Electric Power and Energy Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.

Electric Power and Energy Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-5 | Electric Resistance and Ohm’s Law |
| Topics | Numericals on Electric Power and Energy |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Electric Power and Energy
Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law.
Que-29. How much charge flows through a 250 V-1000 W heater in one minute?
Ans-29 P = VI
I = P/V = Q/t
Q = PV/t
= (1000 x 60)/250
Q = 240 C.
Que-30. Compute the voltage drop across a 2 kW electric heater element whose resistance when hot is 20 Ω.
Ans-30 P = V²/R
V = √(PR)
= √(2000 x 20)
= 2 x 100 = 200 V.
Que-31. A heating element is marked 210 V, 630 W. What is the current drawn by the element when connected to 210 V DC mains? What is the resistance of the element?
Ans-31 P = VI
I = P/V = 630/210 = 3A.
R = V/I
= 210/3 = 70 Ω
Que-32. An electric motor of 1 HP (horse-power) is running at 220 V. What is the current in the motor?
Ans-32 P = VI
I = P/V
I = 746/220 = 3.39 A.
Que-33. An electric press has a resistance of 44 Ω and a current of 5.0 A flows through it. Calculate the power consumed by the press.
Ans-33 P = I²R
P = 5 x 5 x 44 = 1100 W.
Que-34. A current of 4.0 A flows in a heating-wire of 100 W. Determine the resistance of the wire.
Ans-34 P = I²R
R = P/I²
R = 100/4²
R = 6.25 Ω.
Que-35. An electric bulb is rated as 250 V, 750 W. Calculate the (i) Electric current flowing through it, when it is operated on a 250 V supply. (ii) Resistance of its filament.
Ans-35 P = 750 W
V = 250 V
(i) V = IR ⇒ I = V/R
I = 250/(250/3) ⇒ (250×3)/250 = 3A.
(ii) P = V²/R ⇒ R = V²/P
R = (250 x 250)/750
R = 250/3 = 88.3 Ω.
Que-36. Find the ratio of the resistances of a 40 W bulb and a 100 W bulb designed to work at 220 V supply line.
Ans-36 P1 = 40 W and P2 = 100 W
P = V²/R
P1/P2 = R2/R1
= 40/100 = 2/5
R1 : R2 = 5 : 2.
Que-37. Find the resistance of the filament of a 100 W-220 V bulb when glowing. The length and radius of the filament are 0.1 m and 2.5 x 10^5 m. Find the specific resistance of the material of the filament.
Ans-37 R = V²/P
= (220 x 220)/100 = 484 Ω
again R = ρl/A = ρl/πr²
ρ = (Rπr²)/l
= (484 x 3.14 x (2.5 x 1-^-5)²)/0.1
= 9.5 x 10^-6 Ω-m.
Que-38. Find the resistance of a 240 V-200 W electric bulb when glowing. If this resistance is 10 times the resistance at 0°C and the temperature of the glowing filament is 2000°C, then find the temperature coefficient of resistance of the filament.
Ans-38 R = V²/P
= (240 x 240)/200 = 288 Ω.
again Rt = Ro(1+αt)
where Rt is resistance at t°C and Ro is resistance at 0°C and α = coefficient of thermal resistance.
288 = 28.8(1+α2000)
10 = 1+2000α
9 = 2000α
α = 9/2000 = 4.5 x 10¯³ C¯¹
Que-39. A lamp marked ’15 V-20 W’ is connected to a DC source of 25 V and a resistance R in series for full illumination Find (i) the current in the circuit, (ii) the resistance of the lamp, (iii) the resistance R.
Ans-39 P = 20 W, V = 15V
(i) P = VI
20 = 15 x I
I = 20/15 = 4/3 A.
(ii) R = V²/P
R’ = (15)²/20
R’ = 225/20 = 45/4 Ω.
(iii) Supply = 25 V
R = V/I = 25/(4/3) = 75/4 = 18.75
R eq = R’ + R
18.75 = 11.25 + R
R = 18.75 – 11.25
R = 7.5 Ω.
Que-40. In a house having a 220 V line the following three appliances are operating: (i) a 60 W bulb, (ii) a 1000 W heater and (iii) a 40 W radio. Calculate (a) the current drawn by the heater and (b) the current passing through the fuse for this line.
Ans-40 V = 220 V
(a) current drawn by the heater
I = P/V
= 1000/220 = 50/11 A
(b) Total power =1000+60+40 = 1100 W
V = 220V
fuse current = P/V
= 1100/220 = 5A.
Que-41. We have a 30 W-6 V bulb which we want to glow by a supply of 120 V. What will have to be done for it?
Ans-41 Power of bulb = 30 W
Voltage = 6V
current = P/V = 30/6 = 5A
Supply = 120V, current = 5 A
Voltage across resistance = 120 – 6 = 114 V
R = V/I = 114/5 = 22.8 Ω.
Que-42. Two cities are 150 km away from each other. Electric power is transmitted through copper wires from one city to the other. There is a potential-drop of 8 V/km in the wires and the average resistance of the wires is 0.5 Ω/km (i) Calculate the current flowing in the wires. (ii) Find out the loss of electric power in the wires.
Ans-42 (i) current = V/R
= 8/0.5 = 16 A.
(ii) Total resistance = 150 x 0.5 = 75 Ω
current = 16 A
Power loss = I²R
= 16 x 16 x 75 = 19200 W
= 19.2 KW.
Que-43. A 500 W electric heater is designed to work with a 115 V line. If the voltage of the line drops to 110, then what will be the percentage loss of energy liberated?
Ans-43 New Power = (V’/V)² P
= (110/115)² x 500 = 457.5
Power loss = 500 – 457.5 = 42.5
% of energy loss = (42.5/500) x 100 = 8.5%.
Que-44. An electric heater has a rating of 1100 W-220 V. How much electrical energy (in kW-h) will it consume in 4 hours? What is the resistance of its element?
Ans-44 Energy consumed in kWh
= (Pxt)/100 where t in hours
= (1100 x 4)/1000 = 4.4 kWh
again R = V²/P
= (220 x 220)/1100 = 44 Ω
Que-45. Calculate the number of electrons drifting per second through the filament of a 100 W-220 V bulb, when glowing (e = 1.6 x 10^-19 C).
Ans-45 I = P/V = 100/220 = 5/11 A = Q/1sec
5/11 C now Q = ne
n = Q/e = 5/(11×1.6×10^-19)
= 2.84 x 10^18 .
Que-46. Two bulbs B₁ and B2 are connected in series with an AC source of emf 200 V, as shown. The labels on the bulbs read 200V-60W and 200 V-100 W respectively. Calculate the ratio of: (i) the resistances of the bulbs (R1/R2), (ii) the power being consumed when connected in series (P1/P2), (iii) the PD across the bulbs (V1/V2).
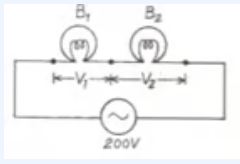
Ans-46 (i) R = V²/P
= R1/R2 = P2/P1 = 100/60
R1:R2 = 5:3
(ii) ratio of power in series
P1/P2 = I²R1/I²R2 {current is same}
P/P2 = R1/R2 = 5:3.
(iii) P.D. = V = IR
V1/V2 = R1/R2 {as current is same in series}
V1/V2 = 5:3.
Que-47. Two resistors R1 = 60 Ω and R2 = 90 Ω are connected in parallel. If electric power consumed by the resistor R1 is 15 W, calculate the power consumed by the resistor R2.
Ans-47 In case of parallel combination voltage is same
P1/P2 = V²/R1 ÷ V²/R2
= R2/R1 = 90/60
15/P2 = 90/60
= P2 = (15×60)/90
= 10 W.
Que-48. A 60 W bulb is switched on in a room. A 240 W heater is also turned on in the same room. The voltage of the mains is 120 V and the resistance of the connecting leads is 6 Ω. What is the change in the voltage at the bulb when the heater is turned on?
Ans-48 Resistance of the bulb is say Rb
Using , p = V²/R or R = V²/P
We have,
Rb = 120²/60 = 240Ω
Similarly for the heater,
Rn = 120²/240 = 60Ω
Now, the equivalent resistance of the bulb and heater together is
R = (RbRn)/(Rb+Rn) = (240×60)/(240+60) = 48Ω
Before the heater was connected, the voltage drop across the bulbs
V2 = 12/(Rb+6) × Rb = 120/(240+6) × 240 = 117V
After the heater is connected, the voltage is drop is
V1 = 120/(R+6) × R = 120/(48+6) × 48 = 106.66V
So, V2−V1 = 10.04V.
— : End of Electric Power and Energy Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends