Circulatory System Class-10 Long and Structured Goyal Brothers ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-8 . We Provide Solutions of Long Answer and Structured Questions of Exercise-8 The Circulatory System. All solutions are given as council prescribe guideline for next upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Ch-8 The Circulatory System Long and Structured Questions
Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brothers publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Dr. K.K. Aggrawal |
| Chapter-8 | The Circulatory System |
| Topics | Solutions of Long and Structured Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
Note :- Before Viewing Goyal Brothers Solutions of Chapter-8 The Circulatory System . Read the whole chapter carefully with figure and make a self written note , highlight the important point.
D. LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Ch-8 The Circulatory System Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-116)
Question 1. What is a blood clot? Describe briefly the three stages of blood clotting.
Answer : 1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug.” 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot
Question 2. What is heartbeat and cardiac cycle?
Answer : The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole
Question 3. What are the two types of circulation of blood present in our body?
Answer : Two pathways come from the heart: The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again. The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again
Question 4. List the differences between blood and lymph.
Answer :
| Lymph | Blood |
|---|---|
| Carries less oxygen and digested food. | Carries more oxygen and digested food. |
| Proteins and minerals | |
| Lymph plasma lacks proteins. | Blood plasma consists of proteins, calcium, and phosphorus. |
Question 5. Give reason:
(i) It is must to know the blood group of both the donor and the recipient before transfusing blood.
(ii) A matured mammalian erythrocyte lacks nucleus and mitochondria.
(iii) Blood flows in arteries under pressure.
(iv) The left ventricle of the heart has a thicker wall than the right ventricle.
Answer :
(i) It’s necessary to match the donor and recipient blood types to prevent hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), clot formation, renal failure, and death. If blood types are incorrectly mixed, the antibodies of one may attack the antigens of the other
(ii) A mature erythrocyte lacks nucleus and mitochondria so as to make place for the accommodation of more hemoglobin and hence more oxygen molecules. Lack of such organelles also provides the peculiar biconcave appearance of RBCs that aids in efficient diffusion
(iii) As the ventricles of the heart contract, they push blood into the small lumen of the arteries with a great force, thus making the blood in the arteries flow in spurts and under pressure
(iv) The left ventricle of your heart is larger and thicker than the right ventricle. This is because it has to pump the blood further around the body, and against higher pressure, compared with the right ventricle.
Question 6. Give the functions of spleen tonsils.
Answer :The left ventricle of your heart is larger and thicker than the right ventricle. This is because it has to pump the blood further around the body, and against higher pressure, compared with the right ventricle.
E. STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
Ch-8 The Circulatory System Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-116)
Question 1. The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its functional activities. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
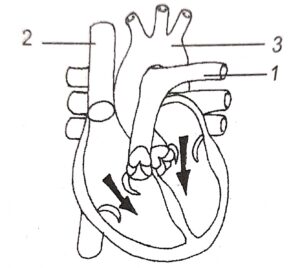
(i) Name the phase.
(ii) Label the parts 1, 2, and 3
(iii) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase ? Give a reason to support your answer.
(iv) Draw well labelled diagrams of part 1 and 2 to show the structural differences between them.
Answer :
(i) Arial systole is the phase.
(ii) 1. Aorta, 2. Pulmonary Artery, 3. Superior Vena Cava
(iii) Upper chambers i.e., both the atria are contracting in this phase because blood is flowing downwards (towards the ventricles).
(iv) 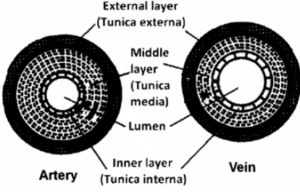
Question 2. The diagram alongside represents circulation in the human body. Answer the questions that follow :
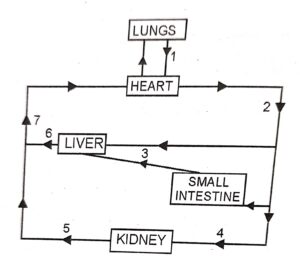
(i) Name the blood vessels labelled 1, 3, 6, and 7.
(ii) Name the blood vessel that supplies the walls of the heart with oxygen.
(iii) Draw a neat labelled diagram of the blood vessel numbered ‘2’ as seen in a cross section.
(iv) Mention one structural difference between blood vessels numbered 4 and 5.
Answer :
(i) 1 – Pulmonary vein,
3 – Hepatic portal vein,
6 – Hepatic vein
7 – Posterior vena cava.
(ii) Coronary artery
(iii) 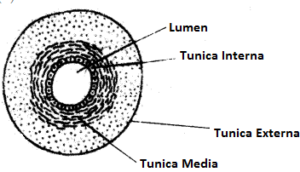
(iv)
| 4 (Renal artery) | 5 (Renal vein) |
| 1. Thick muscular wall2. Narrow lumen
3. Valves absent |
Thin muscular wall
Wide lumen Valves present |
Question 3. The diagram given below show the cross section of two kinds of blood vessels :
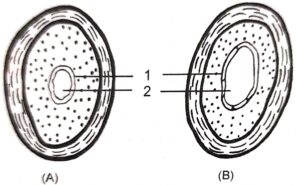
(i) Identify the blood vessels A and B. In each case give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Name the parts numbered 1 and 2.
(iii) When are the sound “LUBB” and “DUP” produced during a heartbeat ? Name the blood vessel that :
(iv) Name the blood vessel that:
(1) begins and ends in capillaries
(2) supplies blood to the walls of the heart
Answer :
(i) A – Artery, B – Vein
A has narrow lumen and thick muscular wall
B has wide lumen and thin muscular wall.
(ii) 1 – Endothelium
2 – Lumen
(iii) “LUBB”: Sound is produced when the two atrioventricular valves shut.
“DUP”: Sound is produced when the two semi lunar valves shut 1 Begins and ends in capillaries: “Hepatic portal Vein”.
2. Supplies blood to the walls of the Heart: “Coronary artery”.
Question 4. The diagrams given below are cross sections of blood vessels :
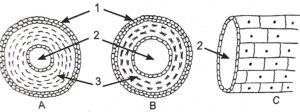
(i) Identify the blood vessels A, B and C.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1 to 3.
(iii) Name the type of blood that flows through A.
(iv) Mention one structural difference between A and B.
(v) In which of the above vessels does exchange of gases actually take place ?
Answer :
(i) 1. Connective tissue layer 2. Lumen 3. Muscular layer
(ii) Oxygenated blood.
(iii) A = Artery, B = Vein, C = Capillary.
(iv)
| A | B |
| 1. Thick muscular and elastic layer as wall. | 1. Thin muscular and less elastic wall. |
| 2. Narrow lumen | 2. Wide lumen. |
(v) In C/Capillary.
Question 5. The diagram below represents the simplified pathway of the circulation of blood. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
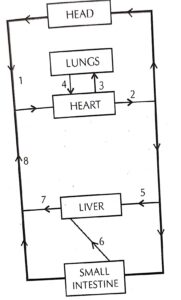
(i) Name the blood vessels labelled 1 and 2.
(ii) State the function of blood vessels labelled 5 and 8.
(iii) What is the importance of the blood vessel labelled 6 ?
(iv) Which blood vessel will contain a high amount of glucose and amino acids after a meal ?
(v) Draw a diagram of the different blood cells as seen in a smear of human blood.
Answer :
(i) (1) Anterior/Superior venacava (2) Dorsal aorta
(ii) Function of 5: Supply oxygenated blood to liver.
Function of 8: Cajry deoxygenated blood from posterior parts of the body to the right auricle of heart.
(iii) Importance of the blood vessel labelled 6: Blood vessel 6 is called Hepatic portal vein. It carries deoxygenated blood from intestine to liver. This blood contains excess glucose, some toxic substances etc. which are sent to liver where they are detoxified and the excess glucose is converted to glycogen and stored. This prevents these substances from directly entering the heart and damaging the heart.
(iv) Blood Vessel-6
(v) 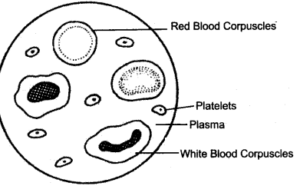
Question 6. Study the given diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow :
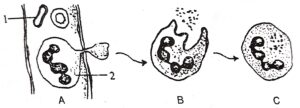
(i) Name the cell labelled 1 and 2.
(ii) Identify the phenomenon in A.
(iii) Mention two shown difference between 1 and 2.
(iv) Name the process occurring in B and C. State the importance of this process in the human beings.
Answer :
(i) 1 – Red blood cell
(ii) Diapedesis(iii)
| RBC | WBC |
| They lack a nucleus. | They have a nucleus. |
| They are biconcave and disc-shaped. | They are spherical and have different sizes. |
(iv) The process which occurs in B and C is phagocytosis. In this process, the WBCs engulf the foreign particles and destroy them, thus preventing the occurrence of disease.
Question 7. The diagram given alongside represents the human heart in one phase of its functions. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow :
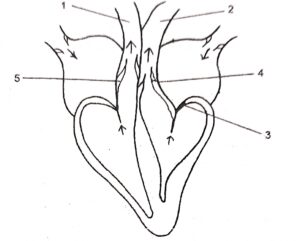
(i) Name the phase.
(ii) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase ? Give a reason to support your answer.
(iii) Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
(iv) What type of blood flows through ‘2’ ?
(v) State the function of the part numbered ‘5’ ?
(vi) Name the membrane that covers the heart.
Answer :
(i) Ventricular Systole.
(ii) Ventricle is contracting because both tricuspid and bicuspid valves are closed whereas both pulmonary semi-lunar and Aortic semilunar valves are open to pump the blood out of the two ventricles.
(iii) 1. Pulmonary artery
2. Aorta
3. Bicuspid/Mitral valve.
4. Aortic semi-lunar valve
5. Tricuspid values.
(iv) Oxygenated blood flows through part 2.
(v) Allow deoxygenated blood to flow from right ventricle to lungs and prevents its back flow.
(vi) Pericardium.
Question 8. The diagram given below represents a section of the human heart. Answer the questions that follow:
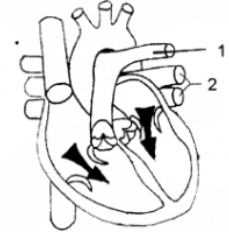
(i) Which parts of heart are in the diastolic phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Label the parts numbered 1 and 2 in the diagram. What type of blood flows through them?
(iii) What causes the heart sounds ‘LUBB’ and ‘DUP’?
(iv) Name the blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles.
(v) Draw neat labelled diagrams of a cross-section of an artery and a vein.
Answer :
(i) Ventricles, as the blood is flowing towards ventricle since tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open.
(ii)
1. Pulmonary artery
2. Left pulmonary veins.
(iii) The LUBB sound is caused due to the closure of the auriculo-ventricular valves while DUP sound is caused due to the closure of the semilunar valve.
(iv) Coronory arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles.
(v)

— : End of Circulatory System Class-10 Long and Structured Goyal Brothers Solutions Ch-8 :–
Return to :- ICSE Biology for Class 10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions