Electric Cell Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
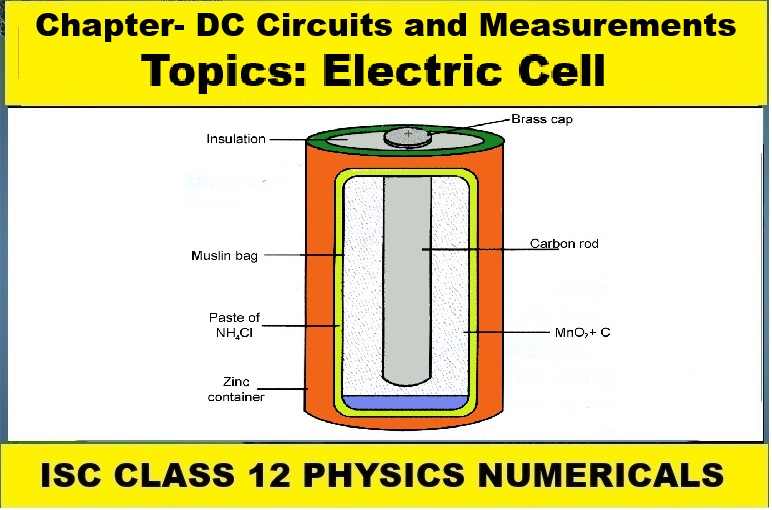
Electric Cell Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-6 | DC Circuits and Measurements. |
| Topics | Numericals on Electric Cell |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Numericals on Electric Cell
Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements
Que-1. A cell has an emf of 5.0 V and an internal resistance of 1.0 Ω. Its terminals are joined through a 9 Ω resistor. Calculate the current in the circuit and PD across the terminals of the cell.
Ans-1 Current in circuit
i = E / (R+r)
= 5 / (9+1)
= 0.5 Amp
PD across the cell
V = E – iR
=> 5 – (0.5 x 1)
=> 4.5 volt
Que-2. The potential difference of a cell in an open-circuit is 6 V which falls to 4 V when a current of 2 A is drawn from the cell. Calculate the emf and internal resistance of the cell.
Ans-2 If a cell has a PD of 6V in an open circuit, it means that the EMF of that cell is 6V.
Internal resistance of cell
V = E – i r
4 = 6 – 2 r
2 r = 2
r = 1 ohm
Que-3. The emf of a cell is 2.0 V. When it is connected to a 25 Ω resistor, the terminal voltage of the cell is found to be 1.8 V. What is the internal resistance of the cell and the current in 25 Ω resistor?
Ans-3 r = R(E/V – 1)
=> r = 25 (2/1.8 – 1)
=> 25 x 0.2 / 1.8 = 2.78 Ω
and i = V/R = 1.8/25 = 0.072 A
Que-4. The potential difference across a cell is 1.8 V when a current of 0.5 A is drawn from it. The PD falls to 1.6 V when a current of 1.0 A is drawn. Find the emf and the internal resistance of the cell.
Ans-4 According to formula
E – V = ir
E – 1.8 = 0.5r —-(i)
E – 1.6 = 1r —–(ii)
(ii) – (i) = 0.2 = 0.5r
=> r = 0.4 Ω
and E = V + ir
=> 1.8 x 0.5 x 0.4 = 2 V
Que-5. A battery supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 2.0 Ω resistor and a current of 0.3 A through a 7.0 Ω resistor. Calculate the emf and the internal resistance of the battery.
Ans-5 i = 0.9 A R = 2 Ω
i = 0.3 A R = 7 Ω
Let emf of all is E and internal resistance r
then according to formula
i = E/R+r
=> 0.9 = E/2+r —–(i)
and 0.3 = E/7+r —–(ii)
(i)/(ii) = 3 = 7+r/2+r
=> 6+3r = 7+r
=> r = 0.5 Ω
again 0.9 = E/2+0.5
E = 2.25 volt
Que-6. A 200 Ω resistor, a voltmeter and a 2.0 V cell of negligible internal resistance are connected in series. The voltmeter reads 1.0 V. Find the resistance of the voltmeter and the current in the circuit.
Ans-6 R = 200 Ω E = 2.0 V
Let resistance of volt meter is R and current through circuit is i then 200 x i = 1 volt {PD across resistance = 2-1 = 1 volt}
=> i = 1/200 = 5 x 10^-3
again R = V/i = 1/5 x 10^-3 = 200 Ω
Que-7. A high-resistance voltmeter connected across the terminals of a battery reads 15 V. When an ammeter is included in the circuit, the voltmeter reads 9.0 V and the ammeter reads 1.5 A. Find (i) internal resistance of the battery and (ii) resistance of ammeter plus the connecting wires.
Ans-7 E = 15 volt V = 9 V i = 1.5 A r = R(E/V -1)
V = iR => R = V/i
=> r = V/i (E/V – 1)
=> r = 9/1.5(15/9 – 1)
=> r = 4 Ω
again r = R(E/V – 1)
=> 4 = R(15/9 – 1)
=> R = 4 x 9 / 6
=> R = 6 Ω
Que-8. In the circuit shown, the resistance of the ammeter A is negligible and that of the voltmeter V is very high. When the key K is open, the reading of voltmeter is 1.53 V On closing the key, the reading of ammeter is 1.00 A and that of the voltmeter drops to 1.03 V. Calculate : (i) emf of the cell, (ii) internal resistance of the cell, (iii) value of R.
Ans-8 (i) EMF of cell = reading of voltmeter when key is open
(ii) r = E – V / i = 1.53 – 1.03 / 1 = 0.5 Ω
(iii) R = V/i = 1.03 / 1 = 1.03 Ω
Que-9. A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is charged by a 200 V DC supply. The resistance in the charging circuit is 38 Ω. What is the value of the charging current?
Ans-9 In case of charging
i = V – E / r
=> i = 200 – 10 / 38 = 190/38 = 5 A
Que-10. Two batteries of emf’s 6.20 V and 12.45 V and internal resistances 0.01 Ω and 0.03 Ω respectively are being charged by a battery charger which supplies in supplies a a current of 20 A. What are the terminal potential differences of the batteries during charging?
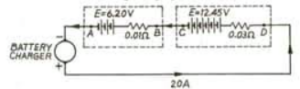
Ans-10 During charging
V – E = i r
V = E + i r
for first battery
V = 6.20 + 20 x 0.01
= 6.40 V
and for second battery
V = 12.45 + 0.03 x 20
= 13.05 Volt
— : End of Electric Cell Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements. :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends