ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-18.2 Class 8 ICSE Ch-18 Maths Solutions. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exe-18.2 Questions for Mensuration as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-18.2 Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Avichal Publishig Company (APC) |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 8th |
| Chapter-18 | Mensuration |
| Writer | ML Aggarwal |
| Book Name | Understanding |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-18.1 Questions |
| Edition | 2023-2024 |
Mensuration Exe-18.2
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-298
Question 1. Each sides of a rhombus is 13 cm and one diagonal is 10 cm. Find
(i) the length of its other diagonal
(ii) the area of the rhombus
Answer:
(i) Side of rhombus = 13 cm.
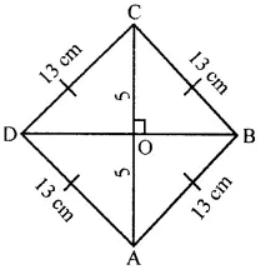
Length of diagonal AC = 10 cm.
∴ OC = 5 cm.
Since the diagonals of rhombus are ± to each other
∴ ∆BOC is rt. angled.
Hence, BC2 = OC2 + OB2
132 = 52 + OB2
⇒ OB2 = 169 – 25 = 144
⇒ OB = √144 = 12 cm
∴ Diagonal BD = 2 × OB = 2 × 12 = 24 cm
(ii) Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d1 × d2
= 1/2 × 10 × 24 = 120 cm2
Question 2. The cross-section ABCD of a swimming pool is a trapezium. Its width AB = 14 m, depth at the shallow end is 1-5 m and at the deep end is 8 m. Find the area of the cross-section.
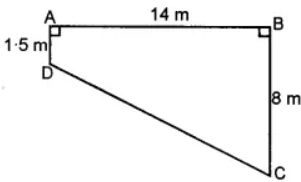
Answer:
Here, two parallel sides of trapezium are AD and BC
and distance between them is 14 m.
∴ Area of trapezium = 1/2 (1·5 + 8) × 14
= 1/2 × 9·5 × 14 = 66 × 5 m2
Question 3. The area of a trapezium is 360 m2, the distance between two parallel sides is 20 m and one of the parallel side is 25 m. Find the other parallel side.
Answer:
Area of a trapezium = 360 m2
Distance between two parallel lines = 20 m
One parallel side = 25 m
Let Second parallel side = 11 m
∴ Area = 1/2 (25 + x) × 20
⇒ 360 = 1/2(25 + x) × 20
∴ x = 36 – 25 = 11 m
∴ Second parallel side = 11 m
Question 4. Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6.5 cm and altitude is 5 cm. If one of its diagonal is 13 cm long, find the length of other diagonal.
Answer:
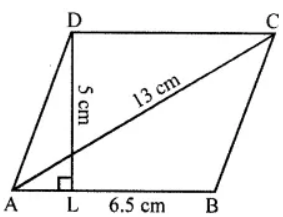
Side of rhombus = 6.5 cm
And altitude = 5 cm
So,
Area of a rhombus = Side × Altitude = 6.5 × 5 = 32.5 cm2
We have, one diagonal = 13 cm
Hence,
Length of other diagonal = (2 x Area)/ One diagonal
= (32.5 x 2)/ 13
= 5 cm
Question 5. From the given diagram, calculate
(i) the area of trapezium ACDE
(ii) the area of parallelogram ABDE
(iii) the area of triangle BCD.
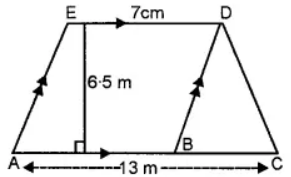
Answer:
(i) Area of trapezium ACDE = ½ × (AC + DE) × h
= ½ × (13 + 7) × 6.5
= ½ × 20 × 6.5
= 65 m2
(ii) Area of parallelogram ABDE = ½ × b × h
= ½ × 6 × 6.5
= 15.5 m2
(iii) Area of ∆BCD = ½ × base × height
= ½ × BC × height
= ½ × 6 × 6.5 [∵ BC = AC – AB = 13 – 7 = 6 m]
= 19.5 m2
Question 6. The area of a rhombus is equal to the area of a triangle whose base and the corresponding altitude are 24.8 cm and 16.5 cm respectively. If one of the diagonals of the rhombus is 22 cm, find the length of the other diagonal.
Answer:
Base of triangle = 24.8 cm and altitude = 16.5 cm
Area = ½ × base × altitude
= ½ × 24.8 × 16.5 cm2
= 204.6 cm2
Area of ∆ = Area of rhombus
But, area of rhombus = 204.6 cm2
Length of one diagonal = 22 cm
Area of rhombus = (First diagonal × Second diagonal)
Second diagonal = (2 × Area)/ First diagonal
= (204.6 × 2)/ 22
= 18.6 cm
Mensuration Exe-18.2
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-299
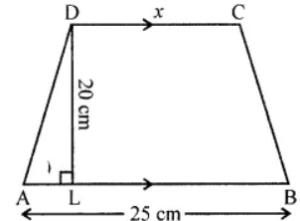
Question 7. The perimeter of a trapezium is 52 cm. If its non-parallel sides are 10 cm each and its altitude is 8 cm, find the area of the trapezium.
Answer:
Perimeter of a trapezium = 52 cm
Length of each non-parallel side = 10 cm
Altitude DL = 8 cm
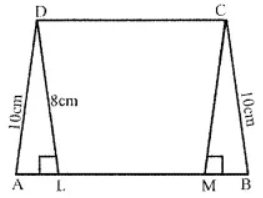
In right ∆DAL (By Pythagoras Theorem)
DA2 = DL2 + AL2
⇒ (10)2 = (8)2 + AL2
⇒ 100 = 64 + AL2
⇒ AL2 = 100 – 64 = 36 = (6)2
∴ AL = 6 cm
Similarly BM = 6 cm
and DC = LM
Also, perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DA
and CD = DA
∴ CD + DA = 2DA
But AB + CD = Perimeter – 2 AD
= 52 – 2 × 10 = 52 – 20 = 32 cm
Now area of trapezium = 1/2 (sum of parallel sides) × altitude
= 1/2 × 32 × 8 = 128 cm2
Question 8. The area of a trapezium is 540 cm2. If the ratio of parallel sides is 7 : 5 and the distance between them is 18 cm, find the lengths of parallel sides.
Answer:
Let, the two parallel sides of trapezium are 7x and 5x.
Height = 18 cm
⇒ Area of trapezium = 1/2 [(Sum of ||gm sides) × height]
540 = 1/2(7x + 5x) × 18
∴ 540 = 1/2 × 12x × 18
or 108x = 540
⇒ x = 5 cm
Hence, two parallel sides are
7x = 7 × 5 = 35 cm
and 5x = 5 × 5 = 25 cm
Question 9. Calculate the area enclosed by the given shapes. All measurements are in cm.
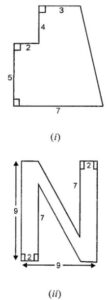
Answer:
(i) Area of trapezium ABCD
= (Sum of opposite ||gm sides) × height
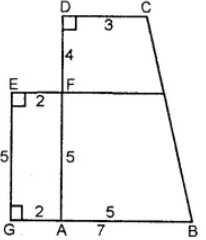
= [(AB + CD) × (AF + FD)]
= [(AB + CD) × (AF + FD)
= [(5 + 3) × (5 + 4)]
= (5 + 3) × 9
= 36 cm2
Area of rectangle GAFE = Length × Breadth
= 2 × 5 = 10 cm2
Total area of the figure = Area of trapezium ABCD + Area of rectangle GAFE
= (36 + 10) cm2
= 46 cm2+
(ii) Area of given figure = Area of rect. ABCD + Area of || gm BIHJ + Area of rectangle EFGH
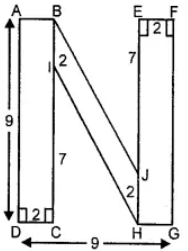
Area of rectangle ABCD = Length × Breadth
= AD × DC
= 9 × 2 = 18 cm2
Area of rectangle EFGH = Length × Breadth
= (EJ + JH) × EF
= (7 + 2) × 2
= 9 × 2 = 18 cm2
Area of parallelogram BIHJ = 2 × 5 = 10 cm2
[Since, distance between BI and HJ = 9 – 2 – 2 = 5 cm]
Total area of the figure = (18 + 18 + 10) cm2 = 46 cm2
Question 10. From the adjoining sketch, calculate
(i) the length AD
(ii) the area of trapezium ABCD
(iii) the area of triangle BCD
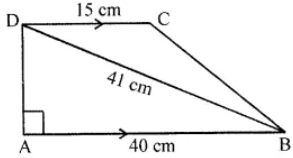
Answer:
(i) In right angled ∆ ABD, by Pythagoras Theorem we have
BD2 = AD2 + AB2
⇒ AD2 = BD2 – AB2
= (41)2 – (40)2
= 1681 – 1600
= 81
∴ AD = √81 = 9 cm
(ii) Area of trapezium ABCD
= (Sum of opposite || gm lines) × height
= (AB + CD) × AD
= (40+ 15) × 9
= 247.5 cm2
(iii) Area of triangle BCD = Area of trapezium ABCD – Area of ∆ ABD
= (247.5 – × 40 × 9) cm2
= (247.5 – 180) cm2
= 67·5 cm2
Question 11. Diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions = 28 cm × 32 cm and inner dimensions 20 cm × 24 cm. Find the area of each section of the frame, if the width of each section is same.
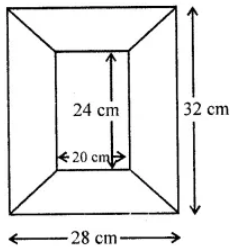
Answer:
Outer length of the frame = 32 cm and outer breadth = 28 cm
Inner length = 24 cm and outer breadth = 20 cm
So, width of the frame = (32 – 24)/ 2 = 4 cm
⇒ Height = 4 cm
Now, area of each portion of length side
= ½ × (24 + 32) × 4
= ½ × 56 × 4
= 112 cm2
And,
Area of each portion of breadth side
= ½ × (20 + 28) × 4
= ½ × 48 × 4
= 96 cm2
Area each section are 112 cm2, 96 cm2, 112 cm2, 96 cm2.
(ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-18.2 Class 8 ICSE Maths )
Question 12. In the given quadrilateral ABCD, ∠BAD = 90° and ∠BDC = 90°. All measurements are in centimetres. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
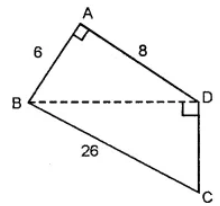
Answer:
In right angled triangle ABD, by Pythagoras Theorem we have
BD2 = AB2 + AD2 = (6)2 + (8)2
= 36 + 64
= 100 cm2
∴ BD = √100 = 10 cm
Area of ∆ABD = ½ × b × h
= ½ × 6 × 8
= 24cm2 …(i)
In ∆ BDC, we have
BD = 10 cm, BC = 26 cm
DC = ?
BC2 = BD2 + DC2
(26)2 = (10)2 + DC2
676 – 100 = DC2
⇒ DC = √576 = 24 cm.
Area of ∆ BDC = ½ × b × h
= ½ × 24 × 10
= 12 cm2 …(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get
Area of ∆ABD + Area of ∆BDC = (24 + 120) cm2
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 144 cm2
Question 13. Top surface of a raised platform is in the shape of a regular octagon as shown in the given figure. Find the area of the octagonal surface.
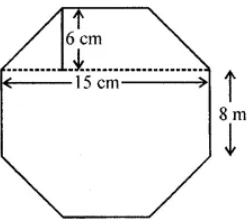
Answer:
Raised surface of platform is in the shape of regular octagon ABCDEFGH.
Each side = 8 cm, join HC
GD = HC = 15 cm, FL = AM = 6 cm
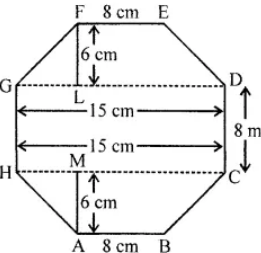
Now in each trapezium parallel sides are 15 cm and 6 cm
and height = 6 cm
∴ Area of each trapezium FEDG
= 1/2(GD + FE) × FL
= 1/2(15 + 8) × 6
= 23 × 3 cm2 = 69 cm2
Area of trapezium FEDG = Area of trapezium ABCH = 69 cm2
and area of rectangle HCDG
= HC × CD = 15 × 8 = 120 cm2
Total area = Area of trapezium FEDG + Area of trapezium ABCH
+ Area of rectangle HCDG.
Total area = 69 + 69 + 120 = 258 cm2
Question 14. In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a rectangle of size 18 cm by 10 cm. In ∆ BEC, ∠E = 90° and EC = 8 cm. Find the area enclosed by the pentagon ABECD.
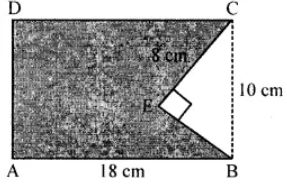
Answer:
Area of rectangle ABCD = Length × Breadth
= 18 × 10 = 180 cm2
In right angled ∆ BEC,
BC2 = CE2 + BE2 (By Pythagoras theorem)
(10)2 = 82 + BE2
∴ BE2 = 100 – 64 = 36
⇒ BE = √36 ⇒ BE = 6 cm.
∴ Area of rt. ∆ BEC = 1/2 × 6 × 8 = 24cm2
Area of pentagon ABECD = Area of rectangle – area of ∆
= (180 – 24) cm2 = 156 cm2
Mensuration Exe-18.2
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-300
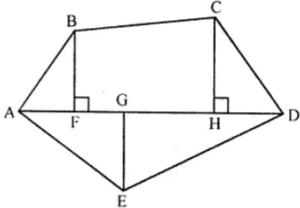
Question 15. Polygon ABCDE is divided into parts as shown in the given figure. Find its area if AD = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AG = 4 cm, AF = 3 cm and perpendiculars BF = 2 cm, CH = 3 cm, EG = 2.5 cm.
Answer:
In the given figure, ABCDE, AD = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AG = 4 cm,
AF = 3cm ⊥ BF = 2 cm CH = 3 cm and ⊥ EG = 2.5 cm
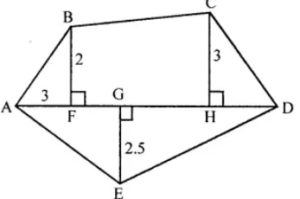
Area of ∆AED = ½ × AD × GE
= ½ × 8 × 2.5
= 10 cm2
Area of ∆ABF = ½ × AF × BF
= ½ × 3 × 2
= 3 cm2
Area of ∆CDH = ½ × HD × CH
= ½ × (AD – AH) × 3
= ½ × (8 – 6) × 3
= ½ × 2 × 3
= 3 cm2
Area of trapezium BFHC = ½ × (BF + CH) × FH
= ½ × (2 + 3) × (AH – AF)
= ½ × 5 × (6 – 3)
= ½ × 5 × 3
= 7.5 cm2
Total area of the figure = Area of ∆AED + Area of ∆ABF + Area of ∆CDH + Area of trapezium BFHC
= 10 + 3 + 3 + 7.5
= 23.5 cm2
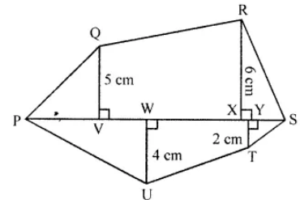
Question 16. Find the area of polygon PQRSTU shown in 1 the given figure, if PS = 11 cm, PY = 9 cm, PX = 8 cm, PW = 5 cm, PV = 3 cm, QV = 5 cm, UW = 4 cm, RX = 6 cm, TY = 2 cm.
Answer:
PS = 11 cm, PY = 9 cm, PX = 8 cm, PW = 5 cm, PV = 3 cm, QV = 5 cm, UW = 4 cm, RX = 6 cm and TY = 2 cm
The figure consists of 4 triangle and 2 trapeziums
VX = PX – PV
= 8 – 3
= 5 cm
XS = PS – PX
= 11 – 8
= 3 cm
YS = PS – PY
= 11 – 9
= 2 cm
WY = PY – PW
= 9 – 5
= 4 cm
Area ∆PQV = ½ × PV × QV
= ½ × 3 × 5 = 15/2
= 7.5 cm2
Area of ∆RXS = ½ × XS × RX
= ½ × 3 × 6
= 9 cm2
Area of ∆PUW = ½ × PW × UW
= ½ × 5 × 4
= 10 cm2
Area ∆YTS = ½ × YS × TY
= ½ × 2 × 2
= 2 cm2
Area of trapezium ∆VX R = ½ × (QV + RX) × VX
= ½ × (5 + 6) × 5
= ½ × 11 × 5 cm2
= 55/7
= 27.5 cm2
Area of trapezium WUTY = ½ × (UW + TY) × WY
= ½ × (4 + 2) × 4
= ½ × 6 × 4
= 12 cm2
Area of the figure = (7.5 + 9 + 10 + 2 + 27.5 + 12) cm2 = 68 cm2.
— End of Mensuration Exe-18.2 Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to : – ML Aggarwal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class -8
Thanks