Magnetic Field due to Current Biot Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-7 Moving Charges and Magnetic Field. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
Magnetic Field due to Current Biot Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-7 Moving Charges and Magnetic Field
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-7 | Moving Charges and Magnetic Field |
| Topics | Magnetic Field due to Current Biot Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law Numerical |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Magnetic Field due to Current Biot Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law Numerical
Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-7 Moving Charges and Magnetic Field
Que-1: A long straight wire in horizontal plane carries a current of 50 A in north to south direction. Find the magnitude and direction of magnetic field at a point 2.5 m east of the wire.
Ans:
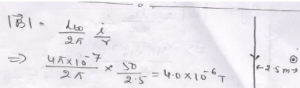
by right hand thumb rule magnetic field will be vertically upward
Que-2: Two infinitely long insulated wires are kept perpendicular to each other. They carry currents I1 = 2 A and I2 = 1.5 A. (i) Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at P. (ii) If the direction of current be reversed in one of the wires, what would be the magnitude of the field?
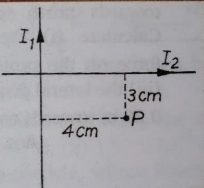
Ans: Since the point P is at right side of both the wire therefore M.F. due to both wire will be down ward perpendicular to plane of paper and its magnitude will be sum of magnitude of magnetic field of two wire.
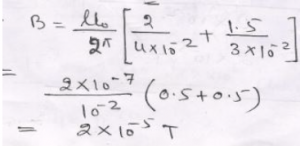
Que-3: An electron-beam carries a current of 5 microampere. Calculate: (i) number of electrons passing through a point per second, (ii) magnetic field produced at a distance of 50 cm.
Ans: Q = I t
N e = I t (Q = n e)
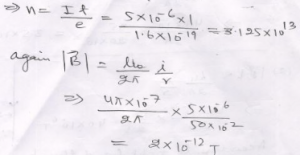
Que-4: Two long, parallel wires are placed at a distance of 16 cm from each other in air. Each wire has a current of 4 A. Calculate the field B at mid-point between them when the currents in them are (i) in the same direction, (ii) in opposite directions.
Ans: In case of same current in two parallel wire magnetic field at mid point will be equal and opposite. so the net field will be zero
However increase of current flowing in anti parallel direction magnetic field due to both the wire will be added

Que-5: A circular coil of wire having 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm, carries a current of 0.40 A. Find the magnetic field at the centre of the coil.
Ans: Magnitude field at the centre of coil having n turn
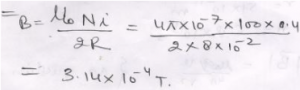
Que-6: An alpha-particle (charge 2e) moves along a circular path of radius 1.0 Å with a uniform speed of 2.0 x 10^6 ms^-1. Calculate the magnetic field produced at the centre of the circular path.
Ans: Magnetic field due to moving charge

Que-7: In the Bohr model of hydrogen atom, the electron circulates around the nucleus in a path of radius 5.1 x 10^-11 m at a frequency 6.8 x 10^15 s^-1. Find the magnetic field set up at the centre of the orbit.
Ans: r = 5.1 x 10^-11 m
n = 6.8 x 10^15 /s

=> 1.6 x 2 x 3.14 x 6.8 x 10^-11 / 5.1 x 10^-11
=> 13.4 T
Que-8: A helium nucleus (charge + 2 e) completes one round of a circle of radius 0.8 m in 2 s. Find the magnetic field at the centre of the circle. (ISC 2006)
Ans:
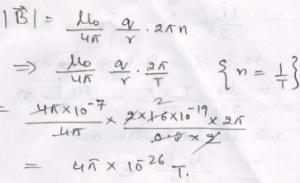
Que-9: A long, straight wire is turned into a loop of radius R = 10 cm, as shown. If a current of 8 A is passed through the loop, find the magnetic field at the centre C of the loop.
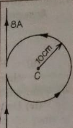
Ans: magnetic field due to straight wire

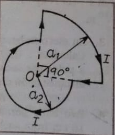
Que-10: The figure shows two semi-circular current-loops of radii a1 and a2. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the common centre O.
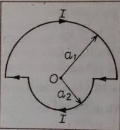
Ans: Magnetic field due to arc

Showing that perpendicular to plane of paper inwardly
Que-11: A current of I ampere is flowing through the adjoining bent wire. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the point O.
Ans: Magnetic field due to bigger arc

Que-12: Compute the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the centre O of the given current-carrying bent wire.
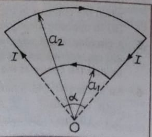
Ans: Magnetic field due to bigger arc

Que-13: A wire A, bent in the shape of an arc of a circle, carrying a current of 2 A and having radius 3 cm and another wire B, also bent in the shape of an arc of a circle, carrying a current of 3 A and having radius 5 cm are placed as shown in the figure. Find net magnetic field at the common centre O.
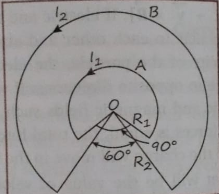
Ans:

Que-14: An air-solenoid has 500 turns of wire in its 40 cm length. If the current in the wire be 1.0 A, find the magnetic field at the axis inside the solenoid.
Ans: Magnetic field due to axis of solenoid

Que-15: A 80 cm long solenoid of diameter 1.8 cm has 5 layers of windings of 400 turns each and carries a current of 8.0 A. Estimate magnetic field inside the solenoid near the centre.
Ans:
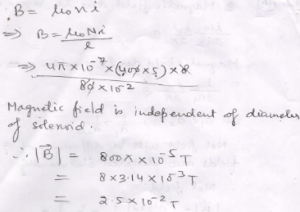
Que-16: The magnetic field at the centre of a 50 cm long solenoid is 4.0 x 10^-2 T. When a current of 8.0 A flows through it. What is the number of turns in the solenoid? (π = 3.14).
Ans:
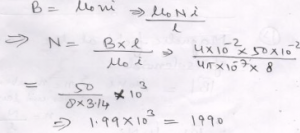
— : End of Magnetic Field due to Current Biot Savart’s Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law Numerical Class-12 Solution Moving Charges and Magnetic Field . :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends