Linear Inequations in One Variables Class 10 OP Malhotra Exe-4 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-4. We Provide Step by Step Solutions / Answer of S Chand OP Malhotra Maths. In this article you would learn how to find solution set of any inequations. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Mathematics.

Linear Inequations in One Variables Class 10 OP Malhotra Exe-4 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-4
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-4 | Linear Inequations in One Variables |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-4 | how to find solution set of any inequations |
| Edition | 2025-2026 |
Exercise – 4
Linear Inequations in One Variables Class 10 OP Malhotra Exe-4 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-4
Que-1: On a bargain counter, the shopkeeper put labels on various goods showing their prices, Rs. P, where P e {real numbers}. Write a mathematical sentence for each of the following labels :
(a) more than Rs. 7.50
(b) not less than Rs. 10
(c) not more than Rs. 22
(d) less than Rs. 11
Sol: (a) more than Rs. 7.50 : > Rs. 7.50
(b) not less than Rs. 10 : ≮ Rs. 10
(c) not more than Rs. 22 : ≯ Rs. 22
(d) less than Rs. 11 : < Rs. 11
Que-2: You are given the following numbers :
-2.6 5.1 -3 0.4 1.2 -3.1 4.7
Fill in the blanks.
(a) A = {A : A ≤ -3} = {…..}
(b) B = {A : A ≤ 1} = {…..}
Sol: Given numbers are ; -2.6, 5.1, -3, 0.4, 1.2, -3.1, 4.7
(a) A = {x : x ≥ -3}
= {-3, -2.6, 0.4, 1.2, 4.7, 5.1}
(b) B = {x : x ≤ 1} = {-3.1, -3, -2.6, 0.4}
Que-3: If the replacement set is {-2, -1, +1, +2, +4, +5, +9}, what is the solution set of each of the following mathematical sentences?
(a) x + (3/2) > (5/2)
(b) x – 4 = – 3
(c) 2x – 5 ≥ 10
(d) 3y ÷ 2 ≤ (5/2)
(e) 4x² = 16
Sol: Replacement set = {-2, -1, +1, +2, +4, +5, +9}
(a) x + (3/2) > (5/2)
⇒ x > (5/2) – (3/2) ⇒ x > (5–3)/2
⇒ x > 2/2 ⇒ x > 1
∴ Solution set = {+2, +4, +5, +9}
(b) x – 4 = – 3
⇒ x = – 3 + 4
⇒ x = 1
Solution set = {+1}
(c) 2x – 5 ≥ 10
⇒ 2x ≥ 10 + 5 ⇒ 2x ≥ 15
⇒ x ≥ y
⇒ A ≥ 7.5
∴ Solution set = {+9}
(d) 3y ÷ 2 ≤ (5/2)
⇒ 3y ≤ (5/2) x 2 ⇒ 3y ≤ 5
⇒ y ≤ 5/3
⇒ y ≤ 1*(2/3)
∴ Solution set = {+1, -1, -2} = {-2. -1, +1}
(e) 4x² = 16
⇒ x² = 16/4
⇒ x² = 4 ⇒ x² = (±2)²
∴ x = ±2,
∴ Solution set = {-2, +2}
Que-4: List the solution set of 30 – 4 (2x – 1) < 30, given that x is a positive integer.
Sol: 30 – 4 (2x – 1) < 30
⇒ 30 – 8x + 4 < 30
⇒ 34 – 8x < 30
⇒ 34 – 30 < 8x ⇒ 4 < 8x ⇒ 8A > 4 ⇒ x > 4/8
⇒ x > 1/2
∴ A is a positive integer,
∴ Solution set = {1, 2, 3, 4, }
Que-5: If the replacement set is {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, what is the solution set of the following mathematical sentences?
(a) x + (4/3) = (7/3)
(b) 2x + 1 < 3 (c) x – 6 > 10 – 6
(d) x + 5 = 20
(e) 2x + 3 ≥ 17
Sol: Replacement set = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
(a) x + (4/3) = (7/3) ⇒ x = (7/3) – (4/3)
⇒ x = (7–4)/3 = 3/3 ⇒ x = 1
∴ Solution set = 1
(b) 2A + 1 – 1 < 3 ⇒ 2x < 3 – 1
⇒ 2A < 2 ⇒ x < 2/2
⇒ x < 1
∴ Solution set = {0}
(c) x – 6 > 10 – 6
⇒ x > 10 – 6 + 6
⇒ x > 10 – 12 ⇒ x > – 2
∴ Solution set = Φ {∵ – 2 ∉ to the given set}
(d) x + 5 = 20 ⇒ x = 20 – 5
⇒ x = 15
∴ Solution set = Φ {∵ 15 ∉ to the given set}
(e) 2A + 3 ≥ 17 ⇒ 2x ≥ 17 – 3
⇒ 2A ≥ 14 ⇒ x ≥ 14/2
⇒ A ≥ 7
∴ Solution set = {7, 8, 9}
Que-6: (a) x ∈ {2, 4, 6, 9} and y ∈ {4, 6, 18, 27, 54}. Form all ordered pairs (x, y) such that x is a factory and x < y. (b) Find the truth set of the inequality x > y + 2 where
(x, y) ∈ {(1, 2), (2, 3), (5, 1), (7, 3), (5, 6), (6, 5)}.
Sol: (a) x ∈ {2, 4, 6, 9} and y ∈ {4, 6, 18, 27, 54}
∵ A is a factor of y and x < y ∴ Ordered pairs will be {(2, 4), (2, 6), (2, 18), (2, 54), (6, 18), (6, 54), (9, 18), (9, 27), (9, 54)} (b) x > y + 2 where
(A, y) ∈ {(1, 2), (2, 3), (5, 1), (7, 3), (5, 6), (6, 5)}
If (A, y) = (1, 2) then 1 > 2 + 2 ⇒ 1 > 4 which is not true
If (A, y) = (2, 3) then 2 > 3 + 2 ⇒ 2 > 5 which is not true
If (A, y) = (5, 1) then 5 > 1 + 2 ⇒ 5 > 3 which is true
∴ (5, 1) is its solution
If (x, y) = (7, 3), then 7 > 3 + 2 ⇒ 7 > 5 which is true
∴ (7, 3) is its solution
If (x, y) = (5, 6). then 5 > 6 + 2 ⇒ 5 > 8 which is not true
If (x, y) = (6, 5). then 6 > 5 + 2 ⇒ 6 > 7 which is not true
∴ Solution or true set is {(5, 1), (7, 3)}
Que-7: Find out the truth sets of the following open sentences; replacement sets are given against them.
(i) 5/x > 7 ; {1, 2}
(ii) 5/x > 2; {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
(iii) x² = 9; {-3, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3}
(tv) x + (1/x) = 2 ; {0, 1,2, 3}
(v) 3x² < 2x ; {-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
(vi) 2 (x – 3) < 1 ; {1, 2, 3, 4, …………… 10}.
Sol: (i) 5/x > 7; {1, 2}
If x = 1, then 5/1 > 7 ⇒ 5 > 7 which is not true
If x = 2, then 5/2 > 7 which is not true
∴ x has no solution
Solution set = Φ
(ii) 5/x > 2; {1,2, 3,4, 5,6}
If x = 1, then 5/1 > 2 which is true 5
If x = 2, then 5/1 > 2 which is true
If x = 3, then 5/2 > 2 which is not true
If x = 4, then 5/4 > 2 which is not true
If x = 5, then 5/5 > 2 ⇒ 1 > 2 which is not true
If x = 6, then 5/6 > 2 which is not true o
∴ Solution set = {1, 2}
(iii) x² = 9; {-3, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3}
If x = -3, then (-3)² = 9 ⇒ 9 = 9 which is true
If x = -2, then (-2)² = 9 ⇒ 4 = 9 which is not true
If x = -1, then (-1)² = 9 ⇒ 1 = 9 which is not true
If x = 1, then (1 )² – 9 ⇒ 1 =9 which is not true
If x = 2, then (2)² – 9 ⇒ 4 = 9 which is not ture
If x = 3, then (3)² = 9 ⇒ 9 which is true
∴ Solution set = {-3, 3}
(iv) x + y = 2 ; {0, 1, 2, 3}
If x = 0, then 0 + (1/0) = 2 which is not true
If x = 1, then 1 + (1/1)= 2 ⇒ 1 + 1 = 2 ⇒ 2 = 2 which is true
If x = 2, then 2 + (1/2) = 2 which not true 1
If x = 3, then 3 + (1/3) = 2 which is not true
∴ Solution set = {1}
(v) 3x² < 2x ; {- 4, – 3, – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4} If x = – 4, then 3 (- 4)² < 2 x (- 4)
⇒ 3 x 16 < – 8 ⇒ 48 < – 8 which is not true If x = – 3, then 3 (- 3)² < 2 x (- 3)
⇒ 3 x 9 < – 6 ⇒ 27 < – 6 which is not true If x = – 2, then 3 (-2)² < 2 x (-2)
⇒ 3 x 4 < – 4 ⇒ 12 < – 4 which is not true If x = – 1, then 3 (-1)² < 2 x (-1)
3 x 1 < – 2 ⇒ 3 < – 2 which is not true
If x = 0. then 3 (0)² < 2 (0) ⇒ 3 x 0 < 2 x 0 ⇒ 0 < 0 which is not true
If x = 1, then 3 (1)² <2xl⇒ 3xl<2 ⇒ 3 < 2 which is not true
If x = 2, then 3 (2)² <2×2⇒ 3×4<4 ⇒ 12 < 4 which is not true
If x = 3, then 3 (3)² <2×3⇒ 3*9<6 ⇒ 27 < 6 which is not true
If x = 4, then 3 (4)² <2×4⇒ 3xl6<8 ⇒ 48 < 8 which is not true
∴ Solution set = Φ
(vi) 2 (x – 3) < 1 ; {2, 3, 4, 10}
If x = 1. then 2 (1 – 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 x (-2) < 1
⇒ – 4 < 1 which is true
If x = 2, then 2 (2 – 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 (-1) < 1
⇒ – 2 < 1 which is true
If x = 3, then 2(3 – 3) < 1
⇒ 2 x 0 < 1
If x = 4, then 2(4 – 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 x 1
⇒ 2 < 1 which is not true
If x = 5, then 2 (5 – 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 x 2 < 1
⇒ 4 < 1 which is not true
If x = 10, then 2 (10 – 3) < 1 ⇒ 2 x 7 < 1
⇒ 14 < 1 which is not true
∴ Solution set = {1, 2, 3}
Que-8: Statement: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of its third side. Let x, x + 1, x + 2 be the lengths of the three sides of a triangle.
(i) Write down the three inequations in x, each of which represents the given statement.
(ii) List the set of possible values of x which satisfy all the three inequations obtained in your answer to part (i) above, given that x is an integer.
Sol: It is given that in a triangle,
Sum of any two sides is greater than the third side
Let x, x + 1 and x + 2 be the lengths of the three sides of a triangle,
(i) then the three inequations can be (a) x > 1 (b) x > 2 (c) x > 3
(ii) When x > 1, then the sides will be (2, 3, 4) When x > 2, then the sides will be (3, 4, 5) and when x > 3, then the side will be (4, 5,6)
Set of solution = {2, 3, 4, }
P.Q. P is the solution set of 8x – 1 > 5x + 2 and Q is the solution set of 7x – 2 ≥ 3 (x + 6), where x ∈ N. Find the set P ∩ Q.
P is the solution set of 8x – 1 > 5x + 2
Q is the solution set of 7x – 2 ≥ 3 (x + 6)
Where x ∈ N.
Now 8x – 1 > 5x + 2
⇒ 8x – 5x > 2 + 1 ⇒ 3x > 3
⇒ x > 3/3 ⇒ x > 1
∴ P = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, }
and 7x – 2 ≥ 3 (x + 6)
⇒ 7x – 2 ≥ 3x + 18
⇒ 7x – 3x ≥ 18 + 2 ⇒ 4x ≥ 20
⇒ x ≥ 20/4 ⇒ x ≥ 5
∴ Q = {5, 6, 7, 8, }
∴ P ∩ Q = {5, 6, 7, 8, }
Que-9: Answer true or false.
(a) If x + 10 = y + 14, then x > y.
(b) | – 4 | – 4 = 8.
(c) If 10 – x > 3, then x < 7. (d) If p = q + 2, then p > q.
(e) If a and b are two negative integers such that, a < b. then (1/a) < (1/a) (f) 3 ∈ {x : 3x – 2 > 5}.
Sol: (a) True
∵ x + 10 = y + 14
⇒ x = y + 14 – 10
⇒ x = y + 4
∴ x > y
(b) False
∵ | – 4 | – 4 = 8
⇒ 4 – 4 = 8 and 0 = 8
Which is not possible
(c) True
∵ 10 – x > 3
∴ 10 – 3 > x ⇒ 7 > x
⇒ x < 7 (d) True ∵ p = q+ 2 ∴ p > q
(d) False
∵ a, b are two negative integers and a < b then (1/a) > (1/b)
(e) True
∵ 3 ∈ {x : 3x – 2 > 5}
3x – 2 ≥ 5 ⇒ 3x ≥ 5 + 2
⇒ 3x ≥ 7 ⇒ x ≥ 7/3
∴ Solution set = {3, 4, 5, 6, …………. } (∵ x ∈ N)
Que-10: Find the solution of the inequation 2 ≤ 2p – 3 ≤ 5.
Hence graph the solution set on the number line given below.
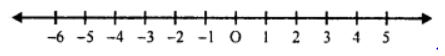
Sol: 2 ≤ 2p – 3 ≤ 5
(i) 2 ≤ 2p – 3
⇒ 2 + 3 < 2p
⇒ 5 ≤ 2p
⇒ (5/2) ≤ 2p
(ii) 2p – 3 ≤ 5
⇒ 2p ≤ 5 + 3
⇒ 2p ≤ 8
⇒ p ≤ (8/2)
⇒ p ≤ 4
From (i) and (ii)
(5/2) ≤ P ≤ 4 ⇒ {2*(1/2)} ≤ p ≤ 4
∴ Solution set = {{2*(1/2)} ≤ P ≤ 4, p ∈ R}
The solution set is given below on the number line.
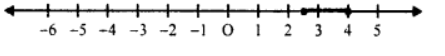
Que-11: If x is a negative integer, find the solution set of (2/3) + (1/3) (x + 1) > 0.
Sol: x is a negative integer
(2/3) + (1/3) (x + 1) > 0.
⇒ (2/3) + (x/3) + (1/3) > 0.
⇒ (2/3) + (1/3) + (x/3) > 0.
⇒ (2+1)/3 + (x/3) > 0 ⇒ (1 + x)/3 > 0
⇒ (x/3) > – 1 ⇒ x > – 3
∴ Solution set = {-2, -1}
Que-12: Write open mathematical sentences, using x for the variable whose graphs would be
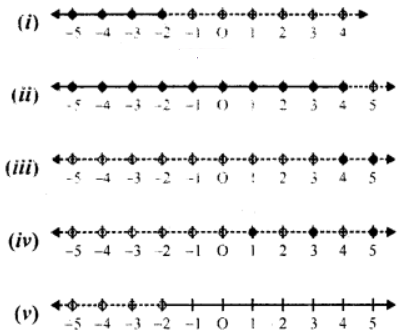
Sol: (i) Here solution set = {x : x ≤ – 2, x ∈ R}
(ii) Here solution set = {x : x ≤ 4, x ∈ R}
(iii) Here solution set = {x : 4 ≤ x ≤ 5, x ∈ N}
(iv) Here solution set = {x : 1 ≤ x ≤ 5, x ∈ N, x is odd}
(v) Here solution set = (x : x > – 2, x ∈ R}
Que-13: Answer true or false
(i) If 2 – x < 0, then x > 2
(ii) The graph of the inequation y ≤ 2x includes the origin
Sol: (i) True
∵ 2 – x < 0 ⇒ 2 < x ⇒ x > 2
(ii) True
∵ y ≤ 2x and origin is (0, 0)
∴ 0 ≤ 2 x 0 ⇒ 0 ≤ 0
Que-14: If 25 – 4x ≤ 16, find :
(i) the smallest value of x when x is a real number
(ii) the smallest value of x when x is an integer.
Sol: 25 – 4x ≤ 16
⇒ 25 – 16 ≤ 4x ⇒ 9 ≤ 4x
⇒ 4x ≥ 9 ⇒ x ≥ 9/4
∴ Smallest value of x when x is a real number
= 9/4 = 2*(1/4) (∵ 9/4 is a real number)
(ii) Smallest value of x when x is a real number = 3 (∵ 3 > 9/4)
Que-15: Given : x ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, find the values of x for which – 3 < 2x – 1 < x + 4.
Sol: – 3 < 2x – 1 < x + 4
(i) – 3 < 2x – 1 ⇒ – 3 + 1 < 2x
⇒ – 2 < 2x ⇒ −2/2 < x ⇒ – 1 < x
(ii) 2x – 1 < x + 4 ⇒ 2x – x < 4 + 1 ⇒ x < 5
From (i) and (ii)
– 1 < x < 5
∴ Solution set will be {1, 2, 3, 4}
Que-16: Solve the inequality : 2x – 10 < 3x – 15.
Sol: 2x – 10 < 3x – 15
⇒ – 10 + 15 < 3x – 2x
⇒ 5 < x ⇒ x > 5
∴ Solution set = {x : x > 5}
Que-17: Solve the inequation : 3 – 2x ≥ x – 12, given that x ∈ N.
Sol: 3 – 2x ≥ x – 12
⇒ 3 + 12 ≥ x + 2x ⇒ 15 ≥ 3x
⇒ 3x ≤ 15 ⇒ x ≤ 15/2
⇒ x ≤ 5
∴ Solution set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} (∵ x ∈ N)
Que-18: x ∈ {real numbers} and – 1 < 3 – 2x ≤ 7, evaluate x and represent it on a number line.
Sol: x ∈ {Real numbers}
-1 < 3 – 2x ≤ 7
(i) – 1 < 3 – 2x ⇒ – 1 – 3 < – 2x
⇒ – 4 < – 2x ⇒ 4 > 2x
⇒ (4/2) x ⇒ 2 > x ⇒ x < 2
(ii) and 3 – 2x < 7 ⇒ – 2x ≤ 7 – 3
⇒ – 2x ≤ 4 ⇒ – x ≤ 42 ⇒ – x ≤ 2
⇒ – 2 ≤ x
From (i) and (ii)
The solution is – 2 ≤ x < 2
Number line
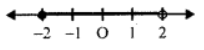
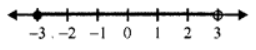
Que-19: Find the range of values of x which satisfies
– 2*(2/3) ≤ x + (1/3) < {3*(1/3)}, x ∈ R
Graph these values of x on the number line.
Sol: – 2*(2/3) ≤ x + (1/3) < {3*(1/3)}
⇒ −8/3 ≤ x + (1/3) < 10/3
(i) −8/3 ≤ x + (1/3) + (1/3) ⇒ (−8/3) – (1/3) ≤ x
⇒ −9/3 ≤ x ⇒ – 3 ≤ x
(ii) x + (1/3) < 10/3 ⇒ (10/3) – (1/3)
⇒ x < 9/3 ⇒ x < 3
From (i) and (ii)
Solution is – 3 < x < 3
Number line
Que-20: Solve and graph the solution set of :
(a) 6 ≥ 2 – x, (x/3) + 2 < 3; x ∈ R
(b) x/2 < (6−x)/4, (2−x)/6 < (7−x)/9; x ∈ R
Sol: (a) 6 ≥ 2 – x ⇒ 6 – 2 ≥ – x
⇒ 4 ≥ – x ⇒ x ≥ – 4 ⇒ – 4 ≤ x … (i)
and (x/3) + 2 < 3 ⇒ x + 6 < 9 (Multiplying by 3)
⇒ x < 9 – 6 ⇒ x < 3 … (ii),
From (i) and (ii)
∴ Solution = – 4 ≤ x < 3
Number line
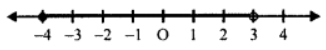
(b) x/2 < (6−x)/4 ⇒ 2x < 6 – x (Multiplying by 4)
⇒ 2x + x < 6 ⇒ 3x < 6
⇒ x < 6/3 ⇒ x < 2 … (i)
and (2−x)/6 < (7−x)/9
⇒ 3 (2 – x) 2 (7 – x)
(Multiplying by L.C.M. of 6, 9 = 18)
⇒ 6 – 3x < 14 – 2x
⇒ 6 – 14 < – 2x + 3x ⇒ – 8 < x … (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
– 8 < x < 2
Number line
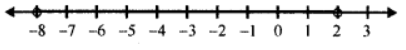
Que-21: Find the range of values of x which satisfy :
−1/3 ≤ (x/2) – {1*(1/3)} < 1/6; x ∈ R
Graph these values of x on the real number line.
Sol: −1/3 ≤ (x/2) – {1*(1/3)} < 1/6
(i) −1/3 ≤ (x/2) – {1*(1/3)} ⇒ −1/6
Multiplying by the L.C.M. of 3, 2 = 6
– 2 < 3x – 8 ⇒ – 2 + 8 ≤ 3x
⇒ 6 ≤ 3x ⇒ 6/3 ≤ x
⇒ 2 ≤ x …. (i)
and (x/2) – {1*(1/3)} < 1/6 ⇒ (x/2) – (4/3) < (1/6)
Multiplying by the L.C.M. of 2, 3,6 = 6
3x – 8 < 1 ⇒ 3x < 1 + 8
⇒ 3x < 9 ⇒ x < 9/3
⇒ x < 3 … (ii)
from (i) and (ii)
2 ≤ x ≤ 3
∴ Number line
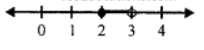
Que-22: Write down the range of real values of x for which the inequation x > 3 and – 2 < x < 5 are both true.
Sol: x > 3
3 < x … (i)
and -2 < x < 5
∴ Range = {-2, -1,0, 1, 2, 3, 4} … (ii)
∴ From (i) and (ii)
Range = {3 < x < 5; x ∈ R}
Que-23: Solve and graph the solution set of 3x – 4 > 11 or 5 – 2x < 7; x ∈ R}
Sol: 3x – 4> 11 ⇒ 3x > 11 + 4
⇒ 3x > 15 ⇒ x > 15/3
⇒ x > 5 … (i)
and 5 – 2x ≥ 7 ⇒ 5 – 7 > 2x
⇒ – 2 ≥ 2x ⇒ −2/2 > x
⇒ -1 > x
⇒ x ≤ – 1, x ∈ R … (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
x > 5 or x ≤ – 1; x ∈ R
Graph of solution
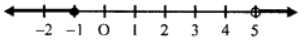
–: End of Linear Inequations in One Variables Class 10 OP Malhotra Exe-4 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-4 :–
Return to : OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-10 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends