Chemical Bond, Valency and Radioactivity Class-8th Goyal Brothers ICSE Chemistry Solutions Ch-4(Atomic Structure) Unit-3(Chemical Bond, Valency and Radioactivity). We Provide Step by Step Answers of Objectives, True and False, Incorrect and Correct , Definitions , Match the followings and Short/Long Question Type answers of Ch-4(Atomic Structure) Unit-3(Chemical Bond, Valency and Radioactivity). Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8
Chemical Bond Valency and Radioactivity Class-8th Goyal Brothers ICSE Chemistry Solutions ch-4 unit-3
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Goyal Brothers |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure |
| Unit-3 |
Chemical Bond Valency and Radioactivity |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
Chemical Bond Valency and Radioactivity Class-8th Goyal Brothers ICSE Chemistry Solutions ch-4 unit-3
Que: A. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the given list :
List : +2, donating, fusion, slow, cancer
1. During nuclear fusion the hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei.
2. Hydrogen and metals form positively charged ions by donating electrons from their valence shell.
3. Uranium atom splits into simpler atoms when its nucleus is hit by slow moving neutrons.
4. Over-exposure to nuclear radiation causes cancer.
5. The valency of an element X with atomic number 12 is +2.
Que: B. Statements given below are incorrect. Write the correct statements :
Question: 1. During nuclear fission nuclei of lighter elements fuse to form heavy nuclei.
Answer: 1. During nuclear fusion nuclei of lighter elements fuse to form heavy nuclei.
Question: 2. Sodium is a radioactive metal.
Answer: 2. Sodium is a reactive metal.
Question: 3. Alpha-particles are nuclei of hydrogen.
Answer: 3. Alpha-particles are nuclei of helium.
Question: 4. Cations are negatively charged particles.
Answer: 4. Anion are negatively charged particles.
Question: 5. Metals always form negatively charged ions.
Answer: 5. Metals always form positive charged ions.
Que: C. Match the statements in Column A, with those in Column B :
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. A slow moving particle used for splitting the nucleus of uranium atom. | (a) Helium nucleus |
| 2. A charged particle formed by the donation of electrons from the valence shell. | (b) Nuclear reactor |
| 3. A phenomenon due to which hydrogen atoms fuse in Sun. | (c) Cation |
| 4. A charged particle having +2 electric charge and 4 amu mass. | (d) Neutron |
| 5. A specially designed vessel in which uranium atoms split to release energy. | (e) Nuclear fusion |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. A slow moving particle used for splitting the nucleus of uranium atom. | (a) Neutron |
| 2. A charged particle formed by the donation of electrons from the valence shell. | (b) Cation |
| 3. A phenomenon due to which hydrogen atoms fuse in Sun. | (c) Nuclear fusion |
| 4. A charged particle having +2 electric charge and 4 amu mass. | (d) Helium nucleus |
| 5. A specially designed vessel in which uranium atoms split to release energy. | (e) Nuclear reactor |
Que: D. Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements :
| Statements | True/False |
| 1. Non-metal form cations by accepting electrons in their valence shell. | F |
| 2. During nuclear fission only slow neutrons can break uranium atom. | T |
| 3. Nuclear radiation under medical supervision can cure cancer. | T |
| 4. The elements which give out high energy radiations on their own are called radioactive elements. | T |
| 5. Hydrogen is a non-metal and hence forms anions. | F |
Que: E. Tick (√) the most appropriate answer :
1. Alpha particles consist of :
(a) 2 protons and three neutrons
(b) 2 protons and two electrons
(c) 2 protons and two neutrons
(d) 2 protons and one electron
Answer: option (c) 2 protons and two neutrons is correct.
2. The nucleus of the stars and sun has :
(a) helium
(b) hydrogen
(c) carbon
(d) phosphorus
Answer: option (b) hydrogen is correct.
3. The radioactive isotope used in the cure of thyroid cancer is :
(a) P-32
(b) Co-60
(c) Na-24
(d) l-131
Answer: option (b) Co-60 is correct.
4. The particle used to split nucleus of uranium is :
(a) alpha particle
(b) proton
(c) slow moving neutron
(d) fast moving neutron
Answer: option (c) slow moving neutron is correct.
5. Metals enter into chemical reaction with non-metals by :
(a) donating electrons from the valence shell
(b) accepting electrons in the valence shell
(c) they can accept or donate electrons depending upon situation
(d) none of these
Answer: option (a) donating electrons from the valence shell is correct.
STUDY QUESTIONS
Chemical Bond Valency and Radioactivity Class-8th Goyal Brothers ICSE Chemistry Solutions ch-4 unit-3
Question: 1. Why do most of elements form ions while entering into a chemical reactions ?
Answer: Elements form ions to gain stability by attaining noble gas configuration. They less or gain electrons to form ions that leads to completely filed outer shell configuration and hence stability.
Question: 2. (a) What kind of ions are formed by the metals? What name is given to these ions?
Answer: Metals generally have 1,2 or 3 electrons in their outer shell. Metals donate or lose 1,2 or 3 electrons to become positively charged ions(cations).
(b) Explain the formation of following ions by drawing geometric diagrams
(i) Sodium
Answer:
(ii) Magnesium
Answer: 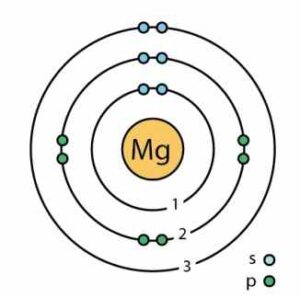
(iii) Aluminum
Answer: 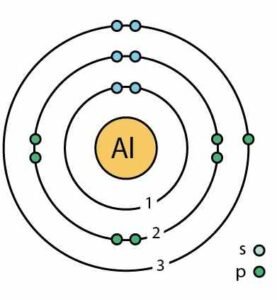
Question: 3. What kind of ions are formed by non-metals? What name is given to these ions?
Answer: Non-metals generally have 4,5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shell. Non-metals accept or gain 3,2 or 1 electrons to become negatively charged ions[anions].
Question: 4. Explain the formation of following ions by drawing geometric diagram :
(a) chloride ion
Answer: 
(b) oxide ion
Answer: 
(c) phosphide ion
Answer: 
Question: 5. What do you understand by the following terms on the basis of structure of atom :
(a) valency
Answer: The number of bonds that an atom can form as part of a compound is expressed by the valency of the element. We all know how electrons in an atom are arranged in shells/orbitals. Valence electrons are those electrons which are present in the outermost orbit of the atom.
(b) positive valency
Answer: The valence of a positively charged ion. The number of electrons an atom can give up sodium has a positive valence of Hydrogen has one valence electron, so to be stable, it can gain or lose one electron.
(c) negative valency
Answer: The valence of a negatively charged ion. The number of electrons an atom can take up. oxygen has a negative valence of 2.
(d) variable valency
Answer: The element exhibits more than one electropositive valency. Such elements are said to have variable valency.
Question: 6. What do you understand by the following terms :
(a) Radioactivity
Answer: The process of self, spontaneous and random emission of a or P and y radiations from the nucleus of elements of atomic number higher than 82, is called radioactivity.
(b) Radioactive substance
Answer: The energy or particles emitted during radioactive decay are referred to as radiation.
- The rate at which a material emits radiation is referred to as its radioactivity.
- The number of disintegrations per unit of time is used to determine the activity of a sample of radioactive material.
- There are a total of 38 radioactive elements in the universe.
- Examples are Radium: Polonium and barium are some radioactive substances.
(c) Nuclear fission
Answer: Nuclear fission, subdivision of a heavy atomic nucleus, such as that of uranium or plutonium, into two fragments of roughly equal mass. The process is accompanied by the release of a large amount of energy.
(d) Nuclear fusion
Answer: The term nuclear fusion is given to the nuclear reactions in which two or more smaller nuclei fuses (or combine) together to form a larger nucleus releasing a huge amount of energy.
(e) Nuclear reactor
Answer: Nuclear reactors are the heart of a nuclear power plant. They contain and control nuclear chain reactions that produce heat through a physical process called fission. That heat is used to make steam that spins a turbine to create electricity.
Question: 7. (a) State the problems caused by nuclear radiations.
Answer: Exposure to very high levels of radiation, such as being close to an atomic blast, can cause acute health effects such as skin burns and acute radiation syndrome (“radiation sickness”). It can also result in long-term health effects such as cancer and cardiovascular disease.
(b) State few uses of nuclear radiation.
Answer: Today, to benefit humankind, radiation is used in medicine, academics, and industry, as well as for generating electricity. In addition, radiation has useful applications in such areas as agriculture, archaeology (carbon dating), space exploration, law enforcement, geology (including mining), and many others.
Question: 8. State any three precautions in running nuclear reactors.
Answer: Three precautions in running nuclear reactors :
- An instrument or structure that can be used to cause fission products to undergo a controlled, self-sustaining nuclear reaction and release energy as a result.
- Due to the exponential increase in the reaction process, nuclear energy can become a powerful blast.
- To control the reaction, we employ Uranium rods. Because its reaction with water and air poses a health risk, the inner environment must be protected from the outside.
— : end of Chemical Bond Valency and Radioactivity Class-8th Goyal Brothers ICSE Chemistry Solutions ch-4 unit-3 :–
Return to- ICSE Class -8 Goyal Brothers Chemistry Solutions
Thanks
Please share with yours friends if you find it helpful.


