Logarithms Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-7C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-7. We Provide Step by Step Solutions / Answer of Complex Problems on Logarithms. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics.

Logarithms Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-7C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-7
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-7 | Indices Exponents |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-7C | Complex Problems on Logarithms with Answer |
| Edition | 2025-2026 |
Complex Problems on Logarithms with Answer
Logarithms Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-7C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-7.
Find the value of the following :
Que-1: log 6
Sol: log 6 = log (2 x 3)
= log 2 + log 3
= 0.3010 + 0.4771
= 0.7781
Que-2: log 12
Sol: log 12 = log (2 x 2 x 3)
= log (2² x 3)
= log 2² + log 3
= 2 log 2 + log 3
= 2 (0.3010) + 0.4771
= 0.6020 + 0.4771
= 1.0791
Que-3: log 15
Sol: log 15 = log (3 x 5)
= log 3 + log 5
= 0.4771 + 0.6990
= 1.1761
Que-4: log 200
Sol: log 200 = log (2³ x 5²)
= log 2³ + log 5²
= 3 log 2 + 2 log 5
= 3 (0.3010) + 0.6990 x 2
= 0.9030 + 1.3980
= 2.3010
Que-5: log 36
Sol: Log 36 – log (4 x 9) = log (2² x 3²)
= log 2² + log 3²
= 2 log 2 + 2 log 3
= 2 (0.3010) + 2 (0.4771)
= 0.6020 + 0.9542
= 1.5562
Que-6: log 80
Sol: log 80 = log (24 x 5)
= log 24 + log 5
= 4 log 2 + log 5
= 4 (0.3010) + 0.6990
= 1.2040 + 0.6990
= 1.9030
Que-7: log 2*(1/3)
Sol: log {2*(1/3)} = log(7/3)
= log 7 – log 3
= 0.8451 – 0.4771
= 0.3680
Que-8: log 11³
Sol: log (11)³
= 3 log 11
= 3 x 1.0414
= 3.1242
Que-9: log {2*(1/3)}^5
Sol: log {2*(1/3)}^5 = log (7/3)^5
= 5 log (7/3)
= 5 [log 7 – log 3]
= 5 [0.8451 – 0.4771]
= 5 (0.3680) = 1.8400
Que-10: If log 6 = 0.7782, find the value of log 36.
Sol: log 6 = 0.7782
log 36 = log (6)²
= 2 log 6
= 2 (0.7782)
= 1.5564
Que-11: Given log10 25 = x, log10 75 = y, evaluate without using logarithmic tables, in terms of x and y.
(i) log10 3
(ii) log102
Sol: (i) log10 3
= (log10) (75/25)
= (log10 75) – (log10 25)
= y – x
(ii) log102 = x
= log 5² = x
= 2 log 5 = x
= log 5 = x/2
= (log10) 2 = log (10/5)
= (log 10) – (log 5)
= 1 – (x/2)
= (2-x)/2
Que-12: Given log 31.87 = x, write down in terms of x.
(i) log (31.87)²
(ii) log10 0.03187
(iii) log10 √31870
Sol: log 31.87 = x
(i) log (31.87)² = 2 log (31.87)
= 2x
(ii) log10 0.03187 = log10 (31.87)/(1000)
= log10 31.87 – log10 1000
= x – 3 (log 1000 = 3)
(iii) log10 √31870 = log10 (31870)^1/2
= (1/2) log10 31870
= (1/2) log (31.87 x 1000)
= (1/2) [log 31.87 + log 1000]
= (1/2) (x + 3) = (x+3)/2
Que-13: Solve the equation
(i) log10 (x + 1) + log10 (A – 1) = log10 11 + 2 log103
(ii) log (10x + 5) – log (x – 4) = 2
Sol: (i) log10 (x + 1) + log10 (A – 1) = log10 11 + 2 log103
⇒ log (x + 1) (x – 1) = log (11 x 3²) (∵ 2 log10 3 = log10 3²)
⇒ log (x² – 1) = log (11 x 9) ⇒ log (x² – 1) = log 99
Comparing we get.
x² – 1 = 99
⇒ x² = 99 + 1
= 100 = (10)²
⇒ x = 10
∴ x = 10
(ii) log (10x + 5) – log (x – 4) = 2
⇒ log (10x+5)/(x−4) = log 100 (∵ log 100 = 2)
Comparing both sides,
(10x+5)/(x−4) = 100/1
100x – 400 = 10x + 5
⇒ 100x – 10x = 5 + 400
⇒ 90x = 405
⇒ x = 405/90 = 45/10 = 4.5
∴ x = 4.5
Que-14: (a) Given 2 log10x + (1/2) log10y = 1, express y in terms of x.
(b) Express as a single logarithm :
2 log 3 – (1/2) log 16 + log 12
Sol: (a) Given 2 log10x + (1/2) log10y = 1
{(log10) x²} + {(log10) y^(1/2)} = log10 10
= {(log10) x²} × y^(1/2) = log10 10
Comparing,
= x² . y^(1/2) = 10
= y^(1/2) = 10/x²
Squaring, y = (10/x²)²
= 100/x^4 = 100x^-4
y = 100x^-4.
(b) 2 log 3 – (1/2) log 16 + log 12
= log 3² – log 16^(1/2) + log 12
= log {3²×12}/(16^(1/2))
= log {(9×12)/4}
= log 27.
Que-15: Given that log10 y + 2log10 x = 2, express y in terms of x.
Sol: log10 y + 2 log10 x = 2
log10 y + log10 x² = log 10^2
log (y × x²) = log 100
y × x² = 100
y = ( 100 / x )²
Que-16: If a = 1 + log10 2 – log10 5, b = 2 log10 3 and c = log10 m – log10 5, find the value of m if a + b = 2c (Do not use log tables).
Sol: a = 1 + log10 2 – log10 5 = log10 10 + log10 2 – log10 5
= log10 (10×2)/5 = log10 4
b = 2 log10 3 = log10 3² = log10 9
c = log10 m – log10 5 = log10 (m/5)
∵ a + b = 2c
∴ log10 4 + log10 9 = 2 log (m/5)
⇒ log (4 × 9) = log (m/5)² = log m²/25
Comparing both sides,
4 x 9 = m²/25
⇒ m² = 4 x 9 x 25
= 900 = (30)²
∴ m = 30
Que-17: Express as a single logarithm
2 + (1/2) log10 9 – 2 log10 5
Sol: 2 + (1/2)log10 9 – 2log10 5
= 2 +(1/2)log10 3² – 2log10 5
= 2log10 + (1/2) × 2log10 3 – 2log10 5
= log 102 + log10 3 – log10 52
= log 100 + log10 3 – log10 25
= log10 {(100×3)/25}
= log10 12.
Que-18: If a = log 12, b – log 6 and c = 2 log √2, find
(i) a – b – c
(ii) 9a-b-c
Sol: a = log 12, b = log 6, c = 2 log √2 = log
(√2)² = log 2
(i) a – b – c = log 12 – log 6 – log 2
= log {12/(6×2)}
= log 1 = 0 (∵ log 1 = 0)
(ii) 9^a-b-c = 9° [∵ a – b – c = 0 proved in (i)]
= 1 (∵ x° = 1)
Que-19: If x = log10 12, y = log4 2 x log10 9 and z = log10 (0.4) then find
(i) x – y – z
(ii) prove that 6x – y- z = 6
Sol: x = log10 12, y = log4 2 x log10 9, z = log10 (0.4)
(i) x = log10 12 = log10 (2² x 3) = log 2² + log 3
= 2 log10 2 + log10 3
y = log4 2 x log109 = log42 x log10 3²
= log4 2 x 2 log10 3 = log4 (4)^(1/2) x = log10 12, y = log4 2 x log10 9, z = log10 (0.4)
(i) x = log10 12 = log10 (2² x 3) = log 2² + log 3
= 2 log10 2 + log10 3
y = log4 2 x log109 = log42 x log10 3²
= log4 2 x 2 log10 3 = log4 (4) (4/10) = log10 4 – log10 10
= log10 2² – 1 = 2 log10 2 – 1
x – y – z = 2 log10 2 + log10 3 – log10 3 – 2 log102 + 1 = 1
(ii) 6x-y-z = 61 = 6 [∵ x – y – z = 1 (proved in (i)]
Hence proved.
Que-20: If p = log10 20 and q = log10 25, find x such that 2 log10 (x + 1) = 2p – q.
Sol: p = log10 20 = log10 (22 x 5) = log10 2² + log10 5
= 2 log 2 + log 5
q = log10 25 = log10 (5²) = 2 log10 5
Now,
2p – q = 2 [2 log10 2 + log10 5] – 2 log10 5
= 4 log10 2 + 2 log10 5 – 2 log10 5
= 4 log10 2 = 2 log10 2²
= 2 log10 4
2 log10(x + 1) = 2 log10 4
Comparing, we get
x + 1 = 4 ⇒ x = 4 – 1 = 3
∴ x = 3
Que-21: Without using logarithm tables, evaluate :
3 + log10 (10-2)
Sol: 3 + log10 (10-2) = 3 + (- 2 log10 10)
= 3 – 2 log10 10 = 3 – 2 x 1
= 3 – 2 = 1 (∵ loga a = 1)
= 1
Que-22: Given log10 x = a, log10 y = b
(i) Write down 10n-1 in terms of x
(ii) Write down 102b in terms of y
(iii) If log10 P = 2a – b, express P in terms of x and y.
Sol: (i) log10 x = a, log10y = b
∵ log10 x = a and log10 y = b
∴ 10n = x … (i)
∴ 10b = y … (ii)
Now,
(i) 10n-1 = (10^a)/(10¹) = x/10 [From (i)]
(ii) 102b = (10b)² = y² [From (ii)]
(iii) log10 P = 2a – b
⇒ log10P = 2 log10x – log10y
⇒ log10 P = log x² – log10 y
⇒ log10 P = log x²/y
Comparing, we get
p = x²/y
Que-23: Simplify without using tables :
2log10 5 + log10 8 − (1/2)log10 4
Sol: 2log10 5 + log10 8 − (1/2)log10 4
= log10 5² + log10 8 – log10 (4)^(1/2)
= log 10 25 + log 8 – log10 2
= log10 {25×8}/2
= log10 100 = 2
Que-24: Given that log102 = x, log10 3 = y, find
(i) log10 60
(ii) log101.2 in terms of x and y
Sol: (i) log10 60 = log10 (2 x 3 x 10)
= log10 2 + log10 3 + log10 10
= x + y + 1 (∵ log10 10 = 1)
(ii) log10 1.2 = log10 (12/10) = log10 12 – log10 10
= log (2² x 3) – log10 10
= 2 log 2 + log 3 – log10 10 (∵ log10 10 = 1)
= 2x + y – 1
Que-25: Given 2 log10 x + 1 = log10 250, find
(i) x
(ii) log102x
Sol: (i) 2 log10 x + 1 = log 250
⇒ log10x² + 1 = log10 250
⇒ log10 x² + log10 10 = log10 250 (∵ loga a = 1)
⇒ log (x² x 10) = log10 250
Comparing both side,
10x² = 250
⇒ x² = 25 = (5)²
∴ x = 5
(ii) log10 2x = log10 2 x 5
= log10 10 = 1
Que-26: (a) Given that log x = m + n and log y = m – n, express the value of log10 (10x/y) in terms of in and n. (b) Solve for x : log10x = – 2.
Sol: (a) log x = m + n, log y = m – n
log10 10x/y² = {log10 10x} − {log10 y²}
= log10 10 + log10 x – 2 log10 y
= 1 + m + n – 2 (m – n)
= 1 + m + n – 2m + 2n
= 1 – m + 3n
(b) log10 x = – 2 = log10 1/100
Comparing we get,
x = 1/100
Que-27: If log {(p+q)/3} = 1/2 = (log p + log q) prove that p² + q² = 7pq.
Sol: Log ((p+q)/3) = 1/2 = (log p + log q)
⇒ log (p+q)/3 = 1/2 (log p×q) = log(pq)^(1/2)
Comparing we get,
(p+q)/3 = (pq)^(1/2)
Squaring both sides,
{(p+q)/3}² = pq
⇒ {p² + q² + 2pq}/9 = pq
⇒ P² + q² + 2 pq
⇒ p² + q² + 2pq = 9pq
⇒ p² + q² = 9pq – 2pq ⇒ 7pq
∴ p² + q² = 2pq
Hence proved.
Que-28: If x² + y² = 51xy, prove that log 1/2 = 1/2 (log x + log y).
Sol: x² + y² = 51xy
⇒ x² + y² – 2xy = 51 xy – 2xy
(Subtracting 2xy)
⇒ (x – y)² = 49xy
= {(x-y)²/49} = xy
= {(x-y)²/7²} = xy
= {(x-y)/7}² = xy
= {(x-y)/7} = √xy
Taking log on both sides,
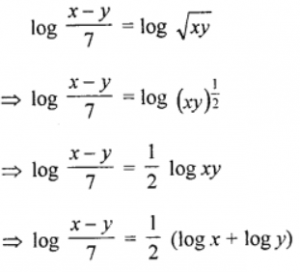
Hence, Proved.
— : End of Logarithms Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-7C ICSE Maths Ch-7 Step by Step Solutions :–
Return to :– OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends