Practical Work Exe-9B Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-9. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-9 Practical Work with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Practical Work Exe-9B Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-9 | Practical Work |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 9B (Action of Heat on a given Substance) |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
B. Exercise – 9B
Practical Work Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-154
Question 1.
Distinguish by heating the following in dry test tube.
(a) Zinc carbonate, copper carbonate and lead carbonate
(b) zinc nitrate and copper nitrate
(c) copper sulphate and copper carbonate
(d) ammonium chloride and iodine
Answer:
(a) zinc carbonate, copper carbonate and lead carbonate :
On heating zinc carbonate, light amorphous white solid changes to pale yellow.
On heating copper carbonate, light green amorphous powder changes to black.
(b) zinc nitrate and copper nitrate :
On heating zinc nitrate, white solid changes to yellow when hot and white when cold.
On heating copper nitrate, bluish green crystalline solid melts to form a bluish green mass and gives off steamy vapours which condense on cooler parts of the test tube.
(c) copper sulphate and copper carbonate :
On heating copper sulphate, blue crystalline solid crumbles to form a white amorphous powder and gives off steamy vapours which condense on cooler parts of the test tube to form a colourless liquid (water).
On strong heating, a black solid is formed and a gas is evolved that turns moist blue litmus red and changes the colour of acidified K2Cr2O7 solution from orange to green suggesting that it is SO2.
(d) ammonium chloride and iodine :
On heating ammonium chloride, white crystalline solid sublimates to form a basic gas (NH3) and acidic gas (HCl). The dense white fumes are noticed that form a white mass on the cooler parts of the test tube.
On heating iodine, violet crystalline solid sublimates to form violet vapours. These vapours settle down on cooler parts of test tube to form violet crystals.
Question 2.
Match the following :
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (a) Pb(NO3)2 | (i) rotten egg smell |
| (b) CO2 | (ii) burns with a pop sound |
| (c) (NH4)2Cr2O7 | (iii) suffocating smell of sulphur |
| (d) HCl | (iv) lime water turns milky |
| (e) NO2 | (v) crackling sound |
| (f) O2 | (vi) residue swells up |
| (g) H2 | (vii) brown gas |
| (h) H2S | (viii) supports combustion |
| (i) SO2 | (ix) fumes with NH3 solution |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (a) Pb(NO3)2 | (v) crackling sound |
| (b) CO2 | (iv) lime water turns milky |
| (c) (NH4)2Cr2O7 | (vi) residue swells up |
| (d) HCl | (ix) fumes with NH3 solution |
| (e) NO2 | (vii) brown gas |
| (f) O2 | (viii) supports combustion |
| (g) H2 | (ii) burns with a pop sound |
| (h) H2S | (i) rotten egg smell |
| (i) SO2 | (iii) suffocating smell of sulphur |
Question 3.
Distinguish by dilute sulphuric acid.
(a) Sodium sulphite and sodium carbonate.
(b) Copper and magnesium.
(c) Sodium sulphide and sodium sulphite.
Answer:
(a) Sodium sulphite and sodium carbonate :
On adding dilute sulphuric acid to sodium sulphite and warming, a colourless gas with suffocating smell of burning sulphur is evolved. The evolved gas turns lime water milky and changes the colour of acidified K2Cr2O7 solution from orange to green suggesting that it is SO2.
Na2SO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O + SO2↑
On adding dilute sulphuric acid to sodium carbonate and warming, a colourless gas is evolved with brisk effervescence. The evolved gas extinguishes a burning wooden splinter and turns lime water milky but has no effect on acidified K2Cr2O7 solution suggesting that it is CO2.
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2↑
(b) Copper and magnesium :
Magnesium on reaction with dil. sulphuric acid produces a colourless, odourless gas with brisk effervescence. The gas evolved is hydrogen as it burns with a pale blue flame producing a pop sound.
Mg+ dil. H2SO4 ⟶MgSO4 +H 2
Copper does not react with dil. sulphuric acid liberating hydrogen as it is lower in metal reactivity series than hydrogen.
(c) Sodium sulphide and sodium sulphite :
When dil. sulphuric acid is added to sodium sulphide and heated, hydrogen sulphide gas is evolved which has the smell of rotten eggs.
Na2S + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2S ↑
On adding dilute sulphuric acid to sodium sulphite and warming, a colourless gas with suffocating smell of burning sulphur is evolved. The evolved gas turns lime water milky and changes the colour of acidified K2Cr2O7 solution from orange to green suggesting that it is SO2.
Na2SO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ Na2SO4 + H2O + SO2↑
Question 4.
Write your observation and a balanced equation in the case of the following substances being heated.
(a) Ammonium dichromate
(b) Copper nitrate
(c) Copper carbonate
(d) Zinc carbonate
(e) Ammonium chloride
Answer:
(a) Ammonium dichromate — Orange red crystalline solid, on heating, swells up and decomposes violently with flashes of light leaving greenish residue. It also gives off steamy fumes, which condense on the cooler parts of the test tube to form tiny droplets of water.
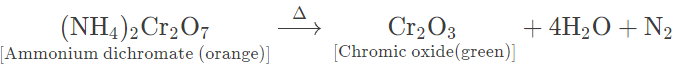
(b) Copper nitrate — Bluish green crystalline solid, on heating, melts to form a bluish green mass and gives off steamy vapours that condense on the cooler parts of test tube.

On further heating, the bluish green mass changes to a black residue of copper (II) oxide and brown coloured nitrogen dioxide gas is evolved along with oxygen gas.
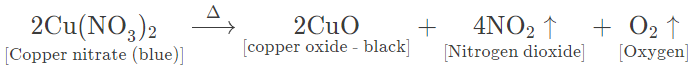
(c) Copper carbonate — Light green amorphous powder changes to black. Carbon dioxide gas is given off which turns lime water milky.
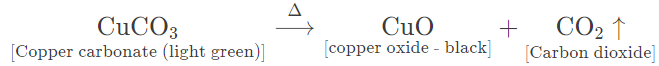
(d) Zinc carbonate — On strong heating, light amorphous white solid changes to pale yellow. Carbon dioxide gas is given off which turns lime water milky.

(e) Ammonium chloride — On heating ammonium chloride, white crystalline solid sublimates to form a basic gas (NH3) and acidic gas (HCl). The dense white fumes are noticed that form a white mass on the cooler parts of the test tube. No residue is left behind.
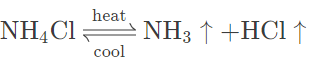
Question 5.
State the original colour of the following substances and colour of residue obtained after heating.
(a) ammonium dichromate
(b) copper carbonate
(c) lead nitrate
(d) zinc carbonate
Answer
| S. No. |
Salt | Original colour | Residue after heating |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | ammonium dichromate | Orange solid | Green solid |
| (b) | copper carbonate | Green solid | Black solid |
| (c) | lead nitrate | White solid | Yellow solid |
| (d) | zinc carbonate | White solid | Yellow when hot, white when cold |
— : End of Practical Work Exe-9B Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends