Speed of Waves Motion Numerical Class-11 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-26. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-11 Physics.
Speed of Waves Motion Numerical Class-11 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-26
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 11 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-26 | Waves Motion |
| Topics | Numericals on Speed of Waves Motion |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
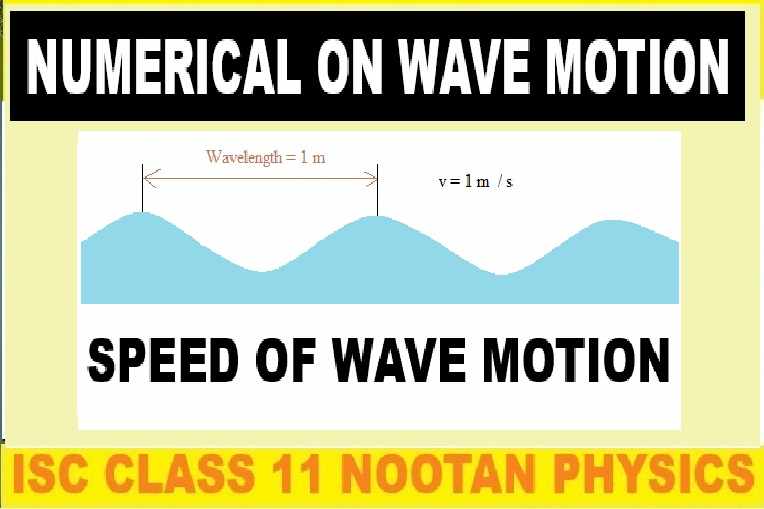
Numericals on Speed of Waves Motion
Class-11 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-26 solutions of Kumar and Mittal
Q-1: The length of a stretched string is 2 m and its mass is 8 x 10^-3 kg. If a tension of 2 kg is applied to the wire then how long will a transverse-wave take in reaching from one end of the wire to the other? (g = 9.8 m s^-2)
Ans-

Q-2: The speed (v) of transverse wave in a stretched string is is 348 m s^-1, when the tension (T) of the string is 3.6 kg-wt. Calculate the speed of the transverse wave in the same string, if the tension of the string is changed to 4.9 kg-wt.
Ans-

Q-3: The diameter of an iron wire is 1.20 mm. If the speed of the transverse wave in the wire be 50.0 m s^-1, then what is the tension in the wire ? The density of iron is 7.7 x 10^3 kg m^-3.
Ans- Suppose that the tension in the wire is T then

Q-4: In a sonometer experiment, the density of the material of the wire used is 7.5 x 10^3 kg m^-3. If the stress in the wire is 3.0 x 10^8 N m^-2 , find out the speed of transverse waves in the wire.
Ans-

Q-5: For steel the Young’s modulus of elasticity is 2.9 x 10^11 N m^-2 and density is 8 x 10^3 kg m^-3. Find the velocity of the longitudinal waves in steel.
Ans-

Q-6: The speed of sound in a liquid is 1500 m s^-1. The density of the liquid is 1.0 × 10^3 kg m^-3. Determine the bulk modulus of elasticity of the liquid.
Ans-
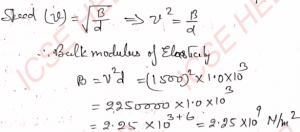
Q-7: The longitudinal waves starting from a ship returns from the bottom of the sea to the ship after 2.64 seconds. If the bulk modulus of water be 220 kg-mm^-2 and the density 1.1 x 10^3 kg m^-3, then calculate the depth of the sea. (g = 9.8 N kg^-1).
Ans-

Q-8: At 10^5 N m^-2 atmospheric pressure the density of air is 1.29 kg m^-3. If γ = 1.41 for air, then calculate the speed of sound in air.
Ans- The speed of sound
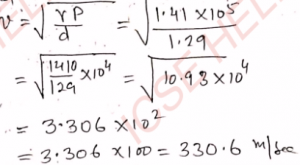
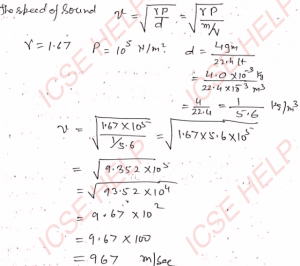
Q-9: At normal temperature and pressure, 1 mole (= 4 g) of helium encloses a volume of 22.4 litre. Determine the speed of sound in helium. (For helium, γ = 1.67, 1 atmospheric pressure = 10^5 N/m²)
Ans-
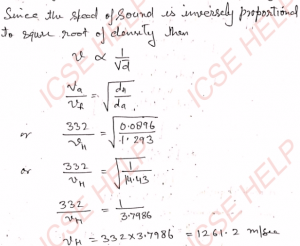
Q-10: The mass of one litre of hydrogen is 0.0896 g and that of one litre of air is 1.293 g. The speed of sound in air is 332 m s^-1. Calculate the speed of sound in hydrogen.
Ans-
Q-11: The speed of sound in air is 332 m s^-1. If the volumes of nitrogen (molecular mass 28) and oxygen (molecular mass 32) in air are in the ratio 4: 1, then find out the speed of sound in oxygen.
Ans-


Q-12: If the speed of sound in helium at 0°C be 960 m s^-1 then what will be the speed of sound in hydrogen at the same temperature? The values of γ for He and H2 are respectively 1.67 and 1.40 and the ratio of their molecular masses is 2: 1.
Ans-

Q-13: Find the ratio of the speeds of sound in hydrogen and carbon dioxide at the same temperature. The values of γ for H₂ and CO2 are 1.4 and 1.3 respectively, and the ratio of their molecular masses is 1:22.
Ans-

Q-14: Find the ratio of the speeds of sound in hydrogen and oxygen at the same temperature. Their molecular masses are 2 and 32 respectively.
Ans-
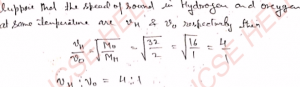
Q-15: If the density of air at normal temperature and pressure be 1.293 kg m^-3 the density of mercury at 0°C be 13.6 x 10^3 kg m^-3, Cp = 0.2417 and Cv = 0.1715, then calculate the speed of sound in air at 100°C. (g = 9.8 N kg^-1)
Ans- we know that

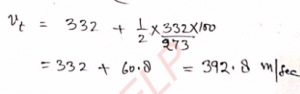
Q-16: The speed of sound in air at 15°C is 340 m s^-1. What are the speeds at 0°C and at 30°C ?
Ans-

Q-17: Calculate the difference in the speed of sounds in air at -3°C, 60 cm pressure of mercury and 30°C, 75 cm pressure of mercury. The speed of sound in air at 0°C is 332 m s^-1.
Ans-
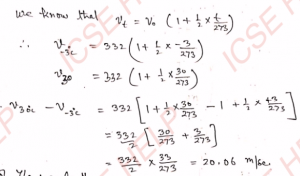
Q-18: The wavelength of a sound note of frequency 500 Hz at 15°C in air is 0.68 m. The density of air at 0°C is 1.29 kg m^-3. Calculate γ for air. The atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 10^5 N m^-2.
Ans-
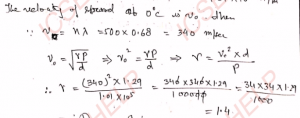
Q-19: Calculate the ratio of the speeds of sound at 0°C and 1092 K in air.
Ans-

Q-20: If the speed of sound at 0°C be 330 m s^-1, then at what temperature will its value become 495 m s^-1 ?
Ans-

Q-21: At what temperature will the speed of sound be double of its value at 27°C ?
Ans-

Q-22: At what temperature will the speed of sound in air be 1.8 times the speed of sound in air at 20°C ?
Ans-

Q-23: At what temperature will the speed of sound in air become 1.2 times the speed of sound at 0°C ?
Ans-

Q-24: Calculate the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is double its velocity at 0°C.
Ans-

Q-25: At what temperature will the speed of sound in hydrogen be the same as in oxygen at 100°C ? Densities of oxygen and hydrogen are in the ratio 16:1.
Ans-

— : End of Progressive Travelling Waves Numerical Class-11 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-25 :–
Return to : – – Nootan Solutions for ISC Physics Class-11
Thanks
Please share with your friends