Absorption by Root Structured Type Answer Concise Class 10 Selina Biology Solutions Concise Biology for ICSE Class 10 Ch-4. In this article you will get the solutions of Structured Type Questions as council latest syllabus. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Absorption by Root Structured Type Answer Concise Class 10 Selina Biology Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10 |
| Book | Selina Concise |
| Chapter-4 | Absorption by Roots-The Process Involved |
| Topics | Solutions of Structured Type Question |
| Session | 2025-26 |
Absorption by Root Structured Type Answer
Que-1: A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After sometime, it assumed a shape as shown below.
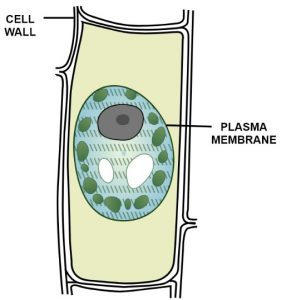
(a) Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
(b) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(c) Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
(d) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
(e) Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
Ans:
(a) Flaccid cell
(b) Plasma membrane
(c) The liquid surrounding the cell is hypertonic solution. It has higher solute concentration outside the cell than the fluids inside the cell.
(d) Cell wall
(e) The cell will become turgid as follows
Ques-2: The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow.
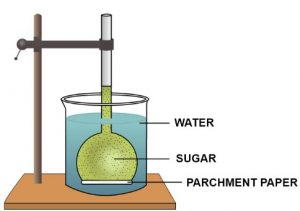
(a) Name the process.
(b) Define the above named process.
(c) What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
(d) What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
(e) Keeping in mind the root-hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to (1) concentrated sugar solution (2) parchment paper and (3) water in the beaker.
(f) Name any other material that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.(g) Mention any two advantages of the process to the plants.
Ans:
(a)Osmosis
(b) Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution or with a lower solute concentration) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution or with a higher solute concentration) through a semi permeable membrane.
(c) After an hour or so, the level of sugar solution in the thistle funnel will rise and the level of water in the beaker will drop slightly.
(d) As a control, take another thistle funnel with plain water filled in it and suspend it in another beaker also containing water. Again mark the level on its stem.
(e) The corresponding parts are mentioned below:
- Concentrated sugar solution → Cell sap (of higher concentration than that of the surrounding water) within the root hair.
- Parchment paper → Cell membrane of root hair.
- Water in the beaker → Water in soil.
(f) The other substance that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment is cellophane paper or animal bladder.
(g) Advantages of the osmosis process are —
- It controls the absorption of water by root hairs from the soil.
- It controls opening and closing of stomata during transpiration through its regulation of the turgidity of guard cells.
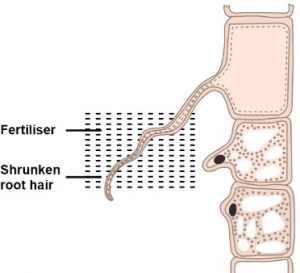
Ques-3:The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
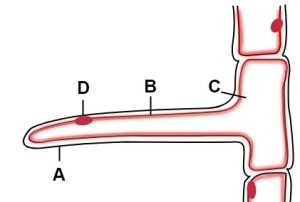
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(b) The root hair cell is in a turgid state. Name and explain the process that caused this state.
(c) Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.(d) Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
Ans: (a) The parts labelled A, B, C and D are:
- A → Cell wall
- B → Cell membrane
- C → Cytoplasm
- D → Nucleus
(b) A root hair gets turgid because of the absorption of water from the surrounding. Absorption of water by root hair is achieved by the process of Osmosis. Root hairs contain cell sap which has a higher concentration of salts as compared to the outside soil water. This causes the water from the surrounding to move in because of endosmosis and in the process the root hair gets turgid.
(c) The cell wall of a root hair is freely permeable and allows both salt and water to pass through whereas the cell membrane of a root hair is semi-permeable and does not allow large dissolved salt molecules to pass through.
(d) Below is the diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
Ques-4: Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
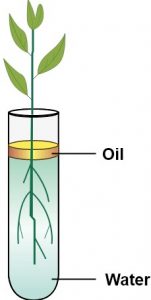
(a) Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
(b) Explain the process mentioned in (a) above
(c) Why is oil placed over water?
(d) What do we observe with regard to the level of water when this set up is placed in (1) bright sunlight (2) humid conditions (3) windy day?
(e) Mention any three adaptations found in the roots of the plant which enable them to carry out the process mentioned in (a).
Ans:
(a) The process of absorption of water by plant roots through osmosis is being studied here.
(b) Absorption of water by the root is by means of root hairs. A root hair contains cell sap which has a higher concentration of salts as compared to the outside soil water. This difference sets of osmosis and the outside soil water diffuses into the root hair. From the cell bearing root hair, water continues to pass to adjoining cells one after another to finally enter the xylem vessels. The turgidity acquired by the cells in the process also helps to push the water upwards through the xylem vessels.
(c) The surface of water is covered with oil to prevent any loss of water by evaporation.
(d) Roots absorb water and hence, the level of water in set up A falls down. Since the surface of water was covered with oil, there will be no effect of factors such as bright sunlight, humid conditions and windy day on the given set up. Hence, the level of water.
(d) Below are the observations with regard to the level of water for the different solutions:
- Bright Sunlight —If set up is placed in bright sunlight, the water level in the test tube is seen to be less when compare to its initial marking as the rate of transpiration is very high.
- Humid Conditions — If this set up is placed in humid conditions, the water level in the test tube decreases from its initial mark, but at a very slow rate as the rate of transpiration is reduced.
- Windy Day — If set up is placed in windy day the rate of transpiration highly increases thus the level of the water in the test tube is seen to decrease fast from its initial marking.
(e) Adaptations in plants to foster the process of absorption of water by plant roots:
- Large surface area provided by rootlets and root hairs.
- Root hairs contain cell sap at a higher concentration than that of the surrounding water
- Root hairs with thin walls.
Ques-5: Three cylinders of potato were carefully dried on a blotting paper and weighed. Each piece weighed 3 grams. Each one was placed in the beaker as shown below:
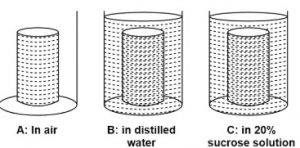
Answer the following questions:
(a) After 48 hours, which potato cylinder would be the heaviest?
(b) The movement of which substance is mainly responsible for the weight change in the potato cylinders?
(c) Name and define the process which is responsible for the movement of substance mentioned in answer(b).
(d) Write specific names of the processes which occur in beakers B and C [kinds of processes defined in answer (c)].
(e) Would there be any difference in the weight of the potato cylinder in beaker A after 48 hours? Give reason.
Ans:-
(a) After 48 hours, Cylinder B kept in distilled water will be the heaviest as distilled water will act as a hypotonic solution for Potato Cylinder. The Potato Cylinder will absorb distilled water from the beaker through the process of endosmosis and its weight will increase.
(b) Movement of water between potato cylinders and beakers is mainly responsible for the weight change in the potato cylinders.
(c) The physical process which is responsible for the movement of substance mentioned in answer (b) is Osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration to their region of lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
(d) The process that takes place in beaker B is osmosis, which is diffusion of water across the membrane of the potato slice cells. Plasmolysis occurs in beaker C as the potato shrinks due to hypotonic solution of 20% sucrose solution.
(d) Beaker B → Endosmosis
Beaker C → Exosmosis
(e) There will be no change in the weight of the potato cylinder in beaker A because it is kept in air. As there is no movement of water between potato cylinder and beaker so no significant change in the weight of the potato cylinder is observed in beaker A.
Ques-6:The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
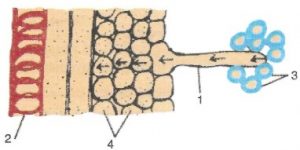
(a) The parts labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are :
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
- Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Root hair, Cortex respectively.
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Cortex, Soil particles respectively.
- Cortex, Soil particles, Xylem vessel, Root hair respectively.
(b) The process that enables the passage of water from soil into the root hair is :
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
(c) The kind of force which exists between a liquid and any surface is called as :
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Suction force
(d) The kind of force between the same kind of liquid molecules is :
- Capillary force
- Transpirational pull
- Adhesive force
- Cohesive force
(e) Sometimes exudation of water occurs from the margin of the leaves in early morning or night. It is termed as:
- Transpiration
- Bleeding
- Guttation
- Osmosis
Ans:
(a) Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
(b) Osmosis
(c) Adhesive force
(d) Cohesive force
(e) Guttation
Ques-7:Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the questions that follow.
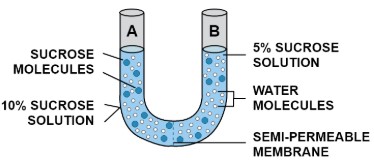
(a) What phenomenon is being studied by this setup?
(b) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (a) above.
(c) What is meant by ‘semipermeable membrane’?
(d) What will you observe in the setup after about half an hour? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans:
(a) Osmosis phenomenon is being studied by this setup.
(b) Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution or with a lower solute concentration) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution or with a higher solute concentration) through a semi permeable membrane.
(c) A semipermeable membrane is a membrane which allows the passage of molecules selectively. It allows a solvent such as water molecules to pass through it freely but prevents the passage of the solute (sugar or salt molecules in solution).
(d) Water molecules will continue to pass from 5% sucrose solution to 10% sucrose solution through the semipermeable membrane due to osmosis. This will continue till the concentration of water molecules becomes the same in both ends of the setup.
Ques-8: Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
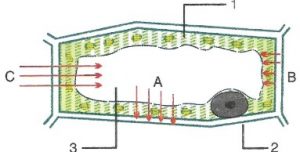
(a) In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent :
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
(b) B in the figure represents :
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
(c) A in the figure represents :
- imbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
(d) C in the figure represents :
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
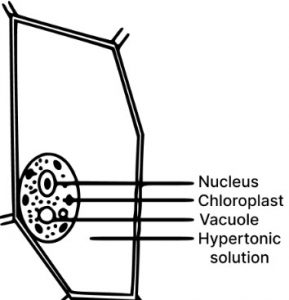
(e) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolysed plant cell.
Ans:
(a) Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
(b) Wall pressure
(c) Turgor pressure
(d) Osmotic pressure
(e) Labelled diagram of a plasmolysed plant cell is given below.
–: End Absorption by Root Structured Type Answer Concise Class 10 Selina Biology Solutions :-
Return to:- Concise Selina ICSE Biology Class-10 Solutions
Thanks
Please Share with your friends


