Power Consumed in AC Circuits Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution 12 Alternating Current Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.

Power Consumed in AC Circuits Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution 12 Alternating Current
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-12 | Alternating Current |
| Topics | Numericals on Power Consumed in AC Circuits |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Numericals on Power Consumed in AC Circuits
Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution 12 Alternating Current
Que-52: A sinusoidal voltage V = 200 sin 314 t is applied to a 10 Ω resistor. Find (i) rms voltage, (ii) rms current and (iii) power dissipated as heat.
Ans-(i) Vrms = Vpeak/√2 = 200/√2 V
(ii) Irms = Vrms/R = 200√2 / 10 = 20√2
(iii) P = Irms² R = (10√2)².10 = 2000 W
Que-53: An 80 V-800 W heater is to be operated on a 100 V 50 Hz supply. Calculate the inductance of the choke required.
Ans- Resistance R = Vh²/Ph = 80²/800 = 8 Ω
Current I = Ph/Vh = 800/80 = 10 A
Impedance Z = Vs/I = 100/10 = 10 Ω
inductive reactance XL² = Z² – R²
=> XL = √(Z²-R²)
=> XL = 6 Ω
Inductance L = XL/2πf
=> 60/100π = 0.02 H
Que-54: Calculate current and power factor for the given AC circuit.
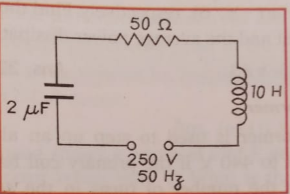
Ans- Current = 0.16 A
Power factor = 0.032
Que-55: In the given circuit, the potential differences across resistance, capacitance and inductance are given. Work out the emf of the source of alternating current and power factor of the circuit.
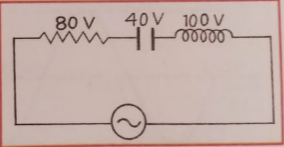
Ans- emf = 100 V
power factor = 0.8
Que-56: A 1.9 H inductor, a 100 µF capacitor and a 25 Ω resistor are connected in series to an AC source of emf given by V = 282 sin 100t volt. Find for the circuit (i) the net reactance, (ii) the impedance, (iii) the rms current and (iv) the rate of dissipation of heat.
Ans-(i) net reactance
= XL – XC

Que-57: In an AC circuit, R = 40 Ω , Z = 50 Ω , V rms =200 V Calculate the average power consumed over a full cycle. (ISC 2003)
Ans- P = (Irms)².R
=> (Vrms/2)² x R
=> (200/50)² x 40 = 640 watt
Que-58: A resistance of 150 Ω and a capacitance of 15 µF are connected in series with an AC source. The peak value of current is 0.20 A. Calculate the average power consumed in the circuit. If the capacitor is removed but the current in kept the same, what is the average power consumed in the resistor alone?(ISC 2007)
Ans- P = 1/2 Vo io = 1/2 (IoR) x Io
=> 1/2 Io² R = 1/2 x 0.20² x 150
=> 3 W
capacitor consumes no power, therefore power consumption will be same 3 W.
Que-59: In an alternating circuit connected to an emf of 100 V and frequency 50 Hz, a resistance of 10 Ω and an inductance of 1/(10π) Η are connected in series. Find out the power dissipated in the circuit.
Ans-

Que-60: An alternating voltage and the corresponding current are given by V = 110 sin (ωt + π/6) and I = 5 sin (ωt – π/6) respectively. Find the impedance of the circuit and the average power dissipation in it.
Ans- here φ = π/6 – (-π/6) = π/3
Z = Vo/io = 110/5 = 22 Ω
and P = vo.io/2 x cos φ
=> 110 x 5/2 x cos π/3
=> 550/4 = 137.5 watt
— : End of Power Consumed in AC Circuits Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution 12 Alternating Current :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends


