Periodic Table ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Notes. The first chapter of ICSE Class 10 Chemistry is Periodic Table. In this article you would get notes and important point of this chapter periodic Table. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Chemistry.
Periodic Table ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Notes
Point to be Discuss
- Need for Classification of Elements
- Early Attempts of Classification
- Mendeleeff PT
- Modern form of PT
- Salient Feature of Modern PT
Need for Classification of Elements
- Simplifies the study
- To make predictions about new elements,
- Understanding of chemical reactions
- Establish Relation among elements
Early Attempts of Classification
Dobereiner Triad:
Li, Na, K: The atomic masses are approximately 7, 23, and 39, respectively. The average of 7 and 39 is 23, which is the atomic mass of sodium
Limitations of Dobereiner’s Triads
- The identification of new elements made this model obsolete.
- Newly discovered elements did not fit into the triads.
- Only a total of 5 Dobereiner’s triads were identified.
- Even several known elements did not fit into any of the triads.
Newland Octave Rules
when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, every eighth element exhibits similar chemical properties
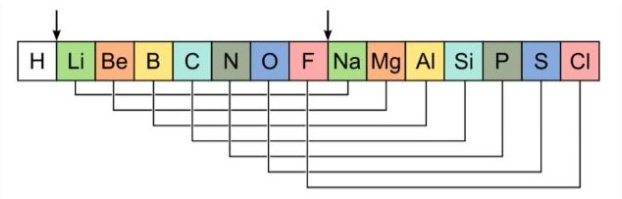
Limitations of Newland’s Law of Octaves
- Several elements were fit into the same slots in Newland’s periodic classification. For example, cobalt and nickel were placed in the same slot.
- Elements with dissimilar properties were grouped together. For example, the halogens were grouped with some metals such as cobalt, nickel and platinum.
- Newland’s law of octaves held true only for elements up to calcium. Elements with greater atomic masses could not be accommodated into octaves.
- The elements that were discovered later could not be fit into the octave pattern. Therefore, this method of classifying elements did not leave any room for the discovery of new elements
Mendeleeff PT
i) Systematic study of the elements: Mendeleev’s classification condensed the study of about 90 elements (only 63 – 65 elements were known at that time but he left a provision for many more) to the study of only 8 groups of elements.
ii) Prediction of new elements and their properties: He left some gaps in his periodic table for the undiscovered elements and could even predict the properties of undiscovered elements.
iii) Correction of certain atomic masses: By placing elements strictly according to the similarity in their properties, he was also able to correct certain atomic masses.
Defects in the Mendeleev’s periodic table:
i. Position of hydrogen: In Mandeleev’s periodic table, position of hydrogen was not made clear. i.e., It can be placed either in group – I or VII.
ii. Separation of chemically similar elements: Certain elements which appear to be chemically similar like Cu and Hg, Au and Pt etc., have been placed in separate groups.
iii. Grouping of chemically dissimilar elements: Certain chemically dissimilar elements have been grouped together in the Mendeleev’s periodic table. e.g., Cu, Ag and Au have no resemblance with alkali metals (Li, Na, K etc),but these have been grouped together in group I.
Inversion in periodic table: Certain pairs of elements had to be placed in the reverse order of atomic masses in order to confirm the periodic law. e.g., Co (58.9) has been placed before Ni (58.7) and Ar (39.9) has been placed before K (39.1) etc.
Position of Isotopes: No separate places were given to isotopes.
Position of lanthanides and actinides: Lanthanide & actinide were not given places in periodic table. From these anomalies, atomic weight does not appear to be a good basis for the periodic classification of elements.
Modern Form of Periodic Table
Moseley believed that atomic number, the number of positive charges in the nucleus, would be a more fundamental property to use in classifying elements
Modern Periodic Law:
the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their properties show a repeating pattern at regular intervals. This means that elements with similar properties appear in groups (vertical columns) on the periodic table
Salient Features of Modern PT
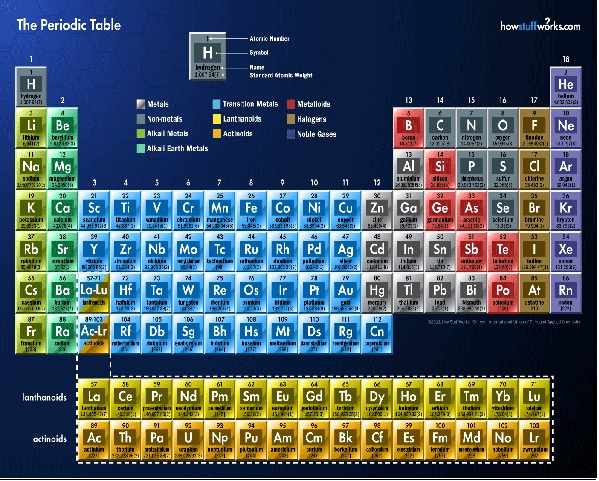
- Arrangement by Atomic Number: Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus).
- Groups (Vertical Columns): There are 18 groups, numbered 1 to 18, where elements within a group have similar properties
- Periods (Horizontal Rows): There are 7 periods, and elements within a period have the same number of electron shells,
- Periodicity of Properties: Properties like electronegativity, metallic character, ionization energy, and atomic radius exhibit periodic trends across periods and down groups,
- Separation of Elements: The table separates elements with similar properties, such as reactive metals, noble gases, and transition metals,
Elements are grouped into s, p, d, and f blocks based on their electronic configurations
— : End of Periodic Table ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Notes Need for Classification :–
- Concise Selina Chemistry Solutions for ICSE Class-10.
- Simplified Dr. Dalal Chemistry Solutions for ICSE Class-10
- Goyal Brothers Prakashan for ICSE Class-10 Chemistry Textbook
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends


