The Nervous System and Sense Organs Class-10 Long Answer Questions Goyal Brothers ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-10. We Provide Solutions of long Answer Questions Questions of Exercise- 10 The Nervous System and Sense Organs. All solutions are given as council prescribe guideline for next upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Ch-10 The Nervous System and Sense Organs Long Answer Questions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brothers publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Dr. K.K. Aggrawal |
| Chapter-10 | The Nervous System and Sense Organs |
| Topics | Solutions of Long Answer Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
D. LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Ch-10 The Nervous System and Sense Organs Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-151)
Question 1. With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the questions that follow:
(i) What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
(ii) What is the shape of the lens during (1) near vision (2) distant vision?
(iii) Name the two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
(iv) Name the cells of the retina and their respective pigments which get activated (1) in the dark (2) in light.
Answer :
(i) The power of accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus on distant as well as nearby objects by changing the focal length of lens. This focal length of eyes is changed with the help of ciliary muscles
(ii) The shape of the lens during (1) near vision is flattened (2) distant vision is rounded or more convex.
(iii) Ciliary muscles and suspensory ligament
(iv) The pigment protein in rods is called rhodopsin, while the pigment protein in cones is called iodopsin. A single rod can contain up to 100 million molecules of rhodopsin in its outer segment discs
Question 2. With reference to the human ear, answer the questions that follow:
(i) Give the technical term for the structure found in the inner ear.
(ii) Name the three small bones present in the middle ear. What is the biological term for them collectively?
(iii) Name the part of the ear associated with (1) static balance (2) hearing (3) dynamic balance.
(iv) Name the nerve, which transmits messages from the ear to the brain.
Answer :
(i) The inner ear consists of tubes and passages called Labyrinth, which consists of two structures namely bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth (the technical name)
Question 3. State whether the following actions are voluntary actions, simple actions or conditioned reflex:
(i) Blinking
(ii) Cleaning the table
(iii) Playing on the keyboard
(iv) Salivating when food is put in the mouth
Answer :
| Blinking | Simple reflex |
| Cleaning the table | Voluntary action |
| Playing on the keyboard | Conditioned reflex |
| Salivating when food is put in the mouth | Simple reflex |
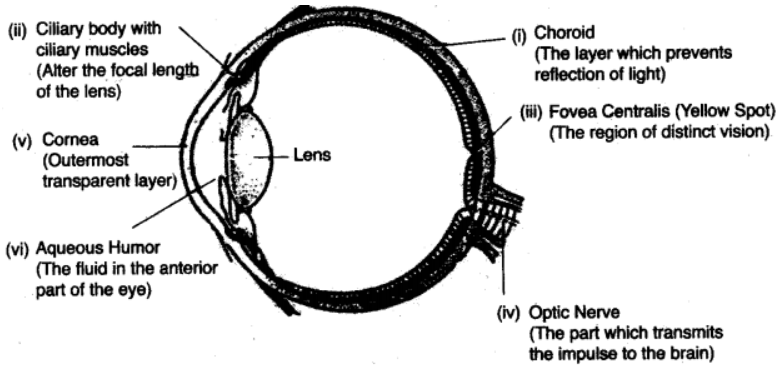
Question 4. Draw a diagram of the human eye as seen in a vertical section and label the part which suits the following functions / descriptions :
(i) The layer which prevents reflection of light.
(ii) The structure that alters the focal length of the lens.
(iii) The region of distinct vision.
(iv) The part which transmits the impulse to the brain.
(v) The outermost transparent layer in front of the eye lens.
(vi) The fluid present in the anterior part of the eye in front of the eye lens.
Answer :
Question 5. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong:
(i) Cyton, Photon, Axon, Dendron.
(ii) Haemoglobin, Glucagon, lodopsin, Rhodopsin
Answer :
(i) Photon
(ii) Glucagon
Question 6. Answer the following :
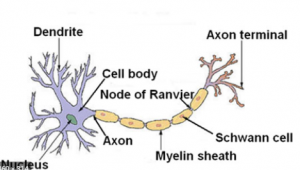
(i) Draw a well-labelled diagram of a neuron showing the following parts Perikaryon, Dendrites, Axon, Node of Ranvier and Myelin sheath.
(ii) State the function of sensory neuron and a motor neuron.
(iii) What is a nerve made up of?
(iv) What is the function of ear ossicles?
Answer :
(i)

(ii) Sensory cells carry afferent impulses to a central interneuron, which makes contact with a motor neuron. The motor neuron carries efferent impulses to the effector, which produces the respons
(iii) Nerves are made up of bundles of axons that work together to facilitate communication between the CNS and PNS. It’s important to note that “peripheral nerve” actually refers to the PNS. Axon bundles are called “tracts” in the CNS. When nerves are damaged or aren’t signaling properly, a neurological disorder can result
(iv) These three ossicles connect the tympanic membrane to the inner ear allowing for the transmission of sound waves. The main function of the middle ear is to transmit the sound waves from the external environment to the inner ea
Question 7. Draw a well labelled diagram of a an name the following parts:
(a) Node of Ranvier
(b) Nissil granules
(c) Cyton
Answer :
Question 8.
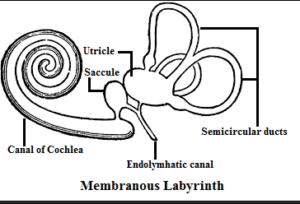
(i) Draw a well-labelled diagram of the membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear
(ii) Based on the diagram drawn above in (i) give a suitable term for each of the following descriptions
(a) The sensory cells that helps in hearing.
(b) The part that is responsible for static balance of the body.
(c) The membrane covered opening that connects the middle ear to the inner ear.
(d) The fluid present in the middle chamber of cochlea.
(e) The structure that maintain dynamic equilibrium of the body.
Answer :
(i)
(ii)
(a) The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing
(b) The vestibular system is the sensory apparatus of the inner ear that helps the body maintain its postural equilibrium
(c) Crossing the middle-ear cavity is the short ossicular chain formed by three tiny bones that link the tympanic membrane with the oval window and inner ear. From the outside inward they are the malleus (hammer), the incus (anvil), and the stapes (stirrup).
(d) The cochlea is filled with a watery liquid, the endolymph, which moves in response to the vibrations coming from the middle ear via the oval window.
(e) Ears perform two main functions, hearing and equilibrium maintenance. The organ of Corti (Cochlea) is responsible for hearing function. Maculae (Saccule and Utricle) are responsible for static equilibrium. Cristae (semicircular canals) are responsible for dynamic equilibrium.
— : End of The Nervous System and Sense Organs Long Answer Questions Class-10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions :–
Return to :- ICSE Biology for Class 10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions


