ML Aggarwal Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs Class 8 ICSE Ch-17 Maths Solutions. We Provide Step by Step Answer of MCQs Questions for Visualising Solid Shapes as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
ML Aggarwal Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Avichal Publishig Company (APC) |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 8th |
| Chapter-17 | Visualising Solid Shapes |
| Writer | ML Aggarwal |
| Book Name | Understanding |
| Topics | Solution of MCQs |
| Edition | 2023-2024 |
Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-286
Mental Maths
Question 1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) A solid made up of polygonal regions is called ………
(ii) Polyhedrons which are not convex are called ………
(iii) A polyhedron is said to be ……… if all of its faces are regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex.
(iv) A polyhedron whose base and top are congruent polygons and whose lateral faces are parallelograms in shape is called a ………
(v) A prism whose base and top are congruent hexagon is called a ………
(vi) A polyhedron whose all lateral faces are triangles is called a ………
(vii) A triangular pyramid is also known as ………
(viii) A rectangular prism is also known as ………
(ix) The polygonal regions forming a polyhedron are called ………
Answer:
(i) A solid made up of polygonal regions is called polyhedron.
(ii) Polyhedrons which are not convex are called concave polyhedron.
(iii) A polyhedron is said to be regular polyhedron if all of its faces are regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex.
(iv) A polyhedron whose base and top are congruent polygons and whose lateral faces are parallelograms in shape is called a prism.
(v) A prism whose base and top are congruent hexagon is called a hexagonal prism.
(vi) A polyhedron whose all lateral faces are triangles is called a triangular pyramid.
(vii) A triangular pyramid is also known as a tetrahedron.
(viii) A rectangular prism is also known as a cuboid.
(ix) The polygonal regions forming a polyhedron are called faces.
Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-287
Question 2. State which of the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) A cylinder is a polyhedron.
(ii) All the prisms and pyramids are polyhedrons.
(iii) A tetrahedron is the only pyramid which can be a regular polyhedron.
(iv) The line segments where the faces of a polyhedron meet are called edges.
(v) F + E = V + 2 is called a Euler’s formula.
(vi) In any prism number of faces is 2 more than number of sides of polygonal base.
(vii) In any pyramid number of edges is twice the number of sides of polygonal base.
(viii) An octagonal prism has 18 vertices.
(ix) All pyramids are prisms.
(x) Lateral faces of a pyramid are triangles.
Answer:
(i) A cylinder is a polyhedron. False
(ii) All the prisms and pyramids are polyhedrons. True
(iii) A tetrahedron is the only pyramid which can be a regular polyhedron. True
(iv) The line segments where the faces of a polyhedron meet are called edges. True
(v) F + E = V + 2 is called a Euler’s formula. False
Correct:
It is F + V = E + 2.
(vi) In any prism number of faces is 2 more than the number of sides of polygonal base. True
(vii) In any pyramid number of edges is twice the number of sides of polygonal base. True
(viii) An octagonal prism has 18 vertices. False Correct:
It has 8 + 8 = 16
(ix) All pyramids are prisms. False
Correct:
Both are different shapes.
(x) Lateral faces of a pyramid are triangles. True
Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-287
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 17):
Question 3. Which of the following is not a 2-dimensional shape?
(a) Triangle
(b) Circle
(c) Sphere
(d) Rectangle
Answer:
Sphere is not a two-dimensional shape, (c)
Question 4. Which of the following is a 3-dimensional shape?
(a) Parallelogram
(b) Cylinder
(c) Square
(d) none of these
Answer:
Cylinder is a 3-dimensional shape. (b)
Question 5, How many parallel and congruent faces does a cylinder have?
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) none
Answer:
A cylinder has two parallel and congruent faces. (c)
Question 6. How many pairs of congruent parallel faces does a rectangular prism have?
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
A rectangular prism has 3 pairs of congruent
and parallel faces. (d)
Question 7. How many congruent isosceles triangle does a square pyramid have?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer:
A square pyramid has 4 congruent isosceles triangles. (b)
Question 8. Which amongst the following is not a polyhedron?
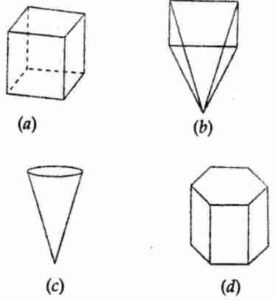
Answer:
Figure (c) is not a polyhedron. (c)
Question 9. Which of the following is not a prism?
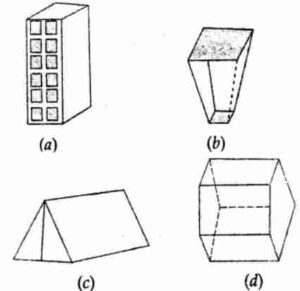
Answer:
Figure (b) is not a prism. (b)
Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-288
Question 10. The number of triangular faces of a triangular prism are
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
A triangular prism has 2 triangular faces, (a)
Question 11. The number of edges in a pentagonal pyramid are
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) 20
Answer:
A pentagonal pyramid has 10 edges. (b)
Question 12. The number of rectangular faces in a hexagonal prism are
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer:
A hexagonal prism has 6 rectangular faces. (a)
Question 13. In a polyhedron E = 15, V = 10, then F is
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
Answer:
E = 15, V = 10
F + V = E + 2
⇒ F = E + 2 – V = 15 + 2 – 10 = 7 (c)
Question 14. In a polyhedron F = 5, E = 8, then V is
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
Answer:
F + V = E + 2
So ⇒ 5 + V = 8 + 2
or ⇒ 5 + V = 10
Hence⇒ V = 10 – 5 = 5 (b)
Question 15. In a polyhedron F = 17, V = 30, then E is
(a) 30
(b) 45
(c) 60
(d) none of these
Answer:
F = 17, V = 30
F + V = E + 2
⇒ E = F + V – 2
⇒ E = 17 + 30 – 2 = 45 (b)
Question 16. A polyhedron have 4 faces, 4 vertices and 6 edges. Name the polyhedron.
(a) A rectangular prism
(b) A triangular prism
(c) A rectangular pyramid
(d) A triangular pyramid
Answer:
A polyhedron has 4 faces, 4 vertices and 6 edges.
∴ It is triangular pyramid. (d)
Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-288
HOTS
Question 1. Which of the following nets can be folded to form a cone?
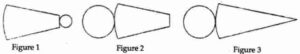
Answer:
Net in figure (3) can be folded to form a cone.
Question 2. Which of the following nets can be folded to form a cylinder?
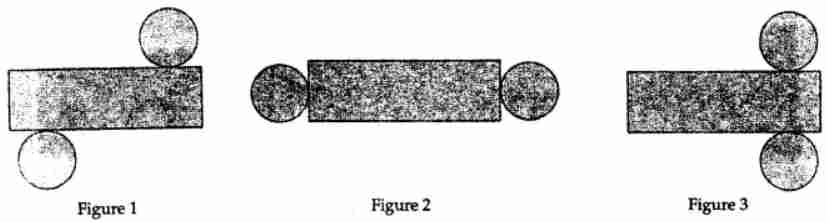
Answer:
Net in the figure (1) and (2) can be folded to form a cylinder.
— End of Visualising Solid Shapes MCQs Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to : – ML Aggarwal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class -8
Thanks