Potentiometer Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
Potentiometer Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-6 | DC Circuits and Measurements. |
| Topics | Numericals on Potentiometer |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Numericals on Potentiometer
Potentiometer Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements.
Que-31. In figure, AB is a potentiometer wire of length 100 cm. The cell of emf 3 V has a negligible internal resistance. What is the reading in voltmeter V, if BC is equal to 70 cm?
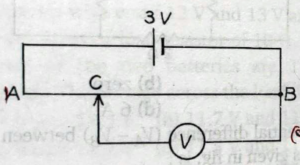
Ans-31 Length of a wire = 100 cm
Potential difference = 3 V
gradient = 3/100 V/cm
Potential difference for 70cm
= (3/100) x 70 = 2.1 V.
Que-32. A 3 V battery of internal resistance 1 Ω is joined to a sliding wire of length 100 cm and resistance 5 Ω. A voltmeter, which takes negligible current, is connected across 60 cm length of the wire. (a) What is the reading of the voltmeter? (b) If the resistance of the voltmeter were 150 Ω, then what would have been its reading?
Ans-32 (a) Battery Voltage = 3 V
Internal Resistance = 1 Ω
100 cm Wire resistance = 5 Ω
So current in Circuit = I
3 – I*1 = I 5
=> 3 = 6I
=> I = 0.5A
60 cm Wire resistance = (60/100) * 5 = 3 Ω
Voltage across 3 Ω = 3 * 0.5 = 1.5 V
reading of the voltmeter = 1.5V
(b) if resistance of the voltmeter were 150 Ω
Parallel resistance between 3 Ω & 150 Ω
= 1/(1/3 + 1/150) = 150/51 Ω
Total Resistance = 1 + 150/51 + 2 = 303/51 Ω
Total current through circuit = 3/(303/51) = 51/101 A
Voltmeter reading = (51/101 ) * (150/51)
= 150/101
= 1.485 V
Que-33. A 10 m long potentiometer wire has a potential gradient of 0.0025 V/cm along its length. Calculate the length of the wire at which null-point is obtained for a 1.025 V standard cell. Also, find the emf of another cell for which the null-point is obtained at 860 cm length. What maximum PD can be measured by this potentiometer?
Ans-33 E = ρl where ρ is potential gradient
E = 0.0025 x l = 1.025
l = 1.025/0.0025 = 410 cm.
again E = 0.0025 x 860
= 2.15 V
max emf = p x total length
= 0.0025 x 1000
= 2.5 volt
Que-34. A potentiometer is being used to compare two resistances. The balancing length for a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is 58.3 cm, while that for an unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What would you do if you failed to find a null-point on the potentiometer wire AB?
Ans-34 From the rule of wheat stone bridge
R/X = 58.3/68.5
10/X = 583/685
X = (10 x 685)/583
X = 1.75 Ω
Que-35. A cell gives a balance with 85 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the terminals of the cell are shorted through a resistance of 7.5 Ω a balance is obtained at 75 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
Ans-35 r = R(l1/l2 – 1)
r = 7.5{(85/75) – 1}
r = (7.5 x 10)/75
r = 1 Ω.
Que-36. A cell of emf 1.25 V gives a balance point at 35.0 cm length of a potentiometer wire. For an other cell, the balance point shifts to 63.0 cm. What is the emf of the second cell?
Ans-36 According to the principle of potentiometer
E1/E2 = l1/l2
1.25/E2 = 35/63
E2 = (63 x 1.25)/35
E2 = 2.25 V.
Que-37. Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emf’s E1 and E2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 360 cm from the end A. Determine (i) E1/E2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell E1 only. (Assume E1 > E2)
Ans-37
Que-38. A potentiometer wire of length 1 m is connected to a driver cell emf 3 V as shown in the figure. When a cell of emf 1.5 V is used in the secondary point is found to be 60 cm. On replacing this cell by a cell of unknown emf, the balance point shifts to 80 cm.
(i) Calculate unknown emf of the cell.
(ii) Explain with reason, whether the circuit works if the driver cell is replaced with a cell of emf 1 V.
(iii) Does the high resistance R, used in the secondary circuit affect the balance point? Justify your answer.
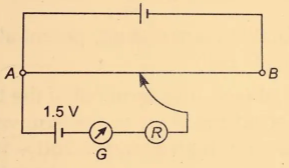
Ans-38 (i) Unknown emf 𝜀2 is given by
𝜀2/𝜀1 = 𝑙2/𝑙1
⇒𝜀2 = (𝑙2/𝑙1) x 𝜀1
Given 𝜀1 = 1.5𝑉, 𝐼1 = 60𝑐𝑚, 𝐼2 = 80𝑐𝑚
∴ 𝜀2 = (80/60) × 1.5𝑉 = 2.0 𝑉.
(ii) The circuit will not work if emf of driver cell is 1 V (less than that of cell in secondary circuit, because total voltage across wire AB is 1 V which cannot balance the voltage V.
(iii) No, since a t balance point no current flows through galvanometer G i.e., cell remains in open circuit.
— : End of Potentiometer Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-6 DC Circuits and Measurements.. :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends