Matter Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3, Matter Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-3. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -3 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Matter Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 6th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-3 | Matter |
| Unit-1 | Matter |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Matter Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
Question: 1. Explain the term ‘matter’. One kind of matter can be distinguished from another by its physical properties and chemical properties. State the main physical properties of matter.
Answer: Matter is the basic substance of which all materials are made of Physical Properties— They are those properties which include state, colour, odour, density etc.
Chemical Properties— They are properties which include reactions of different materials with different chemical. Physical Properties of Matter are : Colour : All matter an be distinguished by their varied- colours.
Odour : Matter shows variation in odour or smell. Solubility : Matter may vary in solubility in water or other solvents.
Melting & Boiling Points : Substances variation in their melting and boiling points.
Question: 2. The three main states of matter are – solids, liquids & gases. Compare the three states with reference to the following characteristics of matter –
a] volume
b] shape
c] compressibility
d] diffusion
Answer:
| Characteristics | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
| Volume | Have a definite volume | Have a definite volume | Have no definite volume |
| Shape | Have a definite shape | Have no definite shape | Have no definite shape |
| Compressibility | Cannot be compressed | Slightly compressible | Highly compressible |
| Diffusion (Intermingling of Molecules) | Cannot diffuse | Shows Diffusion | Diffuses very easily |
Question: 3. Matter in any state is composed of particles. Compare the three states of matter i.e. solids, liquids & gases with reference to :
a] intermolecular space
b] intermolecular force of attraction
c] movement of particles
Answer: (a) Intermolecular space –
- The molecules can move only when there are gaps or space between them, this space is called intermolecular space.
- The molecules of matter are always in motion and attract each other with a force called intermolecular force of attraction due to which they are held together.
- The order of intermolecular spaces are – Solids < Liquids < Gases
(b) Intermolecular forces of attraction
- The molecules of matter are always in motion and attract each other with a force, and this force is called the intermolecular force of attraction due to which they are held together.
- Solids have maximum intermolecular forces of attraction while gases have minimum intermolecular forces of attraction.
(c) movement of particles
- The movement of particles depends upon the intermolecular forces of attraction between the particles. The greater the intermolecular forces of attraction between the particles lesser are the intermolecular spaces between them, and hence, the movement of particles of restricted.
- Due to high kinetic energy and negligible forces of attraction, the particles of a gas are moving at high speeds in all directions while the movement of particles is least in solids.
Question: 4. Describe simple experiment to show that – solids
a] occupy space
b] have mass
c] have a definite volume
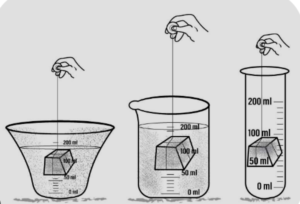
Answer: (a) occupy space : solid-occupies space
‘A’-A measuring cylinder is filled with water to a particular mark- ‘A’.
‘B’-A piece of wooden block- is immersed inside the measuring cylinder. The water level rises up.
‘C’-On removal of the block- the water level in the measuring cylinder falls down back to the mark- ‘A’
Conclusion : The block pushes the water out and occupies its space, hence all solids occupy space.
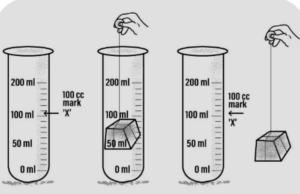
(b) Have mass – A solid has mass
A : A simple scale – is taken, as shown below
B : A solid is placed – on one side of the scale, causes the scale tilts towards one side.
Conclusion – The scale tilts due to the mass of the solid, hence all solids have mass.
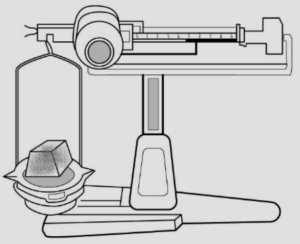
(c) Have a definite volume : A solid placed in any container filled with water displace the same amount of water.
Conclusion : Solid displace water and retain their own volume, hence all solids have a definite volume.
Question: 5. Describe simple experiment to prove that – liquids
a] have mass
b] have a definite volume
c] have no definite shape
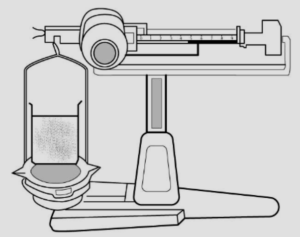
Answer: (a) have mass a liquid occupies mass Experiment : A liquid placed on one side of the scale, causes the scale to tilt towards one side.
Conclusion : The scale tilts due to the mass of the liquid, hence all liquids have mass.
(b) have a definite volume Experiment : A liquid in a measuring cylinder can be poured into any container. The volume of liquid in the container, is the same as that in the measuring cylinder.
Observation : The volume of liquid in the container, is the same as that in the measuring cylinder. Hence, all liquids have a definite volume.

(c) have no definite shape Experiment : A liquid poured into any container takes up the shape of each container. Conclusion : All liquids have no definite shape.

Question: 6. Describe simple experiment to prove that – gases
a] occupy space
b] have mass
c] have no definite volume or shape
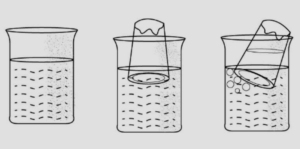
Answer: (a) occupy space Experiment:
‘A’ – A glass beaker or bowl is half filled with water.
‘B’ – An empty glass tumbler [which of course contains air] is inverted an lowered inside it.
‘C’ – On tilting the tumbler, air is displaced and bubbles are seen coming out.
Conclusion : Air or gases occupy space.
(b) Have mass Experiment: An inflated balloon placed on one side of the scale causes it to tilt towards one side. Conclusion : The scale tilts due to the mass of the gas, hence all gases have mass.

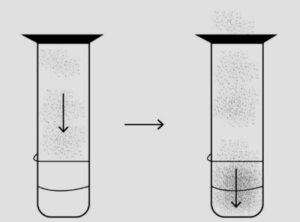
c) Have no definite volume or shape Experiment: A gas takes up the volume of any enclosed space filling it up completely.
Conclusion : Gases take up any volume and hence all gases have no definite volume.
Question: 7. Explain the term ‘Interconversion of matter’. With reference to ice, water & water vapour-show diagrammatically the change of state of matter from solid to liquid to gaseous & back to its original state.
Answer: Interconversion of matter refers to change of one state to another. For example: change of liquid state (water) to solid state (ice).

Question: 8. Explain the term-
a] melting
b] vaporization
c] condensation
d] freezing
e] melting point
f] boiling point
Answer: Matter can change from solid to liquid to gaseous state and back to solid state. This is called change of state of matter.
(a) Melting— The process of conversion of a solid into liquid on heating. e.g. Ice to water.
(b) Vaporization— The process of conversion of a liquid into vapour on heating. e.g. Water to water vapour.
(c) Condensation— The process of conversion of vapour into a liquid. e.g. Water vapour to water.
(d) Freezing— The process of conversion of a liquid into a solid. e.g. Water to ice.
(e) Melting point— The constant temperature at which a solid melts into a liquid. M.P. of ice – 0°C.
(f) Boiling point— The constant temperature at which a liquid starts boiling. B.P. of water – 100°C.
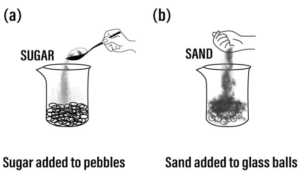
Question: 9. State what would you observe if
a] sugar is added to pebbles taken in a plastic beaker
b] sand is added to glass balls in a beaker.
What would you conclude from this imaginative demonstration.
Answer: Experiment: Add sugar to pebbles taken in a plastic beaker or sand to glass balls in a beaker.
Observation: The sugar or the sand goes into the space between the pebbles & the glass balls respectively.
Conclusion: An imaginative demonstration to show that intermolecular spaces between particles are occupied easily.
Question: 10. With the help of a simple diagram how would you show that – solids expand on heating.
Answer: Solids expand on heating can be shown by:
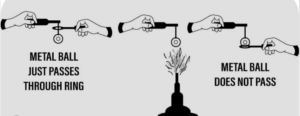
Question: 11. Give reasons for the following:
a] Solids have a definite shape & are highly rigid, while gases have no definite shape & are least rigid.
b] Sugar can be distinguished from talcum powder using water.
c] Water on freezing turns into ice.
d] A bottle of perfume on opening evolves an odour which can be sensed over a long distance.
Answer: (a) Solids have very closely packed atoms with minimum spaces between them while gases have atoms which are for apart with maximum spaces between them. Solids have a definite shape and are highly rigid while gases have no definite shape and are least rigid.
(b) Sugar is soluble in water whereas talcum powder is not.
(c) Every pure substance has a fired melting point or boiling point.
(d) A bottle of perfume on opening evolves an odour because gases diffuse very easily and odour spreads over a large distance.
Question: 12. Complete the statements given below by selecting the correct word/s.
a] Solids and liquids have a definite …volume… but gases do not. [mass, shape, volume]
b] The space between atoms in …gases… is maximum while in …solids… is minimum. [solids, liquids, gases]
c] Conversion a vapour into a liquid is called …condensation… . [vaporization, condensation, freezing]
d] Wax… and …sugar… is an example of a crystalline substance. [wax, sugar, tea]
Question: 13. State which of the following statements are false. If false write the correct statement.
| Statements | Ture/False |
| a] Solids are highly compressible and rigid. | T |
| b] Atoms/molecules in gases move only about their own positions. | F |
| c] The conversion of water to ice is called – freezing. | T |
-: End of Matter Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3 :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.