Conversion of Galvanometer into Ammeter Voltmeter Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-8 Torque on a Current-Loop : Moving coil Galvanometer. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
Conversion of Galvanometer into Ammeter Voltmeter Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-8 Torque on a Current-Loop : Moving coil Galvanometer
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-8 | Torque on a Current-Loop : Moving coil Galvanometer. |
| Topics | Conversion of Galvanometer into Ammeter Voltmeter Numerical |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Conversion of Galvanometer into Ammeter Voltmeter Numerical
Que-10. A galvanometer has a resistance of 100 Ω. A PD of 100 mV between its terminals gives a full-scale deflection. Calculate the shunt resistance required to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter reading up to 5 A.
Ans- Ammeter conversion formula for shunt
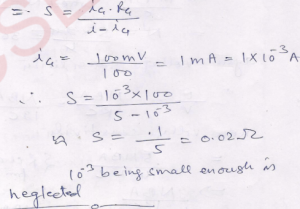
Que-11. A galvanometer of resistance 99 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. Find the value of the shunt required to convert it into an ammeter reading up to a maximum current of 5 A. What is the resistance of the ammeter?
Ans-
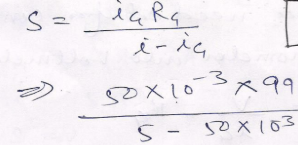
≈ 1 Ω
again shunt and galvanometer are in parallel in ammeter
∴ Net resistance of ammeter
=> 1 x 99 / 1 + 99 = 0.99 Ω
Que-12. The resistance of a galvanometer is 30 Ω and it has 100 divisions on the scale. A current of 0.2 mA produces a deflection of 1 division. What shunt will be required for measuring a current of 5 A?
Ans- Current for full scale deflection
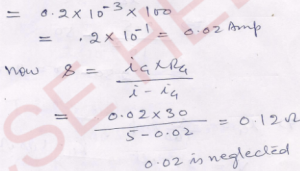
Que-13. Α 80 Ω galvanometer shows a deflection of 1 division per mA. It has 50 divisions on its scale. If a shunt of 2.5 Ω be attached to the galvanometer, what maximum current will this galvanometer measure?
Ans-
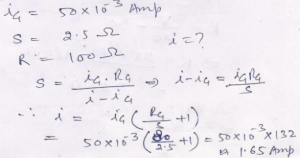
Que-14. The coil of a galvanometer has a resistance of 100 Ω. It shows full-scale deflection for a current of 5 x 104 A. How will you convert it into a voltmeter to read a maximum PD of 5 V?
Ans- Resistance needed for conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter
=> R = V/iG – R
=> (5 / 5 x 10^-4) -100 = 9900 Ω
By adding 9900 Ω resistance in series.
Que-15. Α 50 Ω resistance galvanometer has 25 divisions on its scale. On sending a current of 4.0 × 10- 4 A in it, the pointer gives a deflection of 1 division. How much resistance should be connected in series with the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter of 2.5 V range?
Ans-
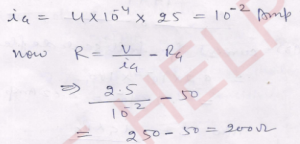
Que-16. The resistance of a voltmeter is 180 Ω. When there is 5 V potential difference across its ends, it gives full. scale deflection. What resistance should be connected in series to obtain a full-scale deflection at 25 V?
Ans-
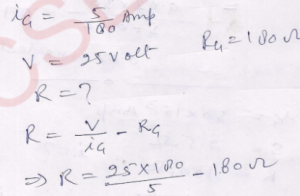
= 720 Ω
Que-17. A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 2 and it shows full-scale deflection for a current of 2.0 mA. How will you convert it into (a) an ammeter of range 0 to 5.0 A, (b) a voltmeter of range 0 to 15.0 V? Also determine the net resistances of the ammeter and the voltmeter.
Ans-(a) By connecting a shunt of 6.0 x 10-30,
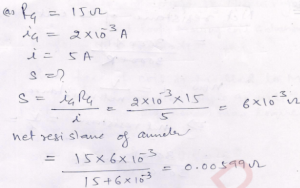
(b) by connecting a 7485 Ω resistor in series; Resistance of ammeter = 0.00599 Ω, Resistance of voltmeter = 7500 Ω.
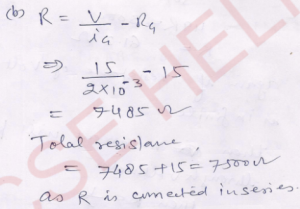
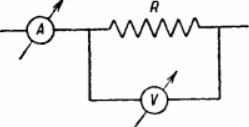
Que-18. The given circuit is used to measure the resistance R. The ammeter reads 2 A and the voltmeter 120 V What is the value of R if the resistance of the voltmeter is 3000 Ω? If the resistance of the voltmeter is taken to be infinitely large, then.
Ans- Net resistance of circuit
=> 3000 x R / 3000 + R
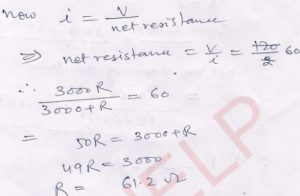
again if resistance of voltmeter is in finite then no current will pass through voltmeter
then R = V/i
=> 120/2 = 60Ω
— : End Conversion of Galvanometer into Ammeter Voltmeter Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-8 :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends