Relations and Functions Class 11 OP Malhotra Exe-2E ISC Maths Solutions Ch-2 Solutions. In this article you would learn about Algebraic Operations, Real Valued and Classification of Functions. Step by step solutions of latest textbook has been given as latest syllabus. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-11 Mathematics.

Relations and Functions Class 11 OP Malhotra Exe-2E ISC Maths Solutions Ch-2
| Board | ISC |
| Publications | S Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 11th |
| Chapter-2 | Relations and Functions |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Exe-2(E) | Algebraic Operations, Real Valued and Classification of Functions. |
Exercise- 2E
Relations and Functions Class 11 OP Malhotra Exe-2E Solution.
Que-1: Let f,g:R→R be defined respectively by f(x) = x+1,g(x) = 2x-3,find (i) f+g (ii) f-g (iii) f/g
Sol: Since f , g : R → R is defined as
f (x) = x + 1, g (x) = 2x – 3
Hence,
(i) (f + g)(x) = f (x) + g (x)
= ( x + 1) + (2x – 3) .
= 3x – 2
Therefore, (f + g)(x) = 3x – 2
Now,
(ii) (f – g)(x) = f (x) – g (x)
= ( x + 1) – (2x – 3)
= x + 1 – 2x + 3
= – x + 4
Therefore, (f – g)(x) = – x + 4
Now,
(iii) f (g/x) = f (x)/g (x), g (x) ≠ 0, x ∈ R
= (x + 1) / (2x – 3), 2x – 3, x ≠ 3/2
Therefore,
f (g/x) = (x + 1)/(2x – 3), 2x – 3, x ≠ 3/2
Que-2: If f(x) = √x and g(x) = x be two function defined over the domain R∪{0}, find the value of
(i) (f+g)(x) (ii) (f-g)(x) (iii) (fg)(x) (iv) (f/g)(x)
Sol: (i) (f+g)(x)
(f+g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)
(f+g)(x) = √x + x
(ii) (f-g)(x)
(f-g)(x) = f(x) – g(x)
(f-g)(x) = √x – x
(iii) (fg)(x)
⇒ (fg)(x) = f(x)g(x)
⇒ (fg)(x) = (√x)(x)
⇒ f(x)g(x)= x √x
(iv) (f/g)(x)
⇒ (f/g)(x) = f(x)/g(x)
⇒ (f/g)(x) = (√x)/(x)
⇒ f(x)/g(x)= 1/√x
Que-3: If the function f : N → N is defined by f (x) = √x, then find {f(25)}/{f(16)+f(1)}.
Sol: Given a function f : N → N defined by f(x) = √x
f (25) = √25 = 5; f (16) = √16 = 4 ; f (1) = √1 = 1
Thus {f(25)}/{f(16)+f(1)}
= 5/(4+1) = 1
Que-4: If f(x) = (x³/2) – (x²/2) + x -16, find f(1/2).
Sol: f(x) = (x³/2) – (x²/2) + x -16
f(x) = ((1/2)³/2) – ((1/2)²/2) + x -16
= (1/16) – (1/8) + (1/2) – 16
= (1-2+8-256)/16
= -249/16.
Que-5: If f (x) = 7x4 – 2x³ – 8x – 5, find f (- 1).
Sol: Given f (x) = 7x4 – 2x³ – 8x – 5
∴ f (- 1) = 7 (- 1)4 – 2 (- 1)³ – 8 (- 1) – 5
= 7 + 2 + 8 – 5 = 12.
Que-6: The function ‘t’ which maps temperature in degree celsius into temperature in degree Fahrenheit is defined by t(C) = (9C/5) + 32, find : (i) t(0) (ii) t(28) (iii) t(-10) (iv) the value of C, when t(C) = 212.
Sol: The given function of temperature is t (C) = 9C/5 + 32
(i) t (0) = = (9 x 0) / 5 + 32 = 0 + 32 = 32
(ii) t (28) = (9 x 28) / 5 + 32
= (252 + 160) / 5
= 412 / 5 = 82.4
(iii) t (- 10) = 9 x (- 10) + 32
= 9 x (- 2) + 32
= – 18 + 32 = 14
(iv) It is given that
t (C) = 212
⇒ 9C/5 + 32 = 212
⇒ 9C/5 = 212 – 32
⇒ C = (180 x 5)/9
= 100
Thus, the value of ‘t’, when t (C) = 212 is 100
Que-7: If f(x) = x², find {f(1.1) – f(1)}/{1.1-1}
Sol: It is given that
f (x) = x²
⇒ f(1.1) = (1.1)² and f (1) = 12
Hence substituting the above values, we get
⇒[f (1.1) – f (1)] / (1.1 – 1)
= [(1.1)² – (1)²] / (1.1 – 1)
= (1.21 – 1) / 0.1
= 0.21 / 0.1
[f (1.1) – f (1)] / (1.1 – 1) = 2.1
Que-8: Let f = {(1,1), (2,3), (0,-1), (-1,-3)} be a function from Z to Z defined by f(x) = ax+b for some integers a and b, Determine a, b.
Sol: Given: f = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (0, – 1), (- 1, – 3)} is a function from Z to Z where Z is the set of integers such that f(x) = ax + b for some integers a and b.
As (1, 1) ∈ f ⇒ x = 1 and y = 1 will satisfy the equation y = f(x) = ax + b ⇒ a + b = 1
Similarly (2, 3) ∈ f ⇒ x = 2 and y = 3 will satisfy the equation y = f(x) = ax + b ⇒ 2a + b = 3
Now by solving the equations a + b = 1 and 2a + b = 3, we get a = 2 and b = – 1
Que-9: If f (x) = {3x−2 when x ≤ 0}
f(x) = {x+1 when x>0}, f (-1) and f (0).
Sol: Given f (x) = {3x−2 when x ≤ 0}
f(x) = {x+1 when x>0}
When x = 1 < 0 ∴ f (x) = 3x – 2
⇒ f (-1 ) = – 3 – 2 = – 5
When x = 0 ∴ f (0)
= 3 x 0 – 2 = – 2
Que-10: If f (x) = log (1−x)/(1+x), show that f (a) + f (b) = f(a+b)/(1+ab).
Sol:
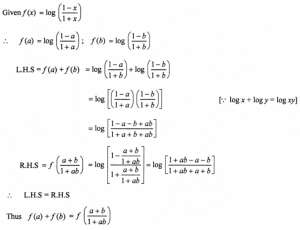
Que-11: If f (x) = 2x√(1-x²), then show that f (sin(x/2)) = sin x.
Sol: Given f (x) = 2√(1-x²)
∴ f(sin(x/2)) = 2sin(x/2)√{1-sin²(x/2)}
= 2sin(x/2)cos(x/2) = sinx
Que-12: If f(x) = cos (log x), then prove that f(1/x)⋅f(1/y) − (1/2)[f(x/y) + f(xy)] = 0
Sol: Given f(x) = cos (logx)
![Que-12: If f(x) = cos (log x), then prove that f(1/x)⋅f(1/y) − (1/2)[f(x/y) + f(xy)] = 0](https://icsehelp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/12-2-300x106.png)
= cos(logx) cos(logy) – (1/2) [cos(logx) cos(logy) + sin(logx) sin(logy) + cos(logx) cos(logy) – sin(logx) sin(logy)]
[∴ cos(-θ) = cosθ; cos(A±B) = cosA.cosB ± sinA.sinB]
= cos(logx) cos(logy) – (1/2) [2cos(logx) cos(logy)]
= 0 = RHS.
Que-13: If y = f (x) = (5x+3)/(4x−5), then show that f (y) = x.
Sol: Given = y = f (x) = (5x+3)/(4x−5)
⇒ y (4x – 5) = 5x + 3
⇒ 4xy – 5y = 5x + 3
⇒ 4xy – 5x = 5y + 3
⇒ x (4y – 5) = 5y + 3
⇒ x = (5x+3)/(4x−5) = f (y) [using (1)]
Que-14: If f(x) = (x-1)/(x+1), then show that.
(i) f(1/x) = -f(x) (ii) f(-1/x) = -1/f(x)
Sol: Given : f(x) = (x-1)/(x+1)
(i) f(1/x) = -f(x)
f(1/x) = {(1/x)-1}/{(1/x)+1}
= (1+x)/(1-x)
= -f(x)
Hence, f(1/x) = -f(x)
(ii) f(-1/x) = -1/f(x)
f(-1/x) = {(1/x)-1}/{(1/x)+1}
= -{(1/x)-1} / -{(1/x)+1}
= (1+x)/(1-x)
= 1/{(1-x)/(1+x)}
= 1/{(x-1)/(x+1)}
= -1/f(x)
Hence, f(-1/x) = -1/f(x)
Que-15: If f(x) = x³ – (1/x³), find the value of f(x) + f(1/x)
Sol: Since f(x) = x³ – (1/x³)
f(1/x) = (1/x³) – 1/(1/x³)
= (1/x³) – x³
Hence, f(x) + f(1x)
= x³ – (1/x³) + (1/x³) – x³
= 0
Que-16: If f (x) = x² + kx + 1, for all x and if it is an even function, find k.
Sol: Given f (x) = x² + kx + 1
since f (x) be an even function
∴ f (- x) = f (x)
⇒ (-x)² – kx + 1 = x² + kx + 1
⇒ x² – kx + 1 = x² + kx + 1
⇒ 2kx = 0
⇒ k = 0
Que-17: If f(x) = x³ – (k – 2) x² + 2x, for all x and if it is an odd function, find k.
Sol: Given f (x) = x³ – (k – 2) x² + 2x
∴ f(-x) = (-x)³ – (k – 2) (-x)² – 2x = -x³ – (k – 2) x² – 2x
Since f be an odd function
∴ f(- x) = – f(x)
⇒ – x³ – (k – 2) x² – 2x = – [x³ – (k – 2) x² + 2x]
⇒ – x³ – (k – 2) x² – 2x = – x³ + (k – 2) x² – 2x
⇒ 2(k – 2) x² = 0
⇒ k – 2 = 0
⇒ k = 2.
Que-18: Is there a function f which is both even and odd ?
Sol: Given f is an even function
∴ f (- x) = f (x) ∀ x … (1)
Also f is given to be an odd function.
∴ f(- x) = – f(x) … (2)
From eqn. (1) and eqn. (2) ; we have
f(x) = – f(x) ⇒ 2 f (x) = 0 ⇒ f (x) = 0
Thus f be a zero function.
Que-19: Prove that f (x) = (1/x)log√{x+√(x²+1)} is an even function.
Sol:
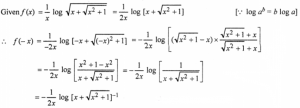
= (1/2x) log [x+√(x²+1)] = f(x)
∴ f be an even number.
–: End Relation and Functions Class 11 OP Malhotra Exe-2E ISC Math Ch-2 Solutions :–
Return to :- OP Malhotra ISC Class-11 S Chand Publication Maths Solutions
Thanks
Please share with your friends