Fundamental Geometrical Concept Class-6 RS Aggarwal ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-14. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-14 Fundamental Geometrical Concept for ICSE Class-6 RS Aggarwal Mathematics .
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-14 A to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6 Mathematics.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal brothers Prakshan |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 6th |
| Chapter-14 | Fundamental Geometrical Concept |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Book Name | Foundation |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-14 A |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Fundamental Geometrical Concept Class-6 RS Aggarwal ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-14
The fundamental geometrical concepts depend on three basic concepts — point, line and plane. The terms cannot be precisely defined. However, the meanings of these terms are explained through examples. It is the mark of position and has an exact location
Point:
It is the mark of position and has an exact location.
- A Point has no length, breadth or thickness.
- It is denoted by a dot made by the tip of a sharp pencil.
- Point is denoted by capital letter.
- In the given figure P, Q, R represents different points
Line:
- It is a straight path which can be extended indefinitely in both the directions.
- the line is shown by two arrowheads in opposite directions.
- It does not have any fixed length.
- A line has no endpoints.
- It is denoted as AB ↔ or BA↔ and is read as line AB or line in the BA.
- It can never be measured.
- Infinite number of points lie on the line.
- Sometimes it is also denoted by small letters of the English alphabet.
Ray:
- A ray is a straight path which can be extended indefinitely in one direction only and the other end is fixed.
- It has no fixed length.
- It has one endpoint called the initial point.
- Ray cannot be measured.
- A number of rays can be drawn from an initial point O.
- Ray OA and ray OB are different because they are extended in different directions.
- Infinite points lie on the ray.
Line Segment:
- line segment is a straight path which has a definite length.
- It has two endpoints.
- line segment is a part of the line.
- It is denoted as AB or BA.
- line segment is read as line segment AB or line segment BA.
- The distance between A and B is called the length of AB
- Infinite number of points lies on a line segment.
- Two line segments are said to be equal if they have the same length.
Plane:
A smooth, flat surface gives us an idea of a plane. The surface of the table, wall, blackboard, etc., is smooth and flat. It extends endlessly in all the directions. It has no length, breadth or thickness. Certain figures like square, rectangle, triangle, and circle on the plane. Hence, these figures are also called plane figures.
Concurrent Lines:
Three or more lines which pass through the same point are called concurrent lines and this common point is called the point of concurrence
Exe-14 A
Page 195-197
Question 1:
Identify and name the line segment and rays in the following figures :
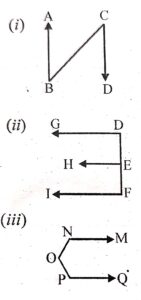
Answer :

Question 2:
What do you mean by collinear points ?
(i) Mark three points which are collinear.
(ii) Mark three points which are non-collinear. Draw lines through these points taking two at a time and name these lines. How many such different lines can be drawn ?
Answer :
(i) Three or more points in a plane are said to be collinear if all lie on the same line.
Points A, B, C are collinear

(ii)
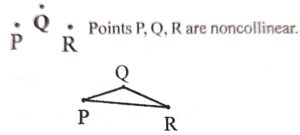
Three lines can be drawn, lines or PQ, QR, and PR
Question 3:
(i) How many lines can be drawn passing through three collinear points ?
(ii) Given three collinear points A, B, C. How many line segments do they determine ? Name them.
Answer :
(i) 1
(ii) AB, BC, AC
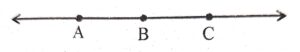
Question 4:
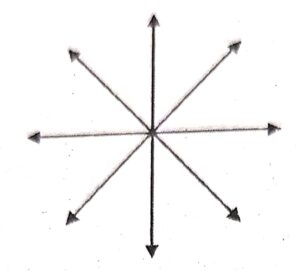
What do you mean by concurrent lines ? Draw four concurrent lines.
Answer :
Three or more than there lines in a plane are said to be concurrent, if all of them pass through the same point.
Question 5:
Count the number of line segments drawn in each of the following 1igures and name them.
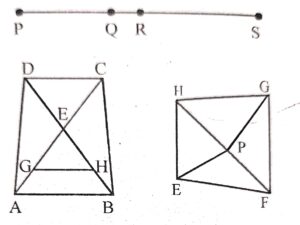
Answer :

Question 6:
Fill in the blanks :
(i) A line segment has …………. end points.
(ii) A line has ………. end points.
(iii) A ray has ……….. end point.
(iv) A line segment has a …………. length.
(v) A line AB is represented by ………….
(vi) A ay AB is represented by …………..
(vii) A point shows a definite ……………
(viii) Two lines intersect in a ……………
(ix) Two planes intersect in a …………..
(x) The minimum number fo points of inter – section of three lines in a plane is ………….
(xi) The maximum number of points of inter- section of three lines in a plane is ……………
Answer :
(i) A line segment has two end points.
(ii) A line has no end points.
(iii) A ray has one end point.
(iv) A line segment has a definite length.
(v) A line AB is represented by AB <—>
(vi) A ay AB is represented by AB —>
(vii) A point shows a definite position.
(viii) Two lines intersect in a points.
(ix) Two planes intersect in a line.
(x) The minimum number fo points of inter – section of three lines in a plane is 0.
(xi) The maximum number of points of inter- section of three lines in a plane is 3.
Question 7:
Look at the adjoining figure carefully and name:
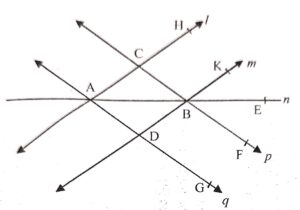
(i) all pairs of parallel lines;
(ii) all pairs of intersecting lines and their point of intersection;
(iii) all set of collinear points;
(iv) concurrent lines and their points of con-currence ;
(v) One set of three non-collinear points.
Answer :
(i) (l, m), (p, q)
(ii) ( l and p ; C), ( l and q ; A), ( land n ; A), (m and n ; B), (m and p ; B), (m and q ; D), (n and P ; B), (n and q :D)
(iii) (A, B, E), (A, C, H), (D, B, K), (C, B, F), (A, D, G)
(iv) ( l, n and q ; A) ; (m, n and p ; B)
(v) A, C, D
Question 8:
Which shape do the following have ?
(i) The wheel of a bicycle
(ii) A blackboard
(iii) A page of a book
(iv) The face of the full moon
(v) A set-square in a geometry box.
(vi) A face of a dice.
Answer :
(i) The wheel of a bicycle Circle.
(ii) A blackboard Rectangle.
(iii) A page of a book Rectangle.
(iv) The face of the full moon Circle
(v) A set-square in a geometry box Triangle.
(vi) A face of a dice Square.
Question 9:
Fill in the blanks :
(i) A triangle has ……… sides and …….. Vertices.
(ii) A rectangle has ……… sides and …….. vertices.
(iii) All the sides of a square are ……….
(iv) The …………… sides of a rectangle are equal.
(v) A circle has ……….. side and …………….. vertex.
Answer :
(i) A triangle has 3 sides and 3 Vertices.
(ii) A rectangle has 4 sides and 4 vertices.
(iii) All the sides of a square are equal.
(iv) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal.
(v) A circle has no side and no vertex.
Question 10:
Consider the line AB <–> shown here with and find whether the statements given below are true or false :
(i) D is a point on ray EB.
(ii) C is a point on ray DA.
(iii) Ray DB is different from ray EB.
(iv) C, D, E are points on line segment CE.
(v) Ray CA is different from ray CB.
Answer :
(i) False Correct is : D is a point on line EB.
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) True
(v) True
Question 11:
State whether the given statements are true or false :
(i) Every ray has a finite length.
(ii) Ray AB is the same as ray BA.
(iii) Line AB is the same as line BA.
(iv) Two points A and B in a plane determine a unique line segment.
(v) One and only one line can be drawn too pass through a given point.
(vi) If points A, B, C are collinear and points
C, D, E are collinear, then the points A, B,
C, D, E, are collinear.
Answer :
(i) False Correct is : Every ray has an infinite length
(ii) False Correct is : Ray AB is different from ray BA
(iii) True
(iv) True
(v) False Correct is : Multiple lines can be drawn to pass through a given point.
(vi) True
–: End of Fundamental Geometrical Concept Class-6 RS Aggarwal Solutions :–
Return to- RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-6 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks