Indices Exponents Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-6C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-6. We Provide Step by Step Solutions / Answer of Questions on Indices Exponents OP Malhotra Maths. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics.

Indices Exponents Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-6C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-6
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-6 | Indices Exponents |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-6C | Problems on Indices Exponents |
| Edition | 2025-2026 |
Exercise- 6C
Indices Exponents Class 9 OP Malhotra ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-6
Que-1: Evaluate:
(i) 5° x 4¯¹ + 8¯¹
(ii) √{(64)^-4.(125)^-2}
(iii) (9¯³×16^(3.2))^(1,6)
(iv) √{(16)^-34×(125)^-2}
(v) (32)^(−2/5).(216)^(−2/3)
Sol: (i) 5^0 × 4¯¹ + 8^(1/3)
= 1 × (1/4) + (2×2×2)^(1/3)
= (1/4) + (2^3)^(1/3)
= (1/4) + 2^(3×1/3)
= (1/4) + 2¹
= 2 + (1/4)
= 2*(1/4)
(ii) √{(64)^-4.(125)^-2}
= [(64)^−4.(125)¯²]^(1/3)
= (64)^(−4×1/3)⋅(125)^(−2×1/3)
= (64)^(−4/3)⋅(125)^(−2/3)
= (4^3)(−4/3) × (5^3)(−2/3)
= 4^{3×(−4)/3) × 5^{3×(−2/3)}
= 4^−4 × 5^−2
= 1/4^4 × (1/5)^2
= 1/(4×4×4×4×5×5)
= 1/6400
(iii) (9¯³×16^(3.2))^(1,6)
= [(3^2)^−3 × (2^4)^(3/2)]^(1/6)
= [(3)^(−6) × (2)^6]^(1/6)
= 3^(−6.1.6) × 2^(6×1/6)
= 3^1 × 2′
= (1/3) × 2 = 2/3
(iv) √{(16)^-34×(125)^-2}
= [2^{4×(−3.4)} × 5^{3×(−2)}]^(1/3)
= [2^−3 × 5^−6]^(1/3)
= [123×56]13
= 1/{(2^3)^(1/3) × (5^6)^(1/3)
= 1/(2¹×5²)
= 1/(2×5×5)
= 1/50
(v) (32)^(−2/5).(216)^(−2/3)
= (2^5)(-2/5) + (6³)^(-2/3)
= (2)^(−2/5×5) + (6)^{3×(−2/3)}
= 2¯² + 6¯²
= (2/6)¯²
= (6/2)²
= (6×6)/(2×2)
= 36/4 = 9
Que-2: (i) (64/125)^(−2/3) + 1/(256/625)^(1/4) + (√25/√64)^0
(ii) 9^(3/2) − 3×(5)^0 − (1/81)^(−1/2)
(iii) (1/4)^(−2) − 3(8)^(2/3) × 4^0 + (9/16)^(−1/2)
(iv) 16^(3,4) + 2(1/2)^−1
(v) (81)^(3/4) − (1/32)^(−2/5) + (8)^(1/3) (1/2)^−2
Sol: (i) (64/125)^(−2/3) + 1/(256/625)^(1/4) + (√25/√64)^0
= {(4)³/(5)³}^(-2/3) + {1/(4^4)/(5^4)}^(1/4) + 1
= {4/5}^3(-2/3) + {1/(4/5)}^4(1/4) + 1
= (4/5)¯² + (1/(4/5)¹ + 1
= (5/4)² + (5/4)¯¹ + 1
= (5/4) + 1
= 9/4 = 2*(1/4).
(ii) 9^(3/2) − 3×(5)^0 − (1/81)^(−1/2)
= (3²)^(3/2) – (3×1) – (1/3^4)^(-1/2)
= 3³ – 3 – (1/3¯²)
= 27 – 3 – 9
= 15.
(iii) (1/4)^(−2) − 3(8)^(2/3) × 4^0 + (9/16)^(−1/2)
= (1/2²)^(-2) – 3(2³)^(2/3) × 1 + [(3/4)²]^(-1/2)
= (1/2)^(-4) – 3 × (2²) + (3/4)¯¹
= 2^4 – 12 + (4/3)
= 16 – 12 + (4/3)
= (48-36+4)/3
= 16/3
= 5*(1/3).
(iv) 16^(3/4) + 2(1/2)^−1
= (2^4)^(3/4) + 2(2)
= 2³ + 4
= 8 + 4
= 12.
(v) (81)^(3/4) − (1/32)^(−2/5) + (8)^(1/3) (1/2)^−2
= (3^4)^(3/4) – (1/2^5)^(-2/5) + (2³)^(1/3) (2)²
= 3³ – 2² + 2³
= 27 – 4 + 8
= 31.
Que-3:
(a) Evaluate : x^(1/2) x y^(-1) x z^(2/3) when x = 9, y = 2, and z = 8.
(b) Evaluate as a fraction :
(27/8)^(2.3) − (1/4)^(−2) + (5)^0
(c) Evaluate as a fraction :
√(1/4) + (0.01)^(−1/2) − (27)^(2/3)
Sol: (a) Substituting value of x, y and z in x^(1/2) . y^(−1) . z^(2/3) we get,
⇒ x^(1/2) . y^(−1) . z^(2/3)
= (9)^(1/2) . (2)^(−1) . (8)^(2/3)
= (3²)^(1/2) × (1/2) × (2³)^(2/3)
= 3 × (1/2) × 2²
= 12/2
= 6.
(b) (27/8)^(2/3) – (1/4)^(-2) + 5^0
= (3³/2³)^(2/3) – (1/2²)^(-2) + 5^0
= [(3/2)³]^(2/3) – [(1/2)²]^(-2) + 1
= (3/2)(3×(2/3)) – (1/2)(2×(-2)) + 1
= (3/2)² – (1/2)^(-4) + 1
= (3/2) × (3/2) – {1/(1/2)^4} + 1
= (9/4) – {1/(1/2)×(1/2)×(1/2)×(1/2)} + 1
= (9/4) – {1/(1/16)} + 1
= (9/4) – 16 + 1
= (9-64+4)/4
= -51/4
= -12*(3/4).
(c) √(1/4) + (0.01)^(−1/2) − (27)^(2/3)
= √{(1/2)×(1/2)} + {(0.1×0.1)^(-1/2)} – (3×3×3)^(2/3)
= (1/2) + [(0.1)²]^(-1/2) – (3/2)^(2/3)
= (1/2) + (0.1)^{2×(-1/2)} – 3 × (3×(2/3))
= (1/2)+(0.1)^(-1) – 3²
= (1/2) + (1/0.1) – 9
= (1/2) + (10/1) – 9
= (1+20-18)/2
= 3/2
= 2*(1/2).
Que-4: Simplify:
(i) [(64)^(5n/6) ⋅ (27)^(−n/6)][(12)^(−n⋅2)] ⋅ 2^6n
(ii) [6.(8)^(n+1) + 16.2^(3n−2)]/[10.2^(3n+1) − 7.(8)^n]
(iii) [4^2n ⋅ 2^(n+1)]/[2^(n−3) ⋅ 4^(2n+1)]
(iv) [(5)^(2n+3) − (25)^(n+2)]/{(125)^(n+1)}^1/3
Sol: (i)
![Simplify: (i) [(64)^(5n/6) ⋅ (27)^(−n/6)][(12)^(−n⋅2)] ⋅ 2^6n](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/4i-217x300.png)
= 2^(12n).3^0
= 2^(12n)
(ii) [6.(8)^(n+1) + 16.2^(3n−2)]/[10.2^(3n+1) − 7.(8)^n]
= [6(2³)^(n+1) + 16(2)^(3n-2)]/[10(2)^(3n+1) – 7^(2³)^n]
= [6(2^(3n+3)) + 16(2)^(3n-2)]/[10(2)^(3n+1) – 7(2^3n)]
= [6×2^(3n)(2³) + 16^(2)^(3n)(2¯²)]/[10(2)^(3n)(2¹) – 7(2^3n)]
= [2^(3n)((6×2³) + (16×(1/2²))]/[2^(3n)((10×2)-7)
= [(6×8)+(16×(1/4))]/(20-7)
= (48+4)/13
= 52/13
= 4
(iii) [4^2n ⋅ 2^(n+1)]/[2^(n−3) ⋅ 4^(2n+1)]
= (2^4n*2^n+1)/(2^n-3*2^4n+2)
= (2^4n+n+1)/(2^n-3+4n+2)
= (2^5n+1)/(2^5n-1)
= 2^5n+1-(5n-1)
= 2^5n+1-5n+1
= 2^1+1
= 2^2
= 4
(iv) [(5)^(2n+3) − (25)^(n+2)]/{(125)^(n+1)}^1/3
![(iv) [(5)^(2n+3) − (25)^(n+2)]/{(125)^(n+1)}^1/3](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/4ii.png)
![(iv) [(5)^(2n+3) − (25)^(n+2)]/{(125)^(n+1)}^1/3](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/4iii-235x300.png)
= -500/25
= -20.
Que-5: If [49^(n+1)⋅(7^n)−(343)^n]/[7^(3m)⋅2^n] = 3/343, prove that m = (n + 1)
Sol: So we have the equation
= 49^n + 1 x 7^n – 343^n / 7^3m x 2^4 = 3 / 343
We can write this as
= (7^2)^n + 1 x 7^n – (7^3)^n / 7^3m x 2^4 = 3 / 7^3
We get by the law of exponents a^m x a^n = a^m + n
= 7^2n + 2 x 7^n – 7^3n / 7^3m x 2^4 = 3/7^3
= 7^2n + 2 + n – 7^3n / 7^3m x 48 = 1/7^3
= 7^3n + 2 – 7^3n / 7^3m x 48 = 1/7^3
= 7^3n x 7^2 – 7^3n / 7^3m x 48 = 1/7^3
= 7^3n (7^2 – 1) / 7^3m x 48 = 1/7^3
= 7^3n x 48 / 7^3m x 48
= 1/7^3
7^3n x 7^3
= 7^3m
Since bases are same exponents are equal.
So 3n + 3 = 3m
3(n + 1) = 3m
n+1 = m
Que-6: If 2205 = 3a x 5b x 7c
(i) Find the numerical values of a, b and c
(ii) Hence evaluate 3a x 5-b x 7-c
Sol: (i) 2205 = 3^a x 5^b x 7^c
3^2 . 5^1 . 7^2 = 3^a . 5^b . 7^c
Comparing we get,
a = 2, b = 1, c = 2
(ii) Now 3^a x 5^-b x 7^-c
= (3^a)/(5^b × 7^c)
= 3²/(5¹×7²)
= 9/(5×49)
= 9/245
Que-7: If [{(b^3)(c^−2)}/{(b^−4)(c^3)}]^−3 + [{(b^−1)c}/{(b^2)⋅^(c−2)}]^5 = b^x . c^x, prove that x + y + 6 = 0
Sol: [{(b^3)(c^−2)}/{(b^−4)(c^3)}]^−3 + [{(b^−1)c}/{(b^2)⋅^(c−2)}]^5
⇒ {b^(−9)⋅(c^0)}/{b^(12)⋅^(c^−9)} ÷ {(b^−5)(c)}/{(b^10)⋅^(c−10)}^5 = (b^x) ⋅ (c^1)
⇒ {b^(−9)⋅(c^0)}/{b^(12)⋅^(c^−9)} × {(b^10)⋅^(c−10)}/{(b^−5)(c)}^5 = (b^x) ⋅ (c^1)
⇒ b^(−9−12+10+5) ⋅ c^(6+9−10−15) = b^4 ⋅ c^5
⇒ b^(−21+15) ⋅ c^(15−15) = b^x ⋅ c^1
⇒ b^−6 ⋅ c^0 = b^x ⋅ c^v
Comparing both sides, x = – 6, y = 0
Now R.H.S. = x + y + 6 = – 6 + 6 = 0
= R.H.S.
Que-8: prove that
(i) (x+y)^−1 (x^−1 + y^−1) = 1/xy
(ii) (x^−1 + y^1)^(−1) = xy/(x+y)
(iii) (a+b+c)/{(a^−1 b^−1) + (b^−1 c^−1) + (c^−1 a^−1)} = abc.
(iv) 1/{1+x^(b−a)+x^(c−a)} + 1/{1+x^(a−b)+x^(c−b)} + 1/{1+x^(b−c)+x^(a−c)} = 1.
(v) ab√{(x^a)/(x^b)} ⋅ b√{(x^b)/(x^c)} ⋅ ca√{(x^c)/(x^a)} = 1
Sol: (i) (x+y)^-1 (x^-1) + (y^-1)
= (1/x+y)(1/x+1/y)
= (1/x+y)(y+x/xy)
= 1/xy
hence proved
(ii) {(x^-1)+(y^-1)}^-1 = xy/x+y
{(1/x^-1)+(y^-1)}
= (1/x^-1) + (1/y^-1)
= (x^-1) + (y^-1)/(x^-1)(y^-1)
= {(x+y)^-1}/{(x^-1)(y^-1)}
= (now just reciprocal it)
= xy/x+y
(iii) LHS
= (a+b+c)/{(1/ab)+(1/bc)+(1/ca)}
= (a+b+c)/{(c+a+b)/abc}
On taking reciprocal
= (a+b+c) * (abc) / (c+a+b)
= abc = RHS
Hence proved
(iv) Consider the left hand side:
1/{1+x^(b−a)+x^(c−a)} + 1/{1+x^(a−b)+x^(c−b)} + 1/{1+x^(b−c)+x^(a−c)}
= 1/{1+(x^b)/(x^a)+(x^c)/(x^a)} + 1/{1+(x^a)/(x^b)+(x^c(/(x^b)} + 1/{1+(x^b)/(x^c)+(x^a)/(x^c)}
= 1/[{(x^a)+(x^b)+(x^c)}/x^a] + 1/[{(x^b)+(x^a)+(x^c)}/x^b] + 1/[{(x^c)+(x^b)+(x^a)}/x^c]
= x^a/{(x^a)+(x^b)+(x^c)} + x^b/{(x^b)+(x^a)+(x^c)} + x^c/{(x^c)+(x^b)+(x^a)}
= {(x^a)+(x^b)+(x^c)}/{(x^a)+(x^b)+(x^c)}
= 1
LHS = RHS Proved.
(v) LHS = ab√{(x^a)/(x^b)} ⋅ b√{(x^b)/(x^c)} ⋅ ca√{(x^c)/(x^a)}
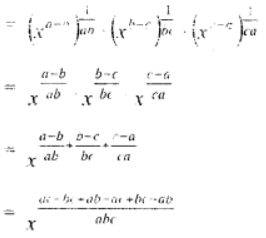
= x^{0/abc}
= x^0
= 1 RHS.
Que-9: Simplify
(i) (p^(1/3) − p^(−1/3)) (p^(2/3) + 1 + p^(−2/3))
(ii) (√11 + √3)^(1/3) (√11 − √3)^(1/3)
Sol: (i) (p^(1/3) − p^(−1/3)) (p^(2/3) + 1 + p^(−2/3))
a = p^1/3
b = p^-1/3
a³ – b³ = (a-b) (a²+ab+b²)
= {p^(1/3)}³ – {p^(-1/3)}³
= p – p¯¹
= p – (1/p).
(ii) (√11 + √3)^(1/3) (√11 − √3)^(1/3)
Let √11 = a and √3 = b
= (a+b)^(1/3) (a-b)^(1/3) = (a²-b²)^(1/3)
= [(√11)² – (√3)²]^(1/3)
= (11-3)^(1/3)
= (8)^(1/3)
= (2³)^(1/3)
= 2^(3×(1/3))
= 2¹ = 2.
Que-10: If 3x = 5y = 45z, prove that x = 2yz/y-z
Sol: 3^x = 5^y = 45^z = a (Suppose)
∴ a^(1/x) = 3, a^(1/y), a^(1/z) = 45
45 = 3 x 3 x 5
⇒ 45 = 3² x 5
⇒ a^(1/z) = a^(2x/) × a^(1/y)
⇒ a^(1/z) = a^(2/x) + (1/y)
Comparing we get,
1/z = (2/x) + (1/y)
⇒ 2/x = (1/z) − (1/y)
⇒ 2/x = (y−z)/yz
⇒ 1/x = (y−z)/2yz
∴ x = 2yz/y−z
Hence Proved.
Que-11: If x = abp-1, y = abq-1 and z = abr-1 prove that xp-r x yr-p.zp-q = 1.
Sol: x = abp-1, y = abq-1 and z = abr-1
L.H.S. = xp-r x yr-p.zp-q = 1
= (abp-1)p-r.(abq-1)r-p.(abr-1)p-q
= ap-r.b(q-r)(p-1).ar-p.b(r-p)(q-1).ap-q.b(p-q)(r-1)
= aq-r+r-p+p-r.bpq-q-rp+r.brq-r-pq+p.bpr-p-qr+q
= a°.bpq-q-r p+r+r q-r-pq+p+pr-p-qr+q
= a°.b° = 1 x 1 = 1 = R.H.S.
— : End of Indices Exponents Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-6C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-6 :–
Return to :– OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends


