Transpiration Class-10 Long and Structured Questions Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-5. We Provide Solutions of long Answer Question and Structured Questions of Exercise-5 Transpiration. All solutions are given as council prescribe guideline for next upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Ch-5 Transpiration Class-10 Long and Structured Questions
( Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions )
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brothers publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Dr. K.K. Aggrawal |
| Chapter-5 | Transpiration |
| Topics | Solutions of Long Answer Questions and Structured Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
D. LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Ch-5 Transpiration Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-70)
Question 1. Name the three types of transpiration. Which of these accounts for maximum transpiration in the plant?
Answer : The three major types of transpiration are: (1) Stomatal Transpiration (2) Lenticular Transpiration and (3) Cuticular Transpiration.
Transpiration mainly takes place through surface of leaves. It is known as Foliar transpiration (more than 90%).
Question 2. Explain the potassium ion exchange theory for the stomatal transpiration.
Answer : K+Ion Concentration Theory: It is a recent theory. According to this theory, the stomatal opening and closing depends on the generation of a potassium ion gradient. ATP produced in the guard cells during photosynthesis is utilised to pump the potassium ions of the adjacent cells into the guard cells
Question 3. What is an anti-transpirant? Name some anti transpirants.
Answer : Sometimes, there is blockage of the stomatal pores which reduce the water loss from the plants. These chemicals are known as anti-transpirants. There are two common examples of anti-transpirants are abscisic acid (ABA) and Phenyl mercuric acetate (PMA)
Question 4. List five adaptations found in desert plants to reduce transpiration.
Answer :
| Adaptation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Leaves reduced to spines | Reduces the surface area for transpiration |
| Reduced number of stomata | Reduces the transpiration rate |
| Waxy leaf cuticle | Impermeable to water, which stops evaporation |
Question 5. Define wilting. Why do some plants show wilting of their leaves at noon even in well watered soil?
Answer : During noon the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of absorption of water by roots. Due to the excessive transpiration the cells of leaves lose their turgidity and wilt.
Question 6. How does the rate of transpiration get affected by:
(a) Wind velocity (b) Intensity of light (c) Humidity
Answer :
(a) Wind velocity- Directly
(b) Intensity of light – Directly
(c) Humidity – Inversely
Question 7. Mention four disadvantages of transpiration to the plant.
Answer : (i) Some plants will die due to excessive water loss by transpiration.
(ii) Due to the high rate of transpiration plants suffer from loss of turgidity.
E. STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
Ch-5 Transpiration Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-71)
Question 1. The given figure represents the vertical section of a leaf. So,
(i) Name the structure shown in the leaf section.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1 to 5.
(iii) How many leaf veins have been shown in this section?
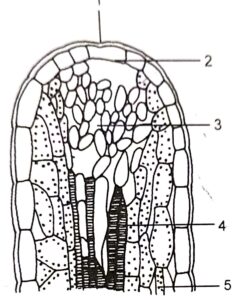
Answer :
(i) ………………
(ii) 1 – Upper Epidermis; 2 -Guard cell ; 3 – Phloem; 4 – Xylem ; 5 – Palisade layer / chloroplast
(ii) The two arrows show the release of oxygen and water vapours during the daytime and carbon dioxide and very less amount of oxygen is released during the night.
(iii) One vein has been shown in this section.
Question 2. Given below is an apparatus used to study a particular process in plants. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
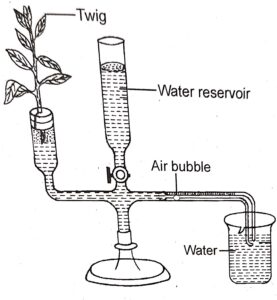
(i) Name the apparatus.
(ii) Mention one limitation of this apparatus
(iii) Which phenomenon Is studied with the help of this apparatus.
(iv) What is the function of the part marked ‘reservoir?
(v) What is the role of the air bubble in the experiment?
Answer :
(i) Ganong’s Potometer.
(ii) Any changes in the outside air temperature may affect the position of the air bubble in the capillary tube.
(iii) Transpiration.
(iv) Reservoir helps in bringing back the bubble to its original position. This can be done by releasing some water into the capillary tube by opening the stop-cock.
(v) The rate of water uptake can be calculated by timing the movement of air bubble over a fixed distance on the scale.
Question 3. Given below is an experimental set up to study a particular process :
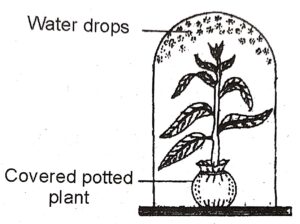
(i) Name the process being studied.
(ii) Explain the process named in (0) above.
(iii) Why is the pot covered with a plastic sheet?
(iv) Mention one way in which this process is beneficial to the plants.
(v) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
Answer :
(i) Transpiration.
(ii) ‘Loss of water as water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is called as transpiration’.
(iii) Covering the pot with a plastic sheet would prevent the escape of water vapour from the pot.
(iv) Transpiration helps in the ascent of sap by producing a suction force acting from the top of a plant.
(v) A similar empty plastic sheet with its mouth tied, with no potted plant kept in sunlight will show no drops of water.
Question 4. The diagram given below represents a structure found in a leaf. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
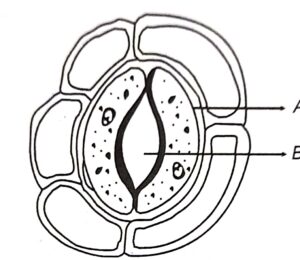
(i) Name the parts labelled A and B.
(ii) What is the biological term for the above structure?
(iii) What is the function of the part labelled A?
(iv) Mention two structural features of A, which help in the function mentioned in (ii) above.
(v) Where is this structure likely to be found in a leaf?
(vi) How does the above structure help the plant ?
(vii) How many other cells are found surrounding this structure as seen in the diagram ?
Answer :
(i) Part A = Guard Cells. Part B = Stoma.
(ii) Biological term for the above structure is stomata.
(iii) Part labelled A, i.e., guard cells control the opening and dosing of stomata.
(iv) 1. Guard cells are structurally bean shaped.
2. Wall of guard cells are differently thick. It has inner wall facing towards the stomatal pore is thick and outer wall is thin. By changing the turgidity and flaccidity, guard cells control the opening and closing of stomata.
(v) This structure is more likely to be found on the lower epidermis of the leaves.
(vi) Plants absorb a large amount of water from the soil but only a fraction of.it is used by plants and most of this absorbed water is lost from the aerial parts of the plant in the form of water vapour. It is called transpiration.
(vii) There are five (5) other cells surrounding this structure.
Question 5. The figure given below represents an experimental set up with a weighing machine to demonstrate particular process in plant. The experimental set up was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
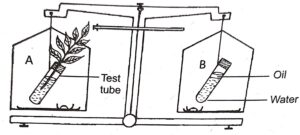
(i) Name the process intended for study.
(ii) Define the above mentioned process.
(iii) What is observed when the weight of the test tube (A & B) is taken before and after the experiment? Give reasons to justify your observation in A and B.
(iv) What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental set up?
Answer :
(i) The process that intended for study by this experiment is transpiration.
(ii) Transpiration is the process in which water is lost in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
(iii) After the experiment, we observe test tube A is raised up i.e., a loss of weight. In test tube B, the weight remains unchanged.
Reason : In test tube A, loses weight due to the plant transpires and loses water. In B there is no plant so there is no transpiration and the oil on the surface prevents direct evaporation and so weight remains unchanged.
(iv) As a control experiment.
Question 6. The diagram of an apparatus given below demonstrates a paniadar process in plants. Study the same and answer the Questions that follow.
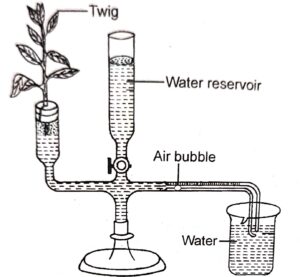
(i) Name the apparatus.
(ii) Which phenomenon is demonstrated, by this apparatus
(iii) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (ii) above.
(iv) State two limitations of using this apparatus.
(v) What is the importance of the air bubble in, the experiment ?
(vi) Name the structures in a plant through which the above process takes place.
Answer :
(i) Ganong’s potometer
(ii) Transpiration
(iii) The process in which water is given out in the form of vapour through the aerial parts of the plant.
(iv) 1. The small twig can not remain alive for a long time.
2. Introducing a single air bubble is practically very difficult.
(v) The movement of the air bubble shows the amount of water transpired by the twig in a given time.
(vi) 1. Cuticle 2. Stomata 3. Lenticel
— : End of Transpiration Class-10 Long and Structured Questions Goyal Brothers Solutions :–
Return to :- ICSE Biology for Class 10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks