Water Exe-3C Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-3. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-3 Water with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Water Exe-3C Structured Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-3 | Water |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of (Soft and hard Water) Exercise – 3C Structured/Application/Skill Answer |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
Exercise – 3C Structured/Application/Skill Answer Type
Water Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-55
Question 1.
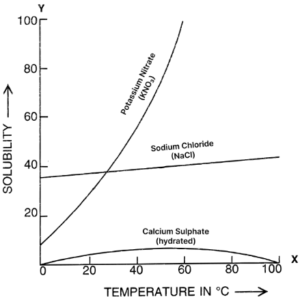
The following figure shows the solubility curves of NaCl, KNO3 and hydrated calcium sulphate.

(a) Identify and label the curves with the salt it represents.
(b) State the factors on which the solubility depends.
(c) Solubility of which salt(s) shows :
(i) Endothermic process
(ii) Exothermic process?
Answer:
(a) The labelled curves are shown below:
(b) Solubility of a solid in a solvent depends on the following factors:
- Size of solute particles — The smaller the size of the solute particles, the greater is its total surface area exposed to the solvent. Therefore, greater is the solubility of that solute.
- Stirring — This brings more of the solvent in contact with the solute and thus increases the rate of formation of solution.
- Temperature — The solubility of a gas in a liquid always decreases with rise in temperature. But the solubility of most solids in water usually increases with rise in temperature.
In case of NaCl, solubility increases only a little with increase in temperature.
In case of KNO3, solubility increases considerably with increase in temperature.
In case of calcium sulphate, solubility decreases (after attaining a certain temperature) with further rise in temperature.
(c)
(i) In an endothermic process, the solubility of a solute increases with an increase in temperature.
For example: solubility of KNO3 increases with rise in temperature and solubility of NaCl increases only a little with increase in temperature.
(ii) In an exothermic process, the solubility increases on lowering the temperature.
For example: solubility of calcium sulphate in water decreases on increasing the temperature.
— : End of Water Exe-3C Structured Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends