Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Solutions Selina Chapter-6. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exercise-6(A), MCQs-6(A), Numericals-6(A), Exercise-6(B), MCQ-6(B), Numericals-6(B), Exercise-6(C) and MCQ-6(C) Questions of Exercise-6 Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-6 | Spectrum (Exe-6B and 6C) |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise-6(A), MCQs-6(A), Numericals-6(A), Exercise-6(B), MCQ-6(B), Numericals-6(B), Exercise-6(C) and MCQ-6(C) |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Solutions Selina Chapter-6
-: Select Exercise :-
Exercise-6(A), MCQs-6(A), Numericals-6(A),
Exercise-6(B), MCQ-6(B), Numericals-6(B), Exercise-6(C) and MCQ-6(C)
Note:- Read the chapter Spectrum carefully and then solve the example given in your text book before starting Solution of Chapter – 6 “Spectrum” exercise.
Exercise 6 (B) “Spectrum” Concise Physics Solutions Selina Publishers
Page 144
Question 1
(a) Give a list of at least five radiations, in the order of their increasing wavelength, which make up the complete electromagnetic spectrum.
(b) Name the radiation mentioned by you in part (a) has the highest penetrating power.
Answer 1
(a) Five radiations , in the order of their increasing frequencies are:
Infrared waves, Visible light, Ultraviolet, X-rays and Gamma rays.
(b) Gamma rays have the highest penetrating power
Question 2
(a) Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, radio waves, gamma rays and micro waves.
(b) Name the radiation is used for satellite communication?
Answer 2
(a) Gamma rays, X-rays, infrared rays, micro waves, radio waves.
(b) Microwave is used for satellite communication.
Question 3
A wave has a wavelength of 10-3 nm. (a) Name the wave. (b) State its one property different from light.
Answer 3
(a) Gamma ray.
(b) Gamma rays have strong penetrating power.
Question 4 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
A wave has wavelength 50Å. (a) Name the wave. (b) State the speed in vacuum. (c) State its one use.
Answer 4
(a) The wavelength of the wave is 50 Å. Therefore, it is a X-ray.
(b) The speed of the wave will be 3 × 108 m/s in vacuum.
(c) X-rays are used to study atomic arrangement in crystals as well as complex molecules.
Question 5
(a) Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic wave which helps in the study of structure of crystals.
(b) State one more use of the wave named in part (a).
Answer 5
(a) X-rays are used in the study of crystals.
(b) It is also used to detect fracture in bones.
Question 6
State the name and the range of wavelength of the invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
Answer 6
The electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of the spectrum are known as infrared radiations.
Range: 8000 Å to 107Å (or 800 nm to 1 mm)
Question 7
Name three radiations and their wavelength range which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Answer 7
The three radiations beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum are:
1) Ultraviolet radiations – 100 Å to 4000 Å
2) X-rays – 0.1 Å to 100 Å
3) Gamma rays – <0.1 Å
Question 8
Give the range of wavelength of the electromagnetic waves visible to us.
Answer 8
4000  to 8000
to 8000 .
.
Question 9 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
Name the region beyond (i) the red end and (ii) the violet end, of the spectrum.
Answer 9
(i)Infrared
(ii)Ultraviolet
Question 10
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Answer 10
The part of spectrum beyond the red and the violet ends is called the invisible spectrum as our eyes do not respond to the spectrum beyond the red and the violet extremes.
Question 11
Name the radiation which can be detected by (a) thermopile (b) a solution of silver chloride.
Answer 11
(a) infrared radiation
(b) ultra violet radiation
Question 12
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with (a) the ultraviolet rays (b) the visible light and (c) infrared rays.
Answer 12
(i)Ultraviolet rays-wavelength range 100 ![]() to 4000
to 4000 ![]()
(ii)Visible light-wavelength range 4000 ![]() to 8000
to 8000 ![]()
(iii)Infrared radiations-wavelength range 8000 ![]() to 107
to 107 ![]()
Question 13
Name the radiations of wavelength just (a) longer than 8 x 10-7m . (b) shorter than 4 x 10-7 m.
Answer 13
(i)Infrared radiations are longer than 8 x 10-7m.
(ii) ultraviolet radiations are shorter than 4 x 10-7 m.
Question 14
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Answer 14
1) Ultraviolet radiations – 100 Å to 4000 Å
Use: For detecting purity of gems, eggs, ghee, etc.
2) X-rays – 0.1 Å to 100 Å
Use: For detecting fracture in bones, teeth, etc.
Question 15
Give one use each of (a) microwaves (b) ultraviolet radiations (c) infrared radiations (d) gamma rays.
Answer 15
(i)Microwaves are used for satellite communication.
(ii)Ultraviolet radiations are used for detecting the purity of gems, eggs, ghee etc.
(iii)Infrared radiations are used in remote control of television and other gadgets.
(iv)Gamma rays are used in medical science to kill cancer cells
Question 16 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
Name the waves (a) of lowest wavelength, (b) used for taking photographs in dark, (c) produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom, (d) of wavelength nearly 0.1 nm.
Answer 16
Lowest wavelength= gamma rays
Waves used for taking photographs= infrared rays
and waves produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom= gamma rays
while waves having wavelength 0.1nm= X-rays
Question 17
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01  and 9000
and 9000  respectively.
respectively.
(a)Name the two waves.
(b)Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
Answer 17
(a)A- Gamma rays, B-infrared radiations
(b)Ratio of speeds of these waves in vacuum is 1:1 as all electromagnetic waves travel with the speed of light in vacuum.
Question 18
Name two sources, each of infrared radiations and ultraviolet radiations.
Answer 18
All heated bodies such as a heated iron ball, flame, fire etc., are the sources of infrared radiations.
The electric arc and sparks give ultraviolet radiations.
Question 19
What are infrared radiations? How are they detected? State one use of these radiations.
Answer 19
Infrared radiations are the electromagnetic waves of wavelength in the range of 8000  to 107.
to 107.
Detection: If a thermometer with a blackened bulb is moved from the violet end towards the red end, it is observed that there is a slow rise in temperature, but when it is moved beyond the red region, a rapid rise in temperature is noticed. It means that the portion of spectrum beyond the red end has certain radiations which produce a strong heating effect, but they are not visible. These radiations are called the infrared radiations.
Use: The infrared radiations are used for therapeutic purposes by doctors.
Question 20
What are ultraviolet radiations? How are they detected? State one use of these radiations.
Answer 20
The electromagnetic radiations of wavelength from 100 to 4000 are called the ultraviolet radiations.
Detection: If the different radiations from the red part of the spectrum to the violet end and beyond it, are made incident on the silver-chloride solution, it is observed that from the red to the violet end, the solution remains unaffected. However just beyond the violet end, it first turns violet and finally it becomes dark brown. Thus there exist certain radiations beyond the violet end of the spectrum, which are chemically more active than visible light, called ultraviolet radiations.
Use: Ultraviolet radiations are used for sterilizing purposes.
Question 21 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
Name three properties of ultraviolet radiations which are similar to visible light.
Answer 21
(a)Ultraviolet radiations travel in a straight line with a speed of 3 x 108 m in air (or vacuum).
(b)They obey the laws of reflection and refraction.
(c)They affect the photographic plate.
Question 22
Give two properties of ultraviolet radiations which differ from the visible light.
Answer 22
(a)Ultraviolet radiations produce fluorescence on striking a zinc sulphide screen.
(b)They cause health hazards like cancer on the body.
Question 23
Mention three properties of infrared radiations similar to the visible light.
Answer 23
(a)Infrared radiations travel in straight line as light does, with a speed equal to 3 x 108m/s in vacuum.
(b)They obey the laws of reflection and refraction.
(c)They do not cause fluorescence on zinc sulphide screen.
Question 24
Give two such properties of infrared radiations which differ front the visible light.
Answer 24
They do not affect the ordinary photographic film.
Question 25
Name the material prism required for obtaining the spectrum of (a) ultraviolet light, (b) infra red radiation.
Answer 25
(a) Ultraviolet light is obtained by passing radiations through a quartz prism.
(b) Infrared radiations is obtained by passing radiations through a rock salt prism.
Page 145
Question 26
Name the radiations which are absorbed by the green house gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
Answer 26
Water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and ozone are the major greenhouse gases present in the Earth’s atmosphere.
These greenhouse gases absorb the infrared radiations in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Question 27
State one harmful effect each of the (a) ultraviolet and (b) infrared radiation.
Answer 27
Ultraviolet radiation: It causes health hazards like skin cancer.
Infrared radiation: It causes skin burns.
Question 28 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
Give reason for the following:
(i)Infrared radiations are used for photography in fog.
(ii)Infrared radiations are used for signals during war.
(iii)The photographic darkrooms are provided with infrared lamps.
(iv)A rock salt prism is used instead of a glass prism to obtain the infrared spectrum.
(v)A quartz prism is required for obtaining the spectrum of the ultraviolet light.
(vi)Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass.
Answer 28
(i)Infrared radiations are used in photography in fog because they are not much scattered by the atmosphere, so they can penetrate appreciably through it.
(ii)Infrared radiations are used as signals during the war as they are not visible and they are not absorbed much in the medium.
(iii)Infrared lamps are used in dark rooms for developing photographs since they do not affect the photographic film chemically, but they provide some visibility.
(iv)Infrared spectrum can be obtained only with the help of a rock-salt prism since the rock-salt prism does not absorb infrared radiations whereas a glass prism absorbs them.
(v)A quartz prism is used to obtain the spectrum of the ultraviolet radiations as they are not absorbed by quartz, whereas ordinary glass absorbs the ultraviolet light.
(vi)Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass as they are not absorbed by quartz, whereas ordinary glad absorbs the ultraviolet light.
Selina Physics Solutions “Spectrum” Multiple choice type – 6(B)
Page 145
Question 1
The most energetic electromagnetic radiations are:
(a) Microwaves
(b) Ultraviolet waves
(c) X-rays
(d) Gamma rays
Answer 1
Gamma rays
Question 2
The source of ultraviolet light is:
(a) Electric bulb
(b) Red hot iron ball
(c) Sodium vapour lamp
(d) Carbon arc-lamp
Answer 2
Carbon arc-lamp
Question 3
A radiation P is focused by a proper device on the bulb of a thermometer. Mercury in the thermometer shows a rapid increase. The radiation P is:
(a) Infrared radiation
(b) Visible light
(c) Ultra-violet radiation
(d) X-rays
Answer 3
Infrared radiation
Hint: Infrared radiations produce strong heating effect.
Selina Concise Physics Solutions “Spectrum” Numericals – 6(B)
Page 145
Question 1
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500MHz and a wavelength of 60cm.
(a) Calculate the velocity of the wave.
(b) Name the medium through which it is travelling.
Answer 1
(a) Frequency =500MHz =500 x 106Hz
Wavelength= 60 cm=0.6 m
Velocity of wave= frequency x wavelength
=500x 106 x 0.6=3 x 108m/s
(b) Electromagnetic wave is travelling through air.
Question 2
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01  . Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any
. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any
Answer 2
Wavelength = 0.01 = 0.01 x 10-10 m
= 0.01 x 10-10 m
Speed of X-rays =3 x 108m/s
Speed of light = frequency x wavelength
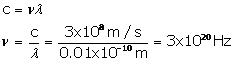
Selina Physics Solution “Spectrum” Exercise – 6(C) ICSE Class-10
Page 147
Question 1
What is meant by scattering of light?
Answer 1
When white light from sun enters the earth’s atmosphere, the light gets scattered i.e., the light spreads in all directions by the dust particles, free water molecules and the molecules of the gases present in the atmosphere. This phenomenon is called scattering of light.
Question 2
How does the intensity of scattered light depend on the wavelength of incident light? State conditions when this dependence holds.
Answer 2
The intensity of scattered light is found to be inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength of light. This relation holds when the size of air molecules is much smaller than the wavelength of the light incident.
Question 3
When sunlight enters the earth’s atmosphere, state which colour of light is scattered (i) the most and (ii) which the least.
Answer 3
Violet colour is scattered the most and red the least as the intensity of scattered light is found to be inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength of light
Question 4 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
A beam of blue, green and yellow light passes through the the Earth’s atmosphere. Name the colour which is scattered (a) the least (b) the most
Answer 4
(a) Yellow light has the highest wavelength out of the three radiations. Hence, it gets scattered the least.
(b) Blue light has the lowest wavelength out of the three radiations. Hence, it gets scattered the most.
Question 5
Which colour of white light is scattered the least? Give reason.
Answer 5
The light having the largest wavelength is scattered the least. Hence, red coloured light is scattered the least.
Question 6
The danger signal is red. Why?
Answer 6
Since the wavelength of red light is the longest in the visible light, the light of red colour is scattered the least by the air molecules of the atmosphere and therefore the light of red colour can penetrate to a longer distance. Thus red light can be seen from the farthest distance as compared to other colours of same intensity. Hence it is used for danger signal so that the signal may be visible from the far distance
Question 7
How would the sky appear when seen from the space (or moon)? Give reason for your answer.
Answer 7
On the moon, since there is no atmosphere, therefore there is no scattering of sun light incident on the moon surface. Hence to an observer on the surface of moon (space), no light reaches the eye of the observer except the light directly from the sun. Thus the sky will have no colour and will appear black to an observer on the moon surface.
Question 8 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
What characteristic property of light is responsible for the blue colour of the sky?
Answer 8
Scattering property of light is responsible for the blue colour of the sky as the blue colour is scattered the most due to its short wavelength.
Question 9
The colour of the sky, in direction other then of the sun is blue. Explain.
Answer 9
As the light travels through the atmosphere, it gets scattered in different directions by the air molecules present in its path. The blue light due to its short wavelength is scattered more as compared to the red light of long wavelength. Thus the light reaching our eye directly from sun is rich in red colour, while the light reaching our eye from all other directions is the scattered blue light. Therefore, the sky in direction other than in the direction of sun is seen blue.
Question 10
Why does the sun appear red at sunrise and sunset?
Answer 10
At the time of sunrise and sunset, the light from sun has to travel the longest distance of atmosphere to reach the observer. The light travelling from the sun loses blue light of short wavelength due to scattering, while the red light of long wavelength is scattered a little, so is not lost much. Thus blue light is almost absent in sunlight reaching the observer, while it is rich in red colour.
Question 11
The sky at noon appears white. Give reason.
Answer 11
At noon, the sun is above our head, so we get light rays directly from the sun without much scattering of any particular colour. Further, light has to travel less depth of atmosphere; hence the sky is seen white.
Question 12 (Exe-6B and 6C Spectrum ICSE Class-10 Concise)
The clouds are seen white. Explain.
Answer 12
The clouds are nearer the earth surface and they contain dust particles and aggregates of water molecules of sizes bigger than the wavelength of visible light. Therefore, the dust particles and water molecules present in clouds scatter all colours of incident white light from sun to the same extent and hence when the scattered light reaches our eye, the clouds are seen white.
Question 13
Give reason why the smoke from fire looks white.
Answer 13
The smoke from the fire looks white because the size of the particle is bigger than the wavelength of light and hence it scatters light of all wavelength which makes it look white.
Concise Selina Physics Solution “Spectrum” – MCQ – 6(C)
Page 147
Question 1
In the white light of Sun, maximum scattering by the air molecules present in the Earth’s atmosphere is for:
(a) Red colour
(b) Yellow colour
(c) Green colour
(d) Blue colour
Answer 1
Blue colour
Hint: When light of certain frequency falls on that atom or molecule, this atom or molecule responds to the light, whenever the size of the atom or molecule comparable to the wavelength of light. The sizes of nitrogen and oxygen molecules in atmosphere are comparable to the wavelength of blue light. These molecules act as scattering centers for scattering of blue light. This is also the reason that we see the sky as blue.
Question 2
To an astronaut in a space-ship, the earth appears:
(a) White
(b) Red
(c) Blue
(d) black
Answer 2
To an astronaut in a space-ship, the earth appears blue due to the large scattering of blue colour of the sunlight by the atmosphere.
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Physics Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with your friends