitate formed is Iron [III] hydroxide which is reddish brown in colour.
(d) Copper [II] sulphate to sodium hydroxide.
Copper [II] sulphate and sodium hydroxide
CuSO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + Cu(OH)2↓ (Copper [II] hydroxide)
The precipitate formed is Copper [II] hydroxide which is pale blue in colour.
(e) Lead nitrate to ammonium hydroxide.?
Lead nitrate and ammonium hydroxide
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NH4OH → 2NH4NO3 + Pb(OH)2↓ (Lead hydroxide)
The precipitate formed is Lead hydroxide which is chalky white in colour.
Question 8. Give examples of exothermic reactions i.e. heat evolved in each of the following:
(a) reaction between a solid and a liquid
(b) reaction between two gases
Give two examples of exothermic reactions seen in everyday life.
Answer 8: (a) Reaction between a solid and a liquid:
CaO + H2O →Ca(OH)3 + Δ
(b) Reaction between two gases are:

Examples of exothermic reactions are:
- Rusting of iron – the reaction is slow and the heat evolved is very less, hence unnoticeable.
- Setting of cement – cement setting liberates heat, hence concrete structures are set slowly.
- Human Body – many chemical reactions in our body are exothermic & provide energy to survive.
Question 9. Give one example in each case where supplying energy [given below] is necessary for a chemical reaction.
(a) Heat energy
(b) Light energy
(c) Electrical energy
(d) Pressure
(e) Catalyst
Answer 9: (a) Heat Energy: On heating the reactants – the reacting particles, collide swiftly and with greater intensity.
Example: Heat on zinc carbonate:
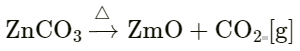
(b) Light Energy: In presence of light – the molecules of the reactants absorb light energy and collide swiftly and react rapidly.
Example: Photosynthesis in plants: Plants manufacture food [glucose] from carbon dioxide and water – in the presence of chlorophyll [green pigment in plants] and sunlight.
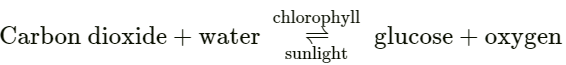
(c) Electrical Energy: It dissociates the reactant in molten or solution state, into ions, which are charged particles and hence respective products are obtained.
Example: Electrolysis of acidified water.
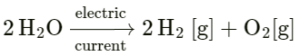
(d) Pressure: It causes the reacting molecules, to come together and collide with greater intensity.
Example: Production of ammonia.
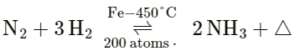
(e) Catalyst: It is a substance which alters the rate of the reaction [i.e. increases or decreases the rate] without taking part in the reaction. It itself remains chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
Example: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia – using catalyst platinum
![]()
Question 10. Representation of the results of a chemical change – is a chemical equation.
For the equation: FeCl3 + 3NH4OH 3NH4Cl + Fe(OH)3 ↓ Answer the following:
(a) Write the word equation for the above molecular equation.
(b) Is the equation given above a balanced equation. Give reasons.
(c) Name the reactants and the products in the above equation.
(d) What is the indications of the arrow between the reactants and the products and of the arrow pointing downwards at the end.
Answer 10: (a) Iron (III) chloride + ammonium hydroxide → Ammonium chloride + Iron (III) hydroxide
(b) Yes, because in this reaction the total number of atoms of each elements in the reactants, on the left side of the equation is equal to the number of products formed on the right side of the equation.
(c) Reactants – Iron (III) Chloride and Ammonium hydroxide, products – Ammonium Chloride and Iron (III) Hydroxide
(d) The arrow between reactants and products indicates the chemical reaction taking place between reactants. The arrow pointing downwards indicates formation of precipitate.
Question 11. Give word equations for the following chemical reactions and give the names of the products formed.
(a) Zn + 2HC1→ ZnCl2 + H2
(b) CuO + H2SO4→CuS04 + H2O
(c) Zn + S → ZnS
(d) ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
(e) NH3 + HCl→ NH4Cl
Answer 11: (a) Zinc + dilute Hydrochloric acid→ Zinc chloride + Hydrogen
(b) Copper + Sulphuric Acid → Copper(II)sulphate + water
(c) Zinc + Sulphur → Zinc Sulphide
(d) Zinc carbonate → Zinc oxide + Carbon dioxide
(e) Ammonia + Hydrogen chloride → Ammonium chloride
(Product formed are highlight in reaction)
– : End of Language of Chemistry Class-7 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-7 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.