Srijan Class-9 Diversity in Living Organism ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-7. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check-1, to 7, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type ( including True False), Application / Skill ( Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Solutions of Srijan Class-9 Diversity in Living Organism ICSE Biology Ch-7
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-7 | Diversity in Living Organism |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check-1, to 7, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 1 (Page 75)
Answer These Question :
Question 1: Write the categories in classification in hierarchical sequence.
Answer : “Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in a decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and vice versa.”
Question 2: Who proposed five-kingdom classification ?
Answer : R.H. Whittaker proposed the five-kingdom classification in 1969. This classification was based upon certain characters like mode of nutrition, thallus organization, cell structure, phylogenetic relationships and reproduction. This form of kingdom classification includes five kingdoms Monera , Protista , Fungi, Plantae and Animalia .
Question 3: Give three characteristics each of Monera and Protista.
Answer :
. Monera consists of cyanobacteria, archaebacteria and eubacteria whereas Protista consists of protozoans, algae and molds. Some of the organisms in Monera and Protista are heterotrophs whereas some of them are autotrophs. The main difference between Monera and Protista is that unicellular prokaryotes are classified into kingdom Monera whereas unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes, which are not either fungi, plants or animals, are classified into kingdom Protista.
Question 4: Give two example of Fungi.
Answer : Mucor, rhizopus, mushroom
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 2 (Page 78)
Question 1: Give any two examples of bryophytes.
Answer : Two examples of bryophytes are (i) Funaria (ii) Riccia
Question 2: Mention two general characteristics of spermatophytes.
Answer : Two general characteristics of spermatophytes.
(i) The plant has root, stem, leaves and seeds.
(ii) They have chlorophyll hence photosynthesis.
Question 3: Give two differences between angiosperms and gymnosperms.
Answer : write any 2
| Angiosperms | Gymnosperms |
| A seed is produced by flowering plants and is enclosed within an ovary | A seed is produced by non-flowering plants and are unenclosed or naked. |
| The lifecycle of these plants are seasonal | These plants are evergreen |
| Has triploid tissue | Has haploid tissue |
| Leaves are flat in shape | Leaves are scalelike and needle-like in shape |
| Hardwood type | Softwood type |
| Reproduction rely on animals | Reproduction rely on wind |
| Reproductive system present in flowers (unisexual or bisexual) | Reproductive system present in cones and are unisexual |
Question 4: Give three differences between monocots and dicots.
Answer :
| Parameter of Comparison | Monocot | Dicot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants with seeds having only one cotyledon are called monocots. | Plants with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots. |
| Leaves | The veins of the leaf of monocot seed plants are parallel. | The veins of the leaf of dicot seed plants have a net-like structure. |
| Flowers | Flowers are present in multiples of three. | Flowers are present in multiples of four or five. |
| Stem | Vascular bundles are scattered. | Vascular bundles are in a ring-like pattern. |
| Roots | Fibrous root-like structure. | Tap root-like structure. |
| Examples | Corn, wheat, rice, sugarcane, banana tree | Mango, orange, tomato, beans, pea |
Question 5: Name the Amphibians of the plant kingdom.
Answer : Bryophytes
Question 6: Name the plants with naked seeds.
Answer : Gymnosperms.
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 3 (Page 80)
A. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
1. The fine pores in the body wall of sponges are called ……………
2. ………………… cells are found only in sponges.
3. Blind sac body plan is found in ……………..
Answer :
1.Ostia
2. Choanocytes
3. Phylum Coelenterate
B. Give functions of the following
1. Osculum : The osculum is an excretory structure in the living sponge, a large opening to the outside through which the current of water exits after passing through the spongocoel.
2. Choanocytes : They create a flow of water and the second is to capture food items as they pass by these cells.
3. Cinoblasts : Cinoblastshelps in catching the prey and in defence.
4. Gastrovascular cavity : Its opening serves both mouth and anus.
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 4 (Page 81)
Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1: Why are flatworms regarded as triploblastic?
Answer : Flatworms have 3 tissue layers, compared to the 2 layers in sponges and cnidarians (jellyfishes, anemones and corals). They also have only one opening for food to enter and waste to leave, like the sponges and cnidarians. This is called a “sac” body plan
Question 2: Why does a tapeworm lack an alimentary canal?
Answer : They usually live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates as adults, and often in the bodies of other species of animals as juveniles. Tapeworms are unique in lacking an alimentary canal. This means that nutrients must be absorbed through the tegument.
Question 3: Name the cell which forms excretory organs of flatworms.
Answer : The excretory organs of flatworms (Platyhelminthes) are flame cells and function like a kidney, removing waste materials.
Question 4: What is a hermaphrodite animal?
Answer : a hermaphrodite animal is an organism that has both male and female reproductive organs. This is common in invertebrates, such as worms, slugs or snails.
Question 5: Name any two diseases caused by roundworms in man.
Answer : If you have a roundworm infection of your intestines (ascariasis), you may not have symptoms. You may see live worms in your poop though. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Cough.
- Disturbed sleep.
- Fever.
- Restlessness.
- Severe abdominal (stomach) pain.
- Vomiting.
- Wheezing.
- Malnutrition.
- Growth delay.
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 5 (Page 82)
Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1: Why are annelids called to have true coelom?
Answer : Do annelids have a true Coelom? Annelids show the presence of a true coelom, derived from embryonic mesoderm and protostomy. Hence, they are the most advanced worms. A well-developed and complete digestive system is present in earthworms (oligochaetes) with a mouth, muscular pharynx, esophagus, crop, and gizzard being present
Question 2: Why are earthworms called farmers’ friends?
Answer : Why earthworms are called a farmer’s friend? Earthworms are said to be always the friend of farmers. The reason is that earthworm increases the fertility of soil by increasing the amount of air and water that gets into the soil, facilitating aeration and increasing drainage
Question 3: What does the name Arthropoda indicate?
Answer : There are four main classes of arthropods. They are crustacea, myriapoda, insecta, and arachnida. Crustacea : These organisms have five or more pairs of legs, two antennae, and no wings. Common examples include crabs, and lobsters. Myriapoda: Have many pairs of legs, one antennae, and no wings
Question 4: Name the aerial arthropods.
Answer : Insect are called aerial arthopods
Question 5: What is exoskeleton?
Answer : a rigid external covering for the body in some invertebrate animals, especially arthropods, providing both support and protection
Question 6: What is haemocoel?
Answer : The body cavity is reduced in some animals and filled with blood, thus it is called haemocoel. The animals belonging to phylum Arthropoda and Mollusca have haemocoel. Haemocoel is the fluid found in the circulatory system of phylum anthropoda. The haemocoel can act as a hydrostatic skeleton. It functions as the circulatory system in insects like grasshoppers.
Question 7: What is the function of trachea?
Answer : The trachea (or windpipe) is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx (or voice box) to the bronchi of the lungs. It is an integral part of the body’s airway and has the vital function of providing air flow to and from the lungs for respiration . The trachea begins at the inferior end of the larynx in the base of the neck
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 6 (Page 83)
Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1: Name the group of animals that have external shell.
Answer : Mollusca
Question 2: Name the divisions of body in a mollusc.
Answer : The visceral mass, or visceropallium, is the soft, nonmuscular metabolic region of the mollusc. It contains the body organs. Mantle and mantle cavity. The mantle cavity, a fold in the mantle
Question 3: Name the surfaces of echinoderms.
Answer : In echinoderms, the side of the body where the mouth is located is referred to as the oral surface. The side of the body that is opposite from the mouth is called the aboral surface. In sea stars, the oral surface is on the underside of the body.
Question 4: Which respiratory pigment is found in molluscs?
Answer : Haemocyanin is the pigment found in the blood of molluscs, crustaceans and arthropods. The active centre of haemocyanin contains two molecules of copper which bind to the single oxygen molecule. The blue colour of this pigment is due to the presence of copper which is blue in colour
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 7 (Page 83)
State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statement by changing the incorrect word/words only.
Question 1: Notochord is replaced by vertebral column in chordates
Answer : False
Question 2: Eggs of frog are larger than those of birds.
Answer : False
Question 3: Mammals are warm-blooded animals.
Answer : True
Question 4: Feathers help in swimming.
Answer : False
Question 5: External ears are found in snakes.
Answer : False
Question 6: Cawed digits and pentadactyl limbs are found in lizards.
Answer : True
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 90)
Ch-7 Diversity in Living Organism ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
1. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) The branch of biology concerned with classification is called ……………
(b) …………….. is the only flying mammal.
(c) Prokaryotic organisms include ……………. and ………….
(d) Cell wall of fungal cells is composed of ……………
(e) Excretory organs of Platyhelminthes are ……………….
(f) Nephridia are the excretory organs of phylum ……………..
Answer :
(a) Taxonomy
(b) Bat
(c) Bacteria, Archaea
(d) Chitin
(e) Flame cells
(f) Annelida
2. Name the following:
(a) Unicellular eukaryotic organism.
(b) Plants that produce seeds having single cotyledon.
(c) Plants with naked seeds.
(d) Plants in which reproductive organs are in the form of cones.
(e) The unit of classification.
(f) The topmost category in classification
(g) Stinging cells of coelenterates.
Answer :
(a) Protista
(b) Monocots
(c) Gymnosperms
(d) Gymnosperms
(e) Species
(f) Kingdom
(g) Nematocysts
3. On the basis of characteristics given below, name phylum or class for each:
(a) Unicellular, microscopic animals.
(b) Animals having tube-within-tube organisation.
(c) Animals having porous body and cellular organisation.
(d) Diploblastic animals having sac-like body organisation and stinging cells.
(e) Animals with soft, cylindrical unsegmented body with a false body cavity.
(f) Diploblastic body organisation with gastrovascular cavity.
(g) Presence of vertebral column, hairy skin and Oviparous in nature.
Answer :
(a) Phylum-Protozoa
(b) Phylum-Annelida
(c) Phylum-Porifera
(d) Phylum-Cnidaria
(e) Phylum-Nemathelminths
(f) Phylum-Cnidaria
(g) Phylum-Chordata
Class- Mammalia
4. Give one example for each of the following:
(a) An aquatic mammal
(b) A burrowing reptile
(c) A flying mammal
(d) A flightless bird
(e) A freshwater sponge
(f) A cartilaginous fish
(g) A burrowing annelid
(h) A freshwater coelenterate
Answer :
(a) Whale
(b) Snakes
(c) Bat
(Ostrich
(e) Spongilla lacustris
(f) Torpedo
(g) Earthworm
(h) Hydra
5. Match the columns.
Column A
(a) Cobra
(b) Peacock
(c) Earthworm
(d) Euglena
(e) Frog
(f) Spongilla
Column B
(i) Protozoa
(ii) Amphibia
(iii) Porifera
(iv) Annelida
(v) Reptilia
(vi) Aves
Answer :
(a) Cobra (v) Reptilia
(b) Peacock (vi) Aves
(c) Earthworm (iv) Annelida
(d) Euglena (i) Protozoa
(e) Frog (ii) Amphibia
(f) Spongilla (iii) Porifera
6. Mention the main functions of each of the following structures:
(a) Tube feet : The tube feet are used for locomotion, attachment to the substratum and for catching the pay.
(b) Feathers : Feathers provides insulation body temperature.
(c) Setae : Earthworm to attch to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion.
(d) Mammary glands : Process milk-producing mammary gland for the nourishment of young ones.
Diversity in Living Organism ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
B. Short Answer Type Questions (Page 91)
Question 1: Give one reason for each of the following characters:
(a) Birds have streamlined body.
(b) Frogs possess web in hind legs.
(c) Fishes have paired fins.
(d) Snakes lack limbs.
(e) Poriferas have perforated bodywall.
(f) Lizards have clawed pentadactyl limbs.
Answer :
(a) Birds have streamlined body- reduce friction of air
(b) Frogs possess web in hind legs-for swimming
(c) Fishes have paired fins- for swimming
(d) Snakes lack limbs to live in hole
(e) Poriferas have perforated bodywall for continue water flow
(f) Lizards have clawed pentadactyl limbs to stick on wal
Question 2: Write two similarities between the following pairs
(a) Pisces and Amphibia
(b) Snakes and lizards
(c) Birds and mammals
(d) Amphibians and reptiles
Answer :
(a) Pisces and Amphibia- external fertilisation and low parental care
(b) Snakes and lizards- creeper and close vascular system
(c) Birds and mammals- warm blooded and 4 chambers
(d) Amphibians and reptiles–closed blood system and has lungs
Question 3: Name the animal groups which exhibit the following characteristics:
(a) Body segmented with jointed appendages and compound eyes.–Arthopoda
(b) Three pairs of walking legs and two pairs of wings–insect
(c) Body soft, covered by mantle and a calcareous shell–mollusca
(d) Body cylindrical covered with scales and belly plate, with a vertebral column but no limbs.–pisces
(e) Soft cylindrical body with a true coelom and nephridia-mollusca
C. Long Answer Type Questions (Page 91)
Diversity in Living Organism ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1: Which classes of vertebrates are called amniotes?
Answer : Amniotes are the group of animals who lay the eggs which have embryonic membranes i.e. chorion, allantoise, amnion.
The classes that come under this group are reptiles, aves, and mammals. The amnion encloses the embryo in a fluid that serves as a cushion and provides an aqueous environment in which it can grow.
Question 2: Name the five kingdoms of five-kingdom classification.
Answer :
R H Whittaker came up with the concept of the five-kingdom classification.
The five-kingdom classification of living organisms included the following kingdoms:
Kingdom Monera
The bacteria are categorized underneath the Kingdom Monera.
They possess the following important features:
- Bacteria occur everywhere and they are microscopic in nature.
- They possess a cell wall and are prokaryotic.
- The cell wall is formed of amino acids and polysaccharides.
- Bacteria can be heterotrophic and autotrophic.
- The heterotrophic bacteria can be parasitic or saprophytic. The autotrophic bacteria can be chemosynthetic or photosynthetic.
Kingdom Protista
Features of Protista:- Protista has the following important features:
- They are unicellular and eukaryotic organisms.
- Some of them have cilia or flagella for mobility.
- Sexual reproduction is by a process of cell fusion and zygote formation.
Kingdom Fungi
The kingdom fungi include moulds, mushroom, yeast etc. They show a variety of applications in domestic as well as commercial purposes.
Features of Kingdom Fungi
- The fungi are filamentous, excluding yeast (single-celled).
- Their figure comprises slender, long thread-like constructions called hyphae. The web of hyphae is called mycelium.
- Some of the hyphae are unbroken tubes which are jam-packed with multinucleated cytoplasm. Such hyphae are labelled Coenocytic hyphae.
- The other type of hyphae has cross-walls or septae.
- The cell wall of fungi is composed of polysaccharides and chitin.
- Most of the fungi are saprophytes and are heterotrophic.
- Some of the fungi also survive as symbionts. Some are parasites. Some of the symbiont fungi live in association with algae, like lichens. Some symbiont fungi live in association with roots of higher plants, as mycorrhiza.
Kingdom Plantae
Features of Kingdom Plantae
- The kingdom Plantae is filled with all eukaryotes which have chloroplast.
- Most of them are autotrophic in nature, but some are heterotrophic as well.
- The Cell wall mainly comprises cellulose.
- Plants have two distinct phases in their lifecycle. These phases alternate with each other. The diploid saprophytic and the haploid gametophytic phase. The lengths of the diploid and haploid phases vary among dissimilar groups of plants. Alternation of Generation is what this phenomenon is called.
Kingdom Animalia
Features of Kingdom Animalia
- All multicellular eukaryotes which are heterotrophs and lack cell wall are set aside under this kingdom.
- The animals are directly or indirectly dependent on plants for food. Their mode of nutrition is holozoic. Holozoic nutrition encompasses ingestion of food and then the use of an internal cavity for digestion of food.
- Many of the animals are adept for locomotion.
- They reproduce by sexual mode of reproduction.
Question 3: Give two salient features of kingdom fungi.
Answer : Features of Kingdom Fungi
- The fungi are filamentous, excluding yeast (single-celled).
- Their figure comprises slender, long thread-like constructions called hyphae. The web of hyphae is called mycelium.
- Some of the hyphae are unbroken tubes which are jam-packed with multinucleated cytoplasm. Such hyphae are labelled Coenocytic hyphae.
- The other type of hyphae has cross-walls or septae.
- The cell wall of fungi is composed of polysaccharides and chitin.
- Most of the fungi are saprophytes and are heterotrophic.
- Some of the fungi also survive as symbionts. Some are parasites. Some of the symbiont fungi live in association with algae, like lichens. Some symbiont fungi live in association with roots of higher plants, as mycorrhiza.
Question 4: Mention two characteristics of kingdom Protista
Answer : Protista has the following important features:
- They are unicellular and eukaryotic organisms.
- Some of them have cilia or flagella for mobility.
- Sexual reproduction is by a process of cell fusion and zygote formation.
Question 5 : Distinguish between bryophytes and pteridophytes (any two differences.)
Answer :
| Character | Bryophytes | Pteridophytes |
| Definition | Bryophytes consist of a leafy or thalloid plant body. | Pteridophytes consist of roots, stems, and leaves. |
| Vascular tissue | Vascular tissue is absent. | Vascular tissue is present. |
| Vasculature system | Bryophytes lack in vasculature system, which means xylem and phloem absent. | Pteridophytes has proper vasculature, which means xylem and phloem is present. |
| Roots | Plants do not have roots, instead, rhizoids are present and help in anchoring. | Roots are present in these plants. |
| Stems or leaves | It does not have any true stems or leaves. | In this plant true stem and leaves are present. |
Question 6: Why are bryophytes known as amphibians of plant kingdom?
Answer : Bryophytes are known as amphibians of the plant kingdom because these plants live in soil but they need water for asexual reproduction. They were non-vascular plants. Asexual reproduction is the main method of reproduction in bryophytes. It occurs through the production of spores. Though bryophytes live on the land, they require water for fertilization. The sperms of bryophytes swim through water to the eggs with the help of their flagella. So bryophytes are called amphibians of the plant kingdom. They include Mosses, liverworts and hornwort
Question 7: What are amnion, chorion yolk sac and allantois?
Answer : Vertebrates have four different extraembryonic membranes: the chorion, the allantois, the yolk sac, and the amnion. In vertebrates that lay eggs, the chorion is the outermost membrane and lines the inside of the eggshell. The allantois is a sac-like extraembryonic membrane that removes waste from the embryo.
Question 8 : What are viviparous animals? Which group of animals are viviparous?
Answer : Fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals all have viviparous members, while none of the group are exclusively viviparous. Developing the young viviparously appears to be a derived trait from oviparous animals.
Question 9: Give five characteristics of class Amphibia.
Answer :
- These can live both on land and in water.
- They are ectothermic animals, found in a warm environment.
- Their body is divided into head and trunk. …
- The skin is smooth and rough without any scales, but with glands that make it moist.
- They have no paired fins.
D. Multiple Choice Questions (Page 91)
Diversity in Living Organism ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1: Which of the following is not a mammal?
(a) Echidna
(b) Dolphin
(c) Turtle
(d) Tiger
Answer : (c) Turtle
Question 2: Which one of the following is a true fish
(a) Silver fish
(b) Devil fish
(c) Jelly fish
(d) Dog fish
Answer : (b) Devil fish
Question 3: Coral forming organisms belong to the phylum
(a) Porifera
(b) Coelenterate
(c) Mollusca
(d) Annelida
Answer : (b) Coelenterate
Question 4: Which of the following is a diploblastic animal?
(a) Hydra
(b) Earthworm
(c) Cockroach
(d) Fila
Answer : (a) Hydra
E Application/Skill-based Question (Page 91)
Diversity in Living Organism ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1: Study the given diagrams and answer the following question:

(a) ldentify figures A to F.
Answer : A. Dryopteris
B. Funiria
C. Pinus
D. Spirogyra
E. Euglena
F. Rhizopus
(b) Which one of them is unicellular and eukaryotic organism?
Answer : E- Euglina is unicellular and eukaryotic organism
(c) Which of them shows (i) Heterotrophic nutrition (ii) Mixotrophic nutrition?
Answer : (i) Heterotrophic nutrition : Rhizopus
(ii) Mixotrophic nutrition : Euglena
(d) Which one of them is nonvascular embryophyte ?
Answer : Funiria
(e) In which of them, xylem lacks vessels while phloem is devoid of companion cells?
Answer : Dryopteris
(f) Which of them is commonly called (i) Bread Mould (ii) Male Shield Fern?
Answer :
(i) Bread Mould : Rhizopus
(ii) Male Shield Fern : Pryopteris
Question 2:
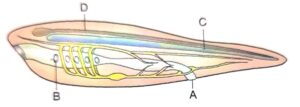
(a) ldentify the given diagram.
Answer : A hypothetical chordates showing main chordate
(b) Label A, B, C and D.
Answer :
A. Anus
B. Heart
C. Notochord
D. Dorsal hollow nerve chord
(c) Name the phylum in which notochord is present.
Answer : Phylum Chordata
(d) Name the subphylum in which notochord is present at some stage in life.
Answer : Cephalochordate
(e) Give an example from the subphylum Vertebrata in which animals have cartilaginous exoskeleton.
Answer : Fish
Question 3: Identify the following giving one reason for each.
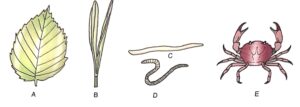
(a) The drawing showing a monocotyledonous leaf.
Answer : Option B showing a monocotyledonous leaf
(b) The drawing showing an annelid.
Answer : Option D Showing an annelid
(c) The drawing showing an arthropod.
Answer : Option E showing an arthropod.
Thanks