Nervous System Srijan Publications Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-10. We Provide Solutions of Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type Questions and MCQs of Exercise-10 Nervous System Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Ch-10. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
Nervous System Srijan Publications Solutions ICSE Class-10 Biology Ch-10
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-10 | Nervous System |
| Topics | Solutions of MCQs, Very short and Short Long Answers Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Ch-10 Nervous System Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-147)
Questions 1. Give one word for the following:
(a) The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain.
Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid
(b) The biological term given to the protective membranes of the brain.
Ans: meninges
(c) The fluid that provides protection and nourishment to the cells of the brain.
Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid.
(d) The part of the brain which is concerned with memory.
Ans: cerebellum
(e) The part of the human brain that controls body temperature.
Ans: the hypothalamus
(d) The nerve which transmits impulses from the receptor to the brain.
Ans: Sensory neurons
(g) Point of contact between two neurons.
Ans: synapse
(h) Protective membranes covering the human brain and spinal cord.
Ans: meninges
(i) Inflammation of meninges.
Ans: Meningitis
Questions 2. Answer the following questions.
(a) What is the maximum length of an axon?
Ans: one meter or more
(b) What is the difference in the distribution of grey and white matter of brain and spinal cord?
Ans: In the brain, grey matter is mainly found in the outer layers, while in the spinal cord it forms the inner core.
(c) What determines the direction of flow of impulse in nerve?
Ans: The nerve impulse flows in one direction only i.e. downwards from the axon. This is because of the polarization generated by sodium ions in the particular direction
(d) Which are the important neurotransmitters?
Ans: Serotonin. , Histamine. ,Dopamine. , Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
(e) State the function of sensory neuron and a motor neuron.
Ans: Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS
(f) What is a nerve made up of?
Ans: Nerves are made up of bundles of axons that work together to facilitate communication between the CNS and PNS. It’s important to note that “peripheral nerve” actually refers to the PNS. Axon bundles are called “tracts” in the CNS
(g) Which part of the nervous system prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’ condition?
Ans: The autonomic nervous system has two parts: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for sudden stress, like if you witness a robbery.
Questions 3. Choose the odd one in each of the following series.
(a) Pons cerebellum, medulla oblongata, cerebrum
(b) Corpus luteum corpus callosum. pons, cerebellum
Answer :
(a) Pons
(b) cerebellum
Questions 4. Differentiate between the following pairs with reference to the aspect in brackets.
(a) Cerebrum and cerebellum (function)
Ans: cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature while cerebellum control body balance
(b)Medulla oblongata and cerebellum (function).
Ans: Cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature while Medulla oblongata control involuntary action
(c) Cerebrum and spinal cord (arrangement of cytons and axons of neurons)
Ans: Axons are placed in inner portion whereas cytons are placed in outer portion of brain but in spinal cord, axons are placed in outer side and cell bodies / cytons are placed in the inner portions
(d) Dendrite and axon (structure)
Ans: Dendrites are one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being an axon. Axons can be distinguished from dendrites by several features including shape, length, and function
(e) Sensory nerve and motor nerve (direction of impulse carried)
Ans : Sensory nerve brings impulses from the receptors i.e. sense organs to the brain or spinal cord. Motor nerve carries impulse from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs such as muscles or glands.
(f) Conditioned and unconditioned reflexes (nature)
Ans: conditioned reflex is a reflex that has been created or modified through a particular training / experience while unconditioned reflexes is inborn
Questions 5. Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternative.
(a) The largest region of brain is ….cerebellum…….. (cerebellum/cerebrum/ medulla)
(b) The seat of memory and intelligence in human brain is ….cerebellum.….. (cerebrum/cerebellum/
(c) The ….hypothalamus…. helps in thermoregulation (thalamus/hypothalamus/ medulla oblongata)
(d) The basic unit of human brain is the ..neuron….. (neuron/axon/cyton)
Questions 6. Define the following terms
(a) Neuron
Ans: fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for receiving sensory input from the external world, for sending motor commands to our muscles,
(b) Axon : also called nerve fibre, portion of a nerve cell (neuron) that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. A neuron typically has one axon that connects it with other neurons or with muscle or gland cells. Some axons may be quite long, reaching, for example, from the spinal cord down to a toe
(c) Axolemma: the plasma membrane of an axon For a short time after the passage of a nerve impulse along a nerve fiber, while the axolemma is still depolarized, a second stimulus, however strong, is unable to excite the nerve
(d) Synapse : synapse, also called neuronal junction, the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell (effector). A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction
(e) De-polarisation: Depolarization in a nerve cell occurs when the cell undergoes an electrical change. Most cells are negatively charged relative to their surroundings. This negative internal charge of the cell shifts to a positive through the process of depolarization. Depolarization though occurs for only a brief period of time
(f) Reflex action: Reflex action is a sudden and involuntary response to stimuli. It helps organisms to quickly adapt to an adverse circumstance that could have the potential to cause bodily harm or even death. Pulling our hands away immediately after touching a hot or cold object is a classic example of a reflex action
Questions 7. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, rewrite the correct from of statements.
(a) Duramater is the outermost layer of meninges. True
(b) Cranial nerves arise from the brain. True
(c) Acetylcholine is a cerebrospinal fluid. False,
Correct : Acetylcholine is a Chief neurotransmitter.
(d) All voluntary actions are controlled by the cerebellum. True
(e) Dilation of the pupil is brought about by the sympathetic nervous system. True
Questions 8. Given below is a set of five terms. Rewrite the terms in logical sequence as directed at the end of the statement.
motor neuron, receptor, sensory neuron, effector, association neuron. (pathway of a nerve impulse)
Answer : Receptor→Sensory Neuron→Spinal cord→Motor neuron→Effector.
B. Short Answer Type Questions
Ch-10 Nervous System Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-148)
Questions 1. Answer the following questions
(a) What are meninges? Name different meninges
Ans: Meninges are three layers of membranes that cover and protect your brain and spinal cord (your central nervous system [CNS]).
Name different meninges
- Dura mater: This is the outer layer, closest to your skull.
- Drachnoid mater: This is the middle layer.
- Pia mater: This is the inner layer, closest to your brain tissue
(b) Mention how impulse is transmitted at a synapse from one neuron to another.
Ans: When a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, the axon releases chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters travel across the synapse between the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. Neurotransmitters bind to the membrane of the dendrite
(c) What are the sub-divisions of the nervous system? Mention the major parts included in each of them.
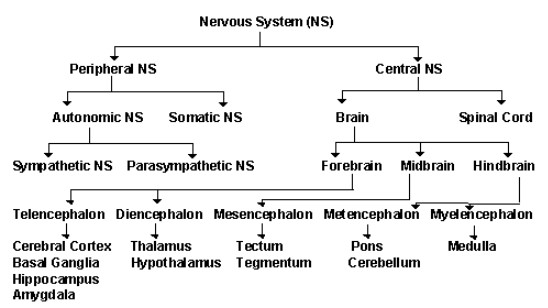
(d) With the help of schematic diagram trace the sequence of events occurring when you step on a sharp object.
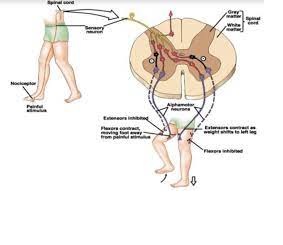
(e) Explain the mechanism of reflex action with suitable example.
Ans: Sensory neuron sends electrical impulses to a relay neuron, which is located in the spinal cord of the CNS. Relay neurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons. Motor neuron sends electrical impulses to an effector. Effector produces a response (muscle contracts to move hand away).
Questions 2. Give reasons for the following
(a) A person walks unsteadily when drunk.
Ans: A drunk person walks clumsily because, due to the effect of alcohol, the cerebellum is unable to coordinate muscular movements properly
(b) Reflex action will not occur, if dorsal root is cut.
Ans: Reflex action occurs through the path of reflex arcs where dorsal root plays the role of transferring information. So if dorsal root is cut Reflex action will not occur
(c) There is comparatively delayed flow of information through brain than spinal cord.
Ans: because to reach the brain the involvement of nervous system is needed but in case of spinal cord the brain involvement is no need
(d) Injury of the medulla oblongata results in death.
Ans : Through pons, it is connected to the midbrain. It is the controlling centre for heart and lung. It regulates involuntary movements such as breathing, respiration, circulation, the function of blood vessels etc. Thus, injury to medulla oblongata leads to death
(e) Conduction of nerve impulse through nerve fibres is described as an electrochemical phenomenon.
Ans: Nerve impulses are signals carried along nerve fibers. These signals convey, to the spinal cord and brain, information about the body and about the outside world. They communicate among centers in the central nervous system and they command your muscles to move. Nerve impulses are electrochemical events.
C. Long Answer Type Questions
Ch-10 Nervous System Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-148)
Questions 1. Draw a well-labelled diagram of a neuron showing the following parts: Perikaryon, Dendrites, Axon, Node of Ranvier and Myelin sheath.
Answer :

Questions 2. Draw a labelled diagram of a myelinated neuron.
Answer :
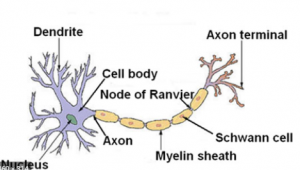
Questions 3. Differentiate between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Answer : The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for the “fight or flight” response during any potential danger. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system inhibits the body from overworking and restores the body to a calm and composed state.
Questions 4. Name different parts of forebrain and mention their functions.
Answer : different parts of forebrain and their functions
- Cerebrum – responsible for complex functions like intersensory associations, memory, and communications.
- Thalamus – it is the major coordinating center for sensory and motor signaling.
- Hypothalamus – it contains a number of centers which control body temperature, urge for eating, and drinking
Questions 5.
(a) What is a reflex arc?
(b) What are the components of a reflex arc?
Answer :
(a) The reflex arc is a sort of neural circuit that starts with a sensory neuron at a receptor and finishes with a motor neuron at an effector (for example, a pain receptor in the fingertip)
(b) 1, a receptor; 2, a sensory neuron; 3, one or more synapses in the CNS; 4, a motor neuron; and 5, a target organ
— : End of Nervous System Srijan Publications Solutions ICSE Class-10 Biology Ch-10. :–
Return to :- Srijan Publication ICSE Biology for Class 10 Solutions
Thanks