Cell The Structural and Functional Unit of Life Class 10 Biology.The Cell topic in biology is very important to understand all other related topics such as gene, chromosome, genetics. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Cell The Structural and Functional Unit of Life Class 10 Biology
Defnition: “A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.”
Discovery of Cell:
Cell was discovered by Robert Hooke. All organisms are made up of cells.

Size of Cells
They are usually between 1 and 100 micrometers in size, which is much smaller than the width of a human hair. Some cells, like red blood cells, are about the size of a small dot, while others, like nerve cells, can be much longer
- Unicellular: Ex Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena
- Multicellular: Man, Mango, Rose.
Mycoplasmas are the smallest known cells. .
Cell Theory
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann suggested the cell theory, which says that all living things are made of cells and that cells are
- Cells are the basic unit of life,
- All living things are made up of cells,
- All cells come from other cells.
Cell Shapes:
Cells come in various shapes, each suited to their specific function in the body. Here are some different shapes of cells:
-
Spherical (Round): Red blood cells
-
Elongated (Long and Narrow): Nerve cells (neurons)
-
Cuboidal (Cube-shaped): Kidney cells
Each of these shapes is designed to help the cell carry out its specific job in the body.
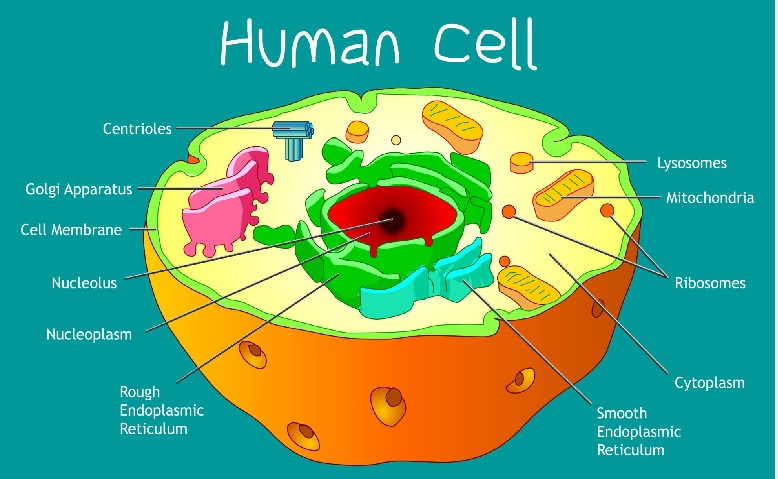
Structure of cell
There are three part:
- Cell membrane,
- Cytoplasm,
- Nucleus
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
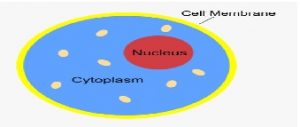
- Structure: A thin, flexible outer layer made of lipids and proteins.
- Function: It acts as a protective barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It also helps in communication with other cells.
Cytoplasm
- Structure: A jelly-like substance that fills the cell, surrounding the organelles.
- Function: It supports and protects the cell’s internal structures and is the site for many metabolic sreactions. It helps in the transport of materials within the cell.
Nucleus
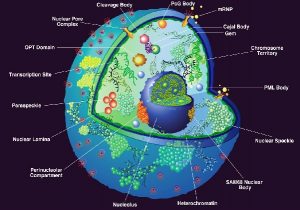
Structure:
- A large, membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA).
- Nuclear Envelope: Double membrane with pores, controls entry/exit of materials.
- Nucleoplasm: Jelly-like substance holding genetic material and other parts.
- Chromatin: DNA wrapped around proteins, condenses during cell division.
- Nucleolus: Makes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) to build ribosomes.
Function:
- It controls the cell’s activities, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction, by
regulating gene expression. It also directs protein synthesis. - The nucleus is a key part of eukaryotic cells, storing and protecting DNA and controlling activities like growth and cell division.
- The nucleus stores DNA, controls gene activity, replicates DNA during cell division, and produces mRNA for protein synthesis
Parts of cell: Characteristics and Functions
| Cell Part | Main Characteristics | Chief Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | A phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Selectively permeable. | Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Provides protection and structural support. |
| Cytoplasm | Gel-like substance inside the cell, composed of water, salts, and proteins. | Serves as the medium for chemical reactions. Houses organelles and supports their function. |
| Nucleus | Surrounded by the nuclear membrane (envelope), contains DNA. | Controls cell activities, stores genetic material (DNA), and coordinates cell division. |
| Nucleolus | Located within the nucleus, composed of RNA and proteins. | Synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assembly of ribosome subunits. |
| Mitochondria | Double-membrane structure with its own DNA. | Produces ATP (energy) through cellular respiration. Often called the “powerhouse” of the cell. |
| Ribosomes | Small particles composed of RNA and proteins. Can be free in cytoplasm or attached to rough ER. | Synthesize proteins by translating messenger RNA (mRNA). |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Network of membranous tubules and sacs. Can be rough (with ribosomes) or smooth (without ribosomes). | Rough ER: Synthesizes and folds proteins. Smooth ER: Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies chemicals. |
| Golgi Apparatus | Stacked membranous sacs, closely associated with ER. | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport. |
| Lysosomes | Membrane-bound vesicles containing digestive enzymes. | Breaks down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders (e.g., bacteria). |
| Centrosome | The centrosome has two centrioles made of microtubules and is surrounded by PCM, which helps form microtubules. | The centrosome organizes microtubules in the cell, helping maintain shape and support transport during interphase. |
| Plastids |
Can be of different types, like chloroplasts (green, for photosynthesis), chromoplasts (colored, for pigment storage), and leucoplasts (colorless, for storing starch, oils, or proteins). | Chromoplasts store pigments. Leucoplasts store nutrients. |
| Chromatin Fibres | Thread-like structures in the nucleus made of DNA and proteins that condense into chromosomes during cell division. | Contains genetic information (DNA) and controls cell activities. |
| Vacuole | Membrane-bound organelle, larger in plant cells. Contains fluid or other substances. | Stores nutrients, water, and waste products. In plant cells, provides turgor pressure for structural support. |
| Cell Wall | Rigid outer layer made of cellulose (in plants), chitin (in fungi), or peptidoglycan (in bacteria). | Provides structural support, protection, and shape. Present in plant, fungal, and bacterial cells. |
| Granules | Small particles in the cytoplasm or organelles, made of proteins, lipids, or other substances. | Involved in storing and processing nutrients or assisting in various cellular processes. |
Differences between Animal and Plant Cells
| Feature | Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Plastids | Absent | Present |
| Cell Wall | Absent. | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent. | Present |
| Vacuole | Small, (if present). | Large |
| Centrioles | Present | Absent |
–: End of Cell The Structural and Functional Unit of Life Class 10 Biology Notes :–
Please share with your friends if helpful
Return to :
Thanks


