Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 10 Biology Notes. A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 10 Biology Notes
The process by which a single parent cell splits to form new cells, known as daughter cells.
Needs for New Cells
- Growth: All living begin their life from single cell which divide to form a cluster of cells
- Replacement: Cell replacement is the process where old or damaged cells are replaced with new ones throughout an organism’s life.
- Repair: This process repairs damaged tissues and replaces worn-out or injured cells, helping the body stay functional and healthy.
- Reproduction: New cells must be produced for reproduction, which is crucial for creating offspring and ensuring the survival of a species through the development of reproductive cells such as sperm and eggs.
Types of Cell Division
1. MITOSIS : Cell Division leading to growth and development.
2. MEIOSIS : Cell division leading to the production of gametes(sperms or eggs).
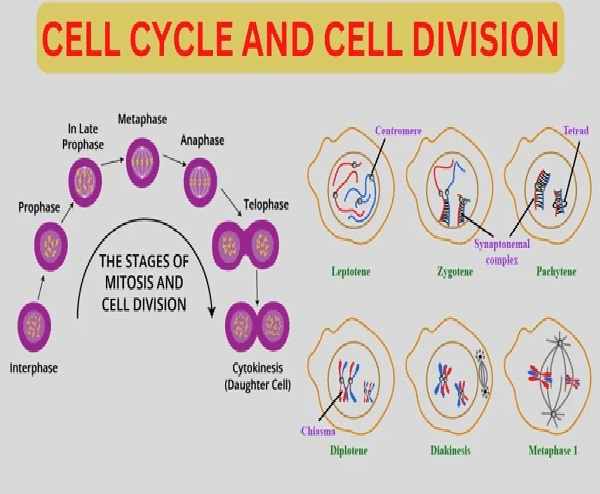
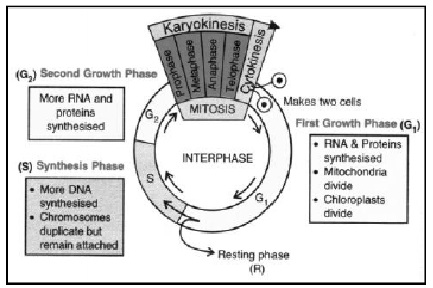
Phases of Cell Cycle
There are two phases
- Inter Phase: Non dividing phase
- Mitosis : Dividing phase
Inter-Phase
Inter phase is the active portion of the cell cycle in which cell prepare for next cell division. Although it is called Resting phase but it is not true actually it is also active phase.
Phases of Inter-Phase
Inter-Phase is sub divided into three phases:
- G1 Phase: RNA and Protien Synthesis, Volume of Cytoplasm Increase,
- S (synthetic) Phase, when DNA is replicated;
- G2 Phase,RNA and Protien Synthesis
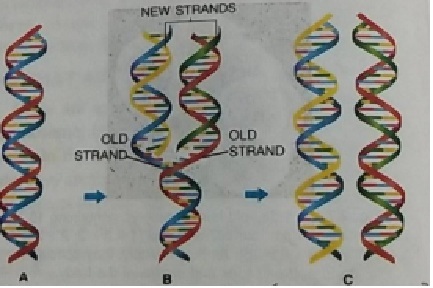
Formation of New DNA
During S Phase More DNA Synthesise by diving chromosome in two daughter cell in which new strand begin to form
Can Cell Cycle go Endlessly ?
- No. Stop permanently
- Eye Ball never divide
- Brain and Nerve Cell do not divide after Embryo stage
- Liver cell once in one year
- Uncontrolled non stop growth Cell causes Cancer
MITOSIS CELL DIVISION
Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical cells with the same genetic information. helps with growth, replacing old cells, and healing wounds and reproduce
Step of Mitosis
The Mitosis cell divides in two steps:
- Karyokinesis: Division of Nucleus
- Cytokinesis: Division of Cytoplasm
Step of Karyokinesis
- Prophase: The nuclear membrane and Nucleolus disappear, chromosomes become visible. Chromosomes (Animal cell) move to opposite sides, and spindle fibres form. each centriole is surrounded by rays called aster. Chromosome start moving toward equator
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align along the equator forming spindle fibre
- Anaphase: The centromeres split, and spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to opposite pole
- Telophase: nuclear membrane and Nucleolus re-appear. Daughter chromosome become chromatin thread
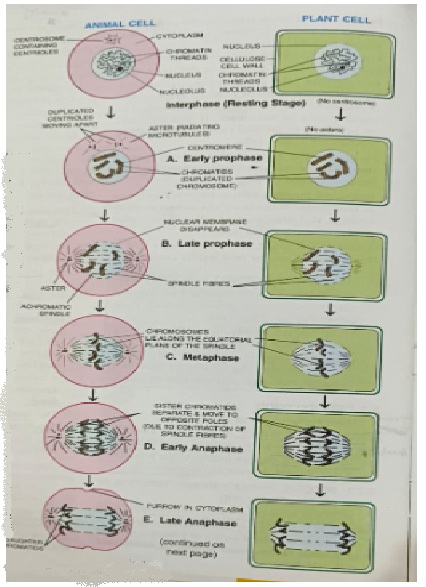
Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm):
A furrow appear in cell membrane in the middle which deepens and finally split into two.
Meiosis
- Meiosis is a type of cell division.
- It reduces the chromosome number by half.
- Results in four non-identical daughter cells.
- Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
- Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction.
- It ensures genetic diversity.
Significance of Meiosis
1. Chromosome Number is Halved: Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, ensuring that gametes (sperm and egg) have only half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. This prevents the chromosome number from doubling with each generation, maintaining the stability of the species’ chromosome count when fertilization occurs.
2.Mixing Up of Genes: During meiosis, genetic recombination occurs through crossing over and independent assortment. This results in the mixing of genes from both parents, contributing to genetic diversity in the offspring. This diversity is vital for evolution and adaptation of species to changing environments.
Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis

–: End of Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 10 Biology Notes :–
Please share with your friends if helpful
Return to :
Thanks


