Rational and Irrational Numbers Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-1C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-1. We Provide Step by Step Solutions / Answer of Rational and Irrational Numbers OP Malhotra Maths . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics.

Rational and Irrational Numbers Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-1C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-1
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-1 | Rational and Irrational Numbers |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-1C | Rationalize the Denominators |
| Edition | 2025-2026 |
Rationalize the Denominators
Rational and Irrational Numbers Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-1C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-1
Simplify:
Que-1: (a) √(1/3)
(b) √(5/12)
(c) √[1*(46/75)]
Sol: (a) 1/√3
= (1×√3)/(√3×√3) [multiply and divide by √3]
= √3/3.
(b) √(5/12) = √5/2√3
= (√5×√3)/(2√3×√3) [multiply and divide by √3]
= √15/6
(c) √[1*(26/75)] = √(121/75)
= √(11×11)/√(3×5×5) = 11/5√3
= (11×√3)/(5√3×√3) [multiply and divide by √3]
= 11√3/15
= (11/15) (√3)
Que-2: √112 – √63 + {224/√28}.
Sol: √112 – √63 + {224/√28}
= 4√7 – 3√7 + [{8×√28×√28}/√28]
= √7 + 16/√7
= 17√7
Que-3: {4√18/√12} – {8√75/√32} + {9√2/√3}
Sol: {4√18/√12} – {8√75/√32} + {9√2/√3}
= [{4√(2*3*3)}/{√2*2*3}] – [{8√5*5*3}/{4*4*2}] + [{9√2}/√3]
= [{4√3}/√2] – 5√6 + [{9√2}/√3]
= 2√6 – 5√6 + 3√6
= √6 (2-5+3)
= √6 ×0
= 0.
Que-4: Rationalize the denominators of
(a) 1/{4-√3}
(b) 2/{√5+√3}
(c) 1/{2√5−√3}
(d) {√3+√2}/{√3−√2}
Sol: (a) 1/{4-√3}
[1/{4-√3}] × [{4+√3}/{4+√3}]
{4+√3}/[4²-√3²]
{4+√3}/[16-3]
{4+√3}/13
(b) 2/{√5+√3}
[2{√5-√3}]/[{√5+√3}{√5-√3}]
[2{√5-√3}]/(5-3)
[2{√5-√3}]/2
{√5-√3}.
(c) 1/{2√5−√3}
[1{2√5+√3}] / [{2√5−√3}{2√5+√3}]
{2√5−√3} / [(2√5)²−(√3)²]
{2√5−√3} / [20-3]
{2√5−√3}/17
(d) {√3+√2}/{√3−√2}
[{√3+√2}{√3+√2}] / [{√3-√2}{√3+√2}]
{√3+√2}² / [(√3)²-(√2)²]
{3+2+(2√3×√2)} / (3-2)
5+2√6.
Que-5: Rationalize the denominator and simplify :
(i) [{4+√5}/{4−√5}] + [{4−√5}/{4+√5}]
(ii) [3/{5−√3}] + [2/{5+√3}]
Sol: (i) [{4+√5}/{4−√5}] + [{4−√5}/{4+√5}]
= [{4+√5}²+{4−√5}²] / [{4+√5}{4−√5}]
= {16+5+8√5+16+5-8√5}/{16-5}
= 42/11
(ii) [3/{5−√3}] + [2/{5+√3}]
= [3{5+√3} + 2{5−√3}] / [{5−√3}{5+√3}]
= {15+3√3+10-2√3} / {(5)²-(√3)²}
= {25+√3}/{25-3}
= {25+√3}/22.
Que-6: Find the values of a and b if
(i) {3+√2}/{3−√2} = a+b√2
(ii) {5+2√3}/{7+4√3} = a+b√3
(iii) [{√7−1}/{√7+1}] − [{√7+1}/{√7−1}] = a+b√7
Sol: (i) (3 + √2)/(3 – √2) = a + b√2
From rationalization
(3 + √2)² / (3 – √2)(3 + √2) = a + b√2
(9 + 2 + 6√2) / (3)² – (√2)² = a + b√2
(11 + 6√2) / (9 – 2) = a + b√2
(11 + 6√2) / 7 = a + b√2
(11/7) + (6/7)√2 = a + b√2
From Comparing
a = 11/7 , b = 6/7
(ii) (5 + 2√3) / (7 + 4√3) = a + b√3
Considering LHS,
LHS: (5 + 2√3) / (7 + 4√3)
(5 + 2√3) / (7 + 4√3) = (5 + 2√3) / (7 + 4√3) × (7 – 4√3) / (7 – 4√3)
= (5 + 2√3)(7 – 4√3) / (7 + 4√3)(7 – 4√3)
By using algebraic identity,
(a² – b²) = (a – b)(a + b)
(7 + 4√3)(7 – 4√3) = (7)² – (4√3)²
= 49 – 16(3)
= 49 – 48
= 1
So, (5 + 2√3)(7 – 4√3) / (7 + 4√3)(7 – 4√3) = (5 + 2√3)(7 – 4√3) / (1)
= (5 + 2√3)(7 – 4√3)
By multiplicative and distributive property,
(5 + 2√3)(7 – 4√3) = 5(7) – 5(4√3) + 7(2√3) – 2√3(4√3)
= 35 – 20√3 + 14√3 – 8(3)
= 35 – 24 – 20√3 + 14√3
= 11 – 6√3
So, 11 – 6√3 = a + b√3
By comparing,
a = 11 and b = -6
(iii) [{√7−1}/{√7+1}] − [{√7+1}/{√7−1}] = a+b√7
Taking L.H.S.
[{√7−1}²-{√7+1}²] / [[{√7+1}{√7-1}]]
[{7+1-2√7}-{7+1+2√7}] / {7-1}
{8-2√7-8-2√7}/6
(-4√7)/6
On comparing with a+b√7 we get,
a = 0 and b = – 2/3.
Que-7: Rationalize the denominator of 1/{√2+√3+√5}.
Sol: [1/{√2+√3+√3}] = [1/{(√2+√3)+√5}]
Rationalizing denominator
= {(√2+√3)−(√5)} / [{(√2+√3)+(√5)}{(√2+√3)-(√5)}]
= {√2+√3−√5} / {(√2+√3)²−(√5)²}
= {√2+√3−√5} / {2+3+2√6-5}
= {√2+√3−√5} / 2√6
Again rationalizing,
= {√2+√3−√5}√6 / (2√6×√6) = {√12+√18−√30}/{2×6}
= [√(4×3)+√(9×2)−√30]/12
= {2√3+3√2−√30}/12.
Que-8: Taking √2 = 1.414 and √3 = 1.732, find without using tables or long division, the value of
(a) 1/{3−√2}
(b) 2/{√3−√2}
Sol: (a) {1/3−√2} = {1/(3+√2)}/{(3−√2)(3+√2)
(Rationalizing the denominator)
= {3+√2}/{(3)²−(√2)²}
= {3+√2}/{9−2}
= {3+√2}/7
= (3+1.414)/7
= 4.414/7 = 0.631.
(b) {2/(√3−√2)} = {2(√3+√2)} / (√3−√2)(√3+√2)
(Rationalizing the denominator)
= {2(√3+√2)} / {(√3)²−(√2)²}
= {2(√3+√2)} / {3−2}
= {2(√3+√2)}
= 2 (1.732 + 1.414) = 2 x 3.146
= 6.292
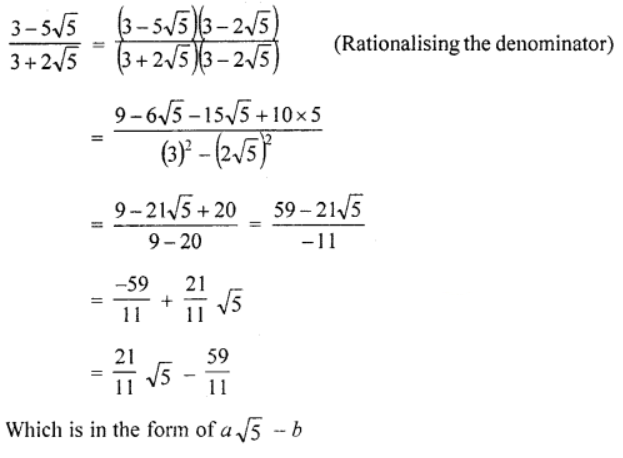
Que-9: Express {3−5√5}/{3+2√5} in the form (a√5 – b) where a and b are simple fractions.
Sol:
Que-10: Prove that [1{√2−1}] + [2/{√3+1}] = √2+√3.
Sol:
![Que-10: Prove that [1{√2−1}] + [2/{√3+1}] = √2+√3.](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/9-4-300x234.png)
Que-11: Simplify:
[6√2/{√3+√6}] − [4√3/{√6+√2}] + [2√6/{√2+√3}]
Sol:
![Que-11: Simplify: [6√2/{√3+√6}] − [4√3/{√6+√2}] + [2√6/{√2+√3}]](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/11-4-240x300.png)
Que-12: Simplify:
(i) [6/{2√3−√6}] + [√6/{√3+√2}] − [4√3/{√6−√2}]
(ii) [7√3/{√10+√3}] − [2√5/{√6+√5}] − [3√2/{√15+√32}]
Sol: (i) [6/{2√3−√6}] + [√6/{√3+√2}] − [4√3/{√6−√2}]
![(i) [6/{2√3−√6}] + [√6/{√3+√2}] − [4√3/{√6−√2}]](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/12-5-253x300.png)
Now from (i), (ii), (iii)
(2√3 + √6) + (3√2 – 2√3) – (3√2 + √6)
= 2√3 + √6 + 3√2 – 2√2 – 3√2 – √6 = 0.
(ii) [7√3/{√10+√3}] − [2√5/{√6+√5}] − [3√2/{√15+√32}]
![(ii) [7√3/{√10+√3}] − [2√5/{√6+√5}] − [3√2/{√15+√32}]](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/12i-192x300.png)
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
(√30 – 3) – (2√30 – 10) – (-√30 + 6)
= √30 – 3 – 27√30 + 10 + √30 – 6
= 10 – 9 = 1.
Que-13: If x = 2 + √3, find the value of x² + 1/x².
Sol: Given that
x = 2 + √3
1/x = 1/2 + √3
= 1 × (2 – √3)/(2 + √3) (2 – √3)
= (2 – √3)/(2² – √3²)
= (2 – √3)/4 – 3
= (2 – √3)
Therefore ,
x² = (2 + √3)
= (2)² + (√3)² + 2 × 2 × √3
= 4 + 3 + 4√3
= 7 + 4√3
1/x² = (2 – √3)²
= (2)² + (√3)² – 2 × 2 × √3
= 4 + 3 – 4√3
= 7 – 4√3
x² + 1/x²
= (7 + 4√3) + (7 – 4√3)
= 7 + 4√3 + 7 – 4√3
= 7 + 7 + 4√3 – 4√3
= 14
Que-14: If x = √2 + 1, find the value of x² + 1/x².
Sol: x = √2 + 1
⇒ x² = ( √2 + 1 )²
⇒ x² = 2 + 1 + 2√2
⇒ x² = 3 + 2√2
⇒ 1 / x = 1 / ( √2 + 1 )
⇒ 1/x = ( √2 – 1 ) / ( √2 + 1 )( √2 – 1 )
⇒ 1/x = ( √2 – 1 ) / ( √2² – 1 )
⇒ 1 / x = ( √2 – 1 ) / ( 2 – 1 )
⇒ 1 / x = ( √2 – 1 ) / 1 = √2 – 1
⇒ 1/x² = ( √2 – 1 )²
⇒ 1/x² = 2 + 1 – 2√2
⇒ 1/x² = 3 – 2√2
Adding x² and 1/x²
⇒ x² + 1/x²
⇒ 3 + 2√2 + 3 – 2√2
⇒ 3 + 3
⇒ 6
Que-15: If x = {5−√21}/2, find the value of
(i) x + 1/x and (ii) x² + 1/x²
Sol: (i) x = (5 – √21)/2
1/x = 2/(5 -√21)
=2(5 + √21)/(5 -√21)(5 + √21)
= (5 + √21)/2
x + 1/x = (5 -√21)/2 + (5+√21)/2 = 5
x + 1/x = 5.
(ii) x² + 1/x² = (x + 1/x)² -2x.1/x
= (x + 1/x)² -2
=(5)² -2
= 23
— : End of Rational and Irrational Numbers Class 9 OP Malhotra Exe-1C ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-1 :–
Return to :– OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends