Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Physics Solutions Chapter-2. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exercise-2(A), MCQs-2(A), Numericals-2(A), Exercise-2(B), MCQ-2(B), Numericals-2(B), Exercise-2(C) and MCQs-2(C) , Numericals-2(C) Questions of Exercise-2 Work Energy and Power ICSE . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-2 | Work Energy and Power |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-2(A), MCQs-2(A), Numericals-2(A), Exe-2(B), MCQ-2(B), Numericals-2(B), Exe-2(C) and MCQs-2(C) , Numericals-2(C) |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Physics Solutions Chapter-2
-: Select Exercise :-
Exe-2(A), MCQs-2(A), Numericals-2(A),
Exe-2(B), MCQ-2(B), Numericals-2(B), Exe-2(C) and MCQs-2(C) , Numericals-2(C)
Exe -2 (A) Work Energy and Power
Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Physics
Page 27
Question 1
Define work. When is work said to be done by a force?
Answer 1
Work is said to be done only when the force applied on a body makes the body move. It is a scalar quantity.
Question 2
How is the work done by a force measured when (i) force is in direction of displacement, (ii) force is at an angle to the direction of displacement?
Answer 2
(i) When force is in direction of displacement, then work done , W = FxS
(ii) When force is at an angle to the direction of displacement, then work done, W= F S cos
Question 3
A force F acts on a body and displaces it by a distance S in a direction at an angle with the direction of force. (a) Write the expression for the work done by the force. (b) What should be the angle between force and displacement so that the work done is (i) zero, (ii) maximum?
Answer 3
(a) When force is at an angle to the direction of displacement, then work done, W= F S cos
(b)
(i)For zero work done, the angle between force and displacement should be 90o as cos 90o=0
W =FScos90o= FSx0=0
(ii)For maximum work done, the angle between force and displacement should be 0o as cos0o=1
Hence, W=FScos 0o=FS
Question 4
A body is acted upon by a force. State two conditions when the work done is zero.
Answer 4
Two conditions when the work done is zero are:
(i)When there is no displacement (S=0) and,
(ii)When the displacement is normal to the direction of the force ( =90o).
Question 5 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
State the condition when the work done by a force is (i) positive, (ii) negative. Explain with the help of examples.
Answer 5
(i) If the displacement of the body is in the direction of force, then work done is positive.
Hence, W= F x S
For example: A coolie does work on the load when he raises it up against the force of gravity. The force exerted by coolie (=mg) and displacement, both are in upward direction.
(ii)If the displacement of the body is in the direction opposite to the force, then work done is negative.
Hence, W =- F x S
For example: When a body moves on a surface, the force of friction between the body and the surface is in direction opposite to the motion of the body and so the work done by the force of friction is negative.
Question 6
A body is moved in a direction opposite to the direction of force acting on it. State whether the work is done by the force or work is done against the force.
Answer 6
Work is done against the force.
Question 7
When a body moves in a circular path, how much work is done by the body? Give reason.
(Hint: The body is acted upon by the centripetal force).
Answer 7
When a body moves in a circular path, no work is done since the force on the body is directed towards the centre of circular path (the body is acted upon by the centripetal force), while the displacement at all instants is along the tangent to the circular path, i.e., normal to the direction of force.
Question 8 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
A satellite revolves around the earth in a circular orbit. What is the work done by the satellite? Give reason.
Answer 8
Work done by the force of gravity (which provides the centripetal force) is zero as the force of gravity acting on the satellite is normal to the displacement of the satellite.
Question 9
State whether work is done or not by writing yes or no, in the following cases?
(a) A man pushes a wall.
(b) A coolie stands with a box on his head for 15 min.
(c) A boy climbs up 20 stairs.
Answer 9
Work is done only in case of a boy climbing up a stair case.
Question 10
A coolie X Carrying a load on his head climbs up a slope and another coolie Y carrying the identical load on his head move the same distance on a frictionless horizontal platform. Who does more work? Explain the reason.
Answer 10
Energy is the capacity to do work and work done is equal to energy spent. Coolie X carrying a load up a slope will do more work as this works involve a change in potential energy, kinetic energy and loss of energy due to friction. Work done in carrying the load in horizontal frictionless surface does not involve change in potential energy and work done by the friction is also zero.
Page 28
Question 11
The work done by a fielder when he takes a catch in a cricket match, is negative. Explain.
Answer 11
Force applied by the fielder on the ball is in opposite direction of displacement of ball. So, work done by the fielder on the ball is negative.
Question 12
Give an example when work done by the force of gravity acting on a body is zero even though the body gets displaced from its initial position.
Answer 12
When a coolie carries a load while moving on a ground, the displacement is in the horizontal direction while the force of gravity acts vertically downward. So the work done by the force of gravity is zero.
Question 13 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
What are the S.I. and C.G.S. units of work? How are they related? Establish the relationship.
Answer 13
S.I unit of work is Joule.
C.G.S unit of work is erg.
Relation between joule and erg :
1joule= 1N x 1m
But 1N =105dyne
And 1m=100 cm= 102 cm
Hence, 1 joule= 105dyne x 102cm
=107dyne x cm=107erg
Thus, 1 Joule= 107 erg
Question 14
State and define the S.I. unit of work.
Answer 14
S.I. unit of work is Joule.
1 joule of work is said to be done when a force of 1 newton displaces a body through a distance of 1 metre in its own direction.
Question 15
Express joule in terms of erg.
Answer 15
Relation between joule and erg :
1joule= 1N x 1m
But 1N =105dyne
And 1m=100 cm= 102 cm
Hence, 1 joule= 105dyne x 102cm
=107dyne x cm=107erg
Thus, 1 Joule= 107 erg
Question 16
A body of mass m falls down through a height h. Obtain an expression for the work done by the force of gravity.
Answer 16
Let a body of mass m fall down through a vertical height h either directly or through an inclined plane e.g. a hill, slope or staircase. The force of gravity on the body is F=mg acting vertically downwards and the displacement in the direction of force (i.e., vertical) is S=h. Therefore the work done by the force of gravity is
W= FS =mgh
Question 17
A boy of mass m climbs up a stairs of vertical height h.
(a) What is the work done by the boy against the force of gravity?
(b) What would have been the work done if he uses a lift in climbing the same vertical height?
Answer 17
Let a boy of mass m climb up through a vertical height h either through staircase of using a lift. The force of gravity on the boy is F=mg acting vertically downwards and the displacement in the direction opposite to force (i.e., vertical) is S=-h. Therefore the work done by the force of gravity on the boy is
W= FS =-mgh
or,the work W=mgh is done by the boy against the force of gravity.
Question 18
Define the term energy and state its S.I unit.
Answer 18
The energy of a body is its capacity to do work. Its S.I unit is Joule (J).
Question 19
What physical quantity does electron volt (eV) measure? How is it related to the S.I. unit of that quantity?
Answer 19
eV measures the energy of atomic particles.
1eV= 1.6 x 10-19J
Question 20 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
Complete the following sentence:
(a) 1 J = _____ calorie.
(b) 1 kWh = ______ J.
Answer 20
1 J = 0.24 calorie
1kWh= 3 cross times 10 to the power of 6 J
Question 21
Name the physical quantity which is measured in calorie. How is it related to the S.I unit of that quantity?
Answer 21
Calorie measures heat energy.
1calorie = 4.18 J
Question 22
Define a kilowatt hour. How is it related to joule?
Answer 22
1kWh is the energy spent (or work done) by a source of power 1kW in 1 h.
1kWh = 3.6 x 106J
Question 23
Define the term power. State its S.I. unit.
Answer 23
The rate of doing work is called power. The S.I. unit of power is watt (W).
Question 24
State two factors on which power spent by a source depends. Explain your answer with examples.
Answer 24
Power spent by a source depends on two factors:
(i) The amount of work done by the source, and
(ii) The time taken by the source to do the said work.
Example: If a coolie A takes 1 minute to lift a load to the roof of a bus, while another coolie B takes 2 minutes to lift the same load to the roof of the same bus, the work done by both the coolies is the same, but the power spent by the coolie A is twice the power spent by the coolie B because the coolie A does work at a faster rate.
Question 25
Differentiate between work and power.
Answer 25
| Work | Power |
| 1. Work done by a force is equal to the product of force and the displacement in the direction of force. | 1. Power of a source is the rate of doing work by it. |
| 2. Work done does not depend on time. | 2. Power spent depends on the time in which work is done. |
| 3. S.I unit of work is joule (J). | 3. S.I unit of power is watt (W). |
Question 26 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
Differentiate between energy and power.
Answer 26
| Energy | Power |
| 1. Energy of a body is its capacity to do work. | 1. Power of a source is the energy spent by it in 1s. |
| 2. Energy spent does not depend on time. | 2. Power spent depends on the time in which energy is spent. |
| 3. S.I unit of energy is joule (J). | 3. S.I unit of power is watt (W). |
Question 27
State and define the S.I unit of power.
Answer 27
S.I unit of power is watt (W).
If 1 joule of work is done in 1 second, the power spent is said to be 1 watt.
Question 28
(a) Name the physical quantity measured in terms of horse power.
(b) How is horse power related to the S. I. unit of power?
Answer 28
(a)Power is measured in terms of horse power.
(b) 1 horse power =746 watt
Question 29
Differentiate between watt and watt hour.
Answer 29
Watt (W) is the unit of power, while watt hour (Wh) is the unit of work, since power x time = work.
Question 30
Name the quantity which is measured in
(a) kWh
(b) kW
(c) Wh
(d) eV
Answer 30
(a) Energy is measured in kWh
(b) Power is measure in kW
(c) Energy is measured in Wh
(d) Energy is meaused in eV
Concept insight: Energy has bigger units like kWh (kilowatt hour) and Wh (watt hour). Similarly bigger unit of power is kW (kilo watt).
The energy of atomic particles is very small, and hence, it is measured in eV (electron volt).
Question 31
Is it possible that no transfer of energy takes place even when a force is applied to a body?
Answer 31
Yes, there is no transfer of energy if the body is acted upon by the force normal to the displacement.
When the body is moving in a circular path, the force is normal to its displacement and the work done is zero.
Thus, there is no transfer of energy.
MCQs-2 (A) Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10
Page 28
Question 1
One horse power is equal to:
(a) 1000 W
(b) 500 W
(c) 764 W
(d) 746 W
Answer 1
(d) 746 W
Question 2
k Wh is the unit of:
(a) Power
(b) Force
(c) Energy
(d) None of these
Answer 2
(c) The unit kWh is the unit of energy.
Numericals-2 (A) ICSE Physics Solutions Selina
Page 28
Question 1
A body, when acted upon by a force of 10 kgf, gets displaced by 0.5 m. Calculate the work done by the force, when the displacement is (i) in the direction of force, (ii) at an angle of 60o with the force, and (iii) normal to the force. (g= 10Nkg-1)
Answer 1
Force acting on the body = 10 kgf = 10 x 10 N = 100 N
Displacement, S=0.5 m
Work done= force x displacement in the direction of force
(i)W =F x S
W = 100 x 0.5= 50 J
(ii)Work = force x displacement in the direction of force
W = F x S cos
W = 100 x 0.5 cos60o
W= 100 x0.5 x 0.5(cos60o=0.5)
W=25 J
(iii)Normal to the force:
Work = force x displacement in the direction of force
W = F x S cos
W = 100 x 0.5 cos90o
W= 100 x 0.5 x 0 =0 J(cos90o =0)
Question 2
A boy of mass 40kg climbs up the stairs and reaches the roof at a height 8m in 5 s. Calculate:
(i) The force of gravity acting on the boy,
(ii)The work done by him against gravity,
(iii)The power spent by boy.
(take g= 10ms-2)
Answer 2
Mass of boy=40 kg
Vertical height moved, h=8m
Time taken, t=5s.
(i) Force of gravity on the boy
F= mg =40 x 10 =400N
(ii)While climbing, the boy has to do work against the force of gravity.
Work done by the boy in climbing= Force x distance moved in the direction of force
Or, W = F x S= 400 x 8= 3200 J
(iii) Power spent = work done/time taken = 3200/5 = 640 W.
Question 3 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
A man spends 6.4 kJ energy in displacing a body by 64 m in the direction in which he applies force, in 2.5 s. Calculate: (i) the force applied and (ii) the power spent (in H.P) by the man.
Answer 3
Work done by man= 6.4kJ
Distance moved, S=64m
(i) Work done by the man= Force x distance moved in direction of force
Work, W= F x S
6.4 x 103 =F x 64

Question 4
A weight lifter lifted a load of 200 kgf to a height of 2.5 m in 5 s. Calculate: (i) the work done, and (ii) the power developed by him. Take g =10N/kg-1.
Answer 4
Force= mg= 200 x 10=2000N
Distance, S= 2.5m
Time , t=5 s
(i)Work done, W= F S
W =2000 x 2.5m= 5000J
(ii)Power developed = work done/ time taken = 5000 J/ 5s = 1000 W.
Question 5
A machine raises a load of 750N through a height of 16m in 5 s. Calculate:
(i) the energy spent by the machine.
(ii) the power of the machine if it is 100% efficient.
Answer 5
(i)Energy spent by machine or work done= F S
Work, W =750 x 16= 12000J
(ii)Power spent= work done/time taken = 2400 W.
Page 29
Question 6
An electric heater of power 3kW is used for 10h. How much energy does it consume?
Express your answer in (i) kWh (ii) joule.
Answer 6
Energy consumed = power x time
(i)Energy = 3 kW x 10 h=30 kWh
(ii)1 kilowatt hour (kWh)= 3.6 x 106 J
30kWh = 30 x 3.6 x 106 J
= 1.08 x 108 J
Question 7 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
A water pump raises 50 litres of water through a height of 25m in 5 s. Calculate the power of the pump required.
(Take g= 10N kg-1 and density of water =1000kg m-3).
Answer 7
Volume of water= 50 L=50 x 10-3 m3
Density of water= 1000 kgm-3
Mass of water= Volume of water x density of water
= 50 x10-3 x1000= 50kg
Work done in raising 50kg water to a height of 25m against the force of gravity is:
W = mg x h= mgh
Power P= work done/ time taken = 50*10*25 J/ 5s = 2500 W.
Question 8
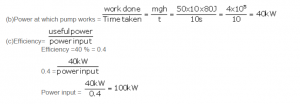
A pump is used to lift 500kg of water from a depth of 80m in 10s. Calculate:
(a) The work done by the pump,
(b) The power at which the pump works, and
(c) The power rating of the pump if its efficiency is 40%. (Take g= 10m s-2).
Answer 8
Work done in raising a 500kg mass to a height of 80m against the force of gravity is:
(a)W = mg x h= mgh
W= 500 x 10 x80 =4 x105J
Question 9
An ox can apply a maximum force of 1000N. It is taking part in a cart race and is able to pull the cart at a constant speed of 30m/s-1 while making its best effort. Calculate the power developed by the ox.
Answer 9
Given, force = 1000N, velocity=30m/s
Power, P= force x velocity
P = 1000 x 30 = 30,000W = 30kW
Question 10
The power of a motor is 40kW. At what speed can the motor raise a load of 20,000 N?
Answer 10
Power =40kW
Force= 20,000N
Power = force x velocity
![]()
Question 11
Rajan exerts a force of 150 N in pulling a cart at a constant speed of 10 m s-1. Calculate the power exerted.
Answer 11
Power exerted due to force is
P= Fv
P = 150 * 10 = 1500 W.
Question 12
A boy weighing 350 N climbs up 30 steps, each 20 cm high in 1 minute. Calculate:
(i) the work done, and
(ii) the power spent.
Answer 12
Total distance covered in 30 steps, S = 30 × 20 cm
= 600 cm
= 6 m
Work done by the boy in climbing = Force × distance moved in direction of force
Work, W = F × S
= 350 × 6
= 2100 J
Power developed = work done / time taken
= 2100 J / 60 s
= 35 W
Question 13 (Work Energy and Power ICSE Class-10)
It takes 20 s for a person A of mass 50 kg to climb up the stairs, while another person B of same mass does the same in 15 s. Compare the (i) work done and (ii) power developed by the persons A and B.
Answer 13
(i) The work done by persons A and B is independent of time. Hence both A and B will do the same amount of work. Hence,
work done by A/work done by B
1/1 = 1:1
(ii)Power developed by the person A and B is calculated as follows:A takes 20 s to climb the stairs while B takes 15 s, to do the same. Hence B does work at a much faster rate than A; more power is spent by B.
Power A/Power B = 15/20 = 3:4
Question 14
A boy of weight 40 kgf climbs up the 15 steps, each 15 cm high in 10 s and a girl of weight 20 kgf does the same in 5 s. Compare :
(i) the work done
(ii) the power developed by them.
Answer 14
(i)
W = Fs = mgh
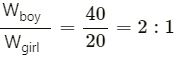
(ii)
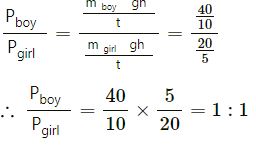
Question 15
A man raises a box of mass 50kg to a height of 2m in 20s, while another man raises the same box to the same height in 50s.
(a) Compare: (i) the work done, and (ii) the power developed by them.
(b) Calculated: (i) the work done, and (ii) the power developed by each man. Take g = 10N kg-1.
Answer 15
(a)
(i)Work done to raise the block of mass 50kg is same for both.
(ii) Power= Work done/time. As the time taken by the first man is less therefore power developed is more
(b)
(i)Work done = 50*10*2 = 1000 J
(ii) Power developed by first man=1000/20=50W
Power developed by second man=1000/50=20W
Question 16
A boy takes 3 minutes to lift a 20 litre water bucket from a 20 m deep well, while his father does it in 2 minutes. (a) Compare: (i) the work, and (ii) power developed by them. (b) How much work each does? Take density of water = 103 kg m-3 and g = 9.8 N kg-1.
Answer 16
(a)
(i) Both the people carry same weight of water to the same height. So, work done is same for both. Hence, Work = 1: 1
(ii) Power developed is
Pboy / Pfather = [(W / tboy) / (W / tfather)]
= tfather / tboy
∴ Pboy / Pfather = 2 / 3
= 2: 3
(b) Mass of water lifted by both is
mw = p × V
= 103 kg / m3 × 20 × 10-3 m3
= 20 kg
So, the work done is
W = mwgh
= 20 × 9.8 × 20
W = 3920 J
W = 3.92 kJ
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Physics Class-10
Thanks



This is very important app for icses thank to my friend who tell about the app
thanks a lot