Respiration in Plants Long Answer Biology Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-7. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-7 Respiration in Plants with Exercise-7 including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Respiration in Plants Exe-7 Long Answer Biology Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-7 | Respiration in Plants |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of D. Long Answer Type |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
D. Long Answer Type
Respiration in Plants Class-9 Biology Concise Solutions
Page 65
Question 1.
Distinguish between the following pairs:
(a) Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
(b) Respiration and combustion
(c) Stomata and lenticels
(d) Photosynthesis and respiration
(e) Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals
Answer:
(a) Difference between Aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
|---|---|
| Proceeds in the presence of oxygen. | Proceeds without using oxygen. |
| Complete breakdown of glucose. | Incomplete breakdown of glucose. |
| End products are carbon dioxide and water. | End-products are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. |
| Energy liberated in large quantity (38 ATP) from one mole of glucose. | Energy liberated in small quantity (2 ATP) from one mole of glucose. |
| Occurs normally throughout life. | Occurs temporarily for short periods. |
(b) Difference between Respiration and combustion:
| Respiration | Combustion |
|---|---|
| Cellular process | Non-cellular process |
| Occurs at body temperature | Occurs at high temperature (at ignition point) |
| Occurs in a series of chemical steps | Occurs in a single step |
| Carried out by enzymes | Carried out by heat |
| Biochemical process | Physico-chemical process |
| Energy released as ATP and heat | Energy released as heat and light |
| Light energy is not produced | Light energy is produced |
(c) Difference between Stomata and lenticels:
| Stomata | Lenticel |
|---|---|
| Stomata are present in leaves and green stems. | Lenticels are present in mature stems, roots and fruits. |
| Stomata are active only during day time. | Lenticels are active both during day and night. |
| Stomata have guard cells and they can be opened and closed. | Lenticels do not have guard cells, they are always open. |
(d) Difference between Photosynthesis and respiration:
| Photosynthesis | Respiration |
|---|---|
| Occurs only in the presence of chlorophyll. | Occurs in all living cells. |
| Occurs only in presence of light. | Occurs at all times. |
| Uses carbon dioxide and water. | Uses oxygen and glucose. |
| Oxygen is released as an end product. | End product is carbon dioxide. |
| Light energy is converted into chemical energy. | Chemical energy is converted into useful energy (ATP) and heat. |
| Results in gain in weight. | Results in loss in weight. |
| Anabolic process. | Catabolic process. |
(e) Difference between Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals:
| Anaerobic respiration in plants | Anaerobic respiration in animals |
|---|---|
| It leads to formation of ethanol | It leads to formation of lactic acid |
| Little heat is released | More heat is released |
(Respiration in Plants Long Answer Class-9 ICSE)
Question 2.
How do the following structures help in respiration in plants?
(a) Lenticels _____________
(b) Stomata _____________
(c) Root hairs ____________
Answer:
(a) Lenticels help the stem to participate in respiration.
(b) Stomata help the leaves to participate in respiration.
(c) Root hairs help the roots to participate in respiration.
D. Long Answer Type
Respiration in Plants Class-9 Biology Concise Solutions
Page 66
Question 3.
How are aerobic and anaerobic respiration different in plants?
Answer:
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in plants:
| Aerobic respiration in plants |
Anaerobic respiration in plants |
| 1. Also Called oxybiotic respiration |
1. Also called anoxybiotic respiration |
| 2. Proceeds in the presence of oxygen |
2. Proceeds in the absence of oxygen |
| 3. Occurs in mitochondria |
3. Occurs in cytoplasm |
| 4. Complete breakdown of glucose |
4. Incomplete breakdown of glucose |
| 5. End-products are carbon dioxide and water |
5. End-products are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide |
| 6. Large quantity of energy is liberated (38ATP) from one mole of glucose |
6. Small quantity of energy is liberated (2ATP) from one mole of glucose |
| 7. Occurs normally throughout the life | 7. Occurs temporarily for short periods |
Question 4.
Explain why respiration is said to be the reverse of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Respiration is said to be the reverse of photosynthesis due to the following reasons:
(1) In respiration, the organic food is broken down into its inorganic compounds, i.e., CO2 and H2O, while in photosynthesis the organic food is synthesized from its inorganic components, i.e., CO2 and H2O.
(2) In respiration, CO2 is given out, while in photosynthesis CO2 is consumed.
(3) In respiration, O2 is consumed, while in photosynthesis O2 is released or evolved.
(4) In respiration, energy is liberated, while in photosynthesis energy is absorbed.
Question 5.
What is respiration? How are respiration and burning similar and how are they different?
Answer:
Oxidation of organic food particularly carbohydrates in living cells to release energy is called respiration.
Similarities between respiration and burning:
(i) Both require oxygen
(ii) Both produce energy
(iii) Both result in the formation of CO2 and water
Differences between respiration and burning:
| Respiration | Burning |
| 1. Occurs in a series of chemical steps | 1. Occurs in a single step |
| 2. Carried out by enzymes | 2. Carried out by heat |
| 3. Biochemical process | 3. Physico-chemical process |
| 4. Energy is liberated in the form of ATP and some heat | 4. Energy is liberated in the form of heat and light |
| 5. No light energy is produced | 5. Light energy is produced |
| 6. Cellular process | 6. Non-cellular process |
| 7. Occurs at body temperature | 7. Occurs at high temperature (at ignition point) |
| 8. No supply of heat energy is required | 8. Supply of heat energy is required |
| 9. The organic compound is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. | 9. The organic compound initially chars and later burns, producing a flame. |
(Respiration in Plants Long Answer Class-9 ICSE)
Question 6.
Describe one experiment each of you would perform to demonstrate the following phenomena: The germinating seeds (a) produce heat, (b) give out carbon dioxide, (c) can respire even in total absence of air.
Answer:
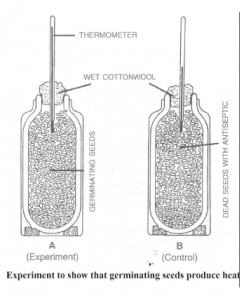
(a) Experiment demonstrating that germinating seeds produce heat.
(1) Take two thermos flasks ‘A’ and ‘B’. (2) Take about 200 bean or pea seeds and soak them in water for more than 24 hours. (3) Divide the seeds into two equal groups. Kill one group of seeds by boiling them and then, wash them with dilute formalin to prevent bacterial decay. Place the live germinating seeds in flask A and the killed one in flask B.
(4) Insert a thermometer in each of the flasks and plug their mouths with cotton wool. Note the initial reading in the thermometer. (5) After few hours, the thermometer in flask A will show a higher reading indicating that the germinating seeds produce heat. There will not be any rise in the temperature of flask B.
(b) Experiment demonstrating that germinating seeds give out carbon dioxide.
(1) Take two flasks ‘A’ and’ B’. (2) Place some wet cotton wool at the bottom of both the flasks. (3) Place some soaked seeds of pea in flask A and an equal number of boiled or dead seeds in flask B. Add some carbolic acid to flask B to prevent the growth of bacteria on dead seeds. (4) Cork the flasks and keep them undisturbed for few days.
(5) After few days, the seeds in flask A will have germinated and the seeds in flask B do not show any signs of germination. (6) The gases in each of the flasks are then tested by removing the cork and tilting the flask over a test tube containing limewater and then shaking up the test tube. (7) The expected CO2 present in flask A will turn limewater milky showing that germinating seeds give out CO2, while the gas in flask B will show no effect on limewater.
(c) Experiment demonstrating that germinating seeds can respire even in total absence of air.
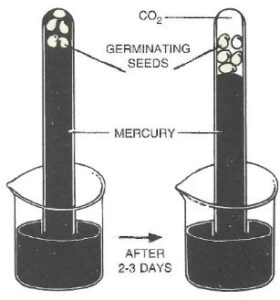
(1) Take few soaked and peeled off pea seeds and push them into the mouth of a test tube filled with mercury and inverted in a beaker of mercury. The seeds will float to the top and will be completely surrounded by mercury. (2) After few days, the level of mercury falls and the presence of some gas in the test tube can be detected. (3) Add some KOH to the test tube. The gas present in the test tube will be absorbed and the level of mercury will again rise showing that the gas was CO2. Hence, we can prove that germinating seeds respire even in the total absence of air.
Question 7.
Draw a neat and labelled, diagram showing the experimental set up (initial and final stages) to demonstrate anaerobic respiration in germinating seeds.
Answer:
Below diagram shows the experimental set up (initial and final stages) to demonstrate anaerobic respiration in germinating seeds:
— : End of Respiration in Plants D. Long Answer Class-9 ICSE Biology Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Biology Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends


