Uniform Circular Motion Class 10 ICSE Physics Notes Chapter-1 Force. In this article you would learn about Centripetal and Centrifugal Force with examples. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Physics.
Uniform Circular Motion Class 10 ICSE Physics Notes Chapter-1 Force
Uniform Circular Motion: Movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed, where the velocity is constantly changing direction
Speed is Uniform But Velocity is Non Uniform
At any point the direction of motion is along the tangent drawn at the point of circular path.
Difference between Uniform Circular Motion and Uniform Linear Motion
- Uniform linear motion involves constant speed and direction along a straight path,
- uniform circular motion involves constant speed but changing direction along a circular path.
A force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed towards the center around which the body is moving.
Examples of Centripetal Force
- A Merry-go-round.
- Turning in a car
- Planet Earth.
- Electron revolve around Nucleus
- Moon moves around the Sun
Centrifugal Force
a force, assumed by observer which appears to act on a body moving in a circular path and is directed away from the center around which the body is moving.
Example of Centrifugal Force
- Weight of an object at the poles and on the equator.
- A bike making a turn.
- Vehicle driving around a curve.
- Equatorial railway.
Example of a Merry-go-Round
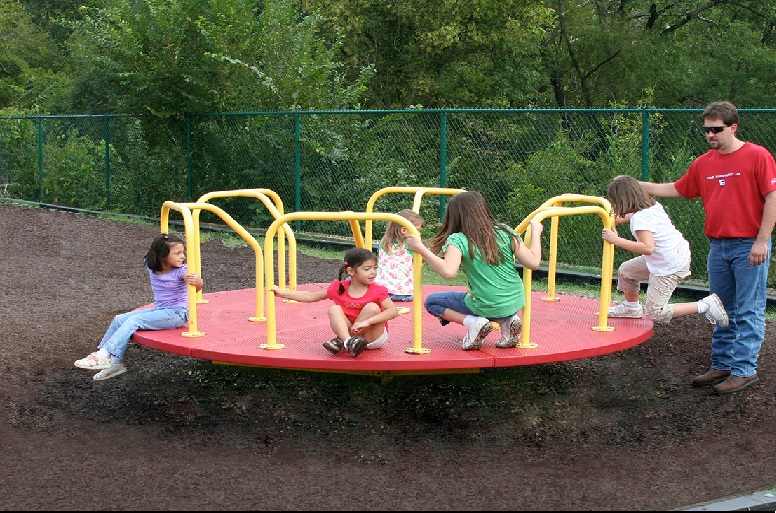

When a kid sits in a merry-go-round and it starts to rotate, the force that pulls the kid toward is the centrifugal force. This force works towards the outward and pulls the object towards the outward too
Differences Between Centripetal Force and Centrifugal Force
| Centripetal Force | Centrifugal Force |
| Its direction is towards the center of curvature. | Its direction is away from the center of curvature. |
| It is observed from the inertial frame of the reference. | It is observed from the non-inertial frame of reference. |
| Its force is towards the axis of rotation. | Its force is outward of the axis of rotation. |
| It is considered a real force. | It is considered a pseudo-force. |
–: End of Uniform Circular Motion Class 10 ICSE Physics Notes Chapter-1 Force :–
Please share with your friends if helpful
Return to :
- Concise Selina Physics Solutions for ICSE Class 10.
- Goyal Brothers Prakashan Physics Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks