Chemical Reactions Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-6, Chemical Reactions Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-6. We Provide Step by Step Solutions to Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
Chemical Reactions Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-6
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-6 | Chemical Reactions |
| Unit-1 | Chemical Reactions |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Chemical Reactions Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-6
Question: 1. State what is a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction is often accompanied by external indications or characteristics which include –
(a) Colour change
(b) Effervescence or gas evolved
(c) Evolution or absorption of heat
(d) Formation of a precipitate.
With reference to each of the above indications, state the external indication seen during –
(i) Addition of dilute acid to an active metal
(ii) Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate
(iii) Addition of water to quicklime
(iv) Thermal decomposition of mercury [II] oxide.
Answer: Chemical reaction : “A chemical reaction is a chemical change where substances react with each other to form a new substance..”
1. Addition of dil. acid to an active metal : addition of dilute acid to an active metal – The test tube becomes hot and hydrogen gas is evolved, which means heat is produced.
2. Addition of dil. hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate : Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate – A white coloured precipitate is formed which is AgCl
3. Addition of water to quick lime : Addition of water to quicklime – The solution boils and heat is produced accompanied by a hissing sound.
4. Thermal decomposition of mercury [II] oxides : Thermal decomposition of mercury oxide – The colour of mercury changes from red to silvery, that is metallic.
Question: 2. State why a direct combination reaction is called a – ‘synthesis reaction’.
Answer: When two or more substances [element with element or element with compound or compound with another compound] combine to form a new compound with new properties. Hence direct combination is called a ‘synthesis reaction’.
Example: Hydrogen (a gas) + Oxygen (a gas) combines to form water (liquid).
2H2 + O2 ⟶ 2H2O
Question: 3. Differentiate between –
(a) Direct combination reaction & a decomposition reaction
(b) Displacement reaction & a neutralization reaction.
Answer: (a) Direct combination reaction – When two substances react chemically to form a new substance which is a compound, it is a direct combination reaction.
Example – H2+O2 → H2O
Decomposition reaction – When a compound breaks up or decomposed into two or more substances that are simpler and can sustain independently.
Example – CuCO3 → CuO + CO2
(b) Displacement reaction: When an element displaces another element in a compound during a chemical reaction, it is a displacement reaction.
Example – AgNO3 + Cu → 2Ag + Cu(NO3)2
Neutralization reaction : When an acid and a base react together to form salt and water, it is a neutralization reaction.
Example – NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Question: 4. Classify the following reactions into –
(a) Direct combination
(b) Decomposition
(c) Displacement
(d) Double decomposition – The reactions are –
(i) Zinc hydroxide on heating gives zinc oxide & water
(ii) Zinc reacts with copper [II] sulphate to give zinc sulphate & copper
(iii) Zinc sulphate reacts with ammonium hydroxide to give ammonium sulphate & zinc hydroxide
(iv) Molten zinc at high temperatures, burns in air to give zinc oxide.
Answer: (i) Zinc hydroxide on heating gives zinc oxide & water — Decomposition
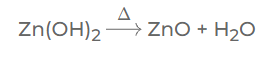
(ii) Zinc reacts with copper [II] sulphate to give zinc sulphate & copper — Displacement
Zn + CuSO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + Cu
(iii) Zinc sulphate reacts with ammonium hydroxide to give ammonium sulphate & zinc hydroxide — Double decomposition
ZnSO4 + 2NH4OH ⟶ (NH4)2SO4 + Zn(OH)2
(iv) Molten zinc at high temperatures, burns in air to give zinc oxide — Direct combination
2Zn + O2 ⟶ 2ZnO
Question: 5. Give balanced equations for –
(i) A direct combination reaction involving two elements, one of which is a non-metal
(ii) A thermal decomposition reaction involving heat on limestone [calcium carbonate]
(iii) An electrolytic decomposition reaction involving a neutral liquid
(iv) A displacement reaction involving a metal above hydrogen in the activity series with copper [II] sulphate solution
(v) A double decomposition neutralization reaction involving an acid & a base
(vi) A white precipitate obtained during a double decomposition reaction involving a silver salt with a sodium salt.
Answer: (i) C + O2 ⟶ CO2


(iv) Zn + CuSO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + Cu
(v) HCl + NaOH ⟶ NaCl + H2O
(vi) AgNO3 + NaCl ⟶ AgCl ↓ + NaNO3
Question: 6. State what is meant by ‘reactivity series of metals’. With reference to – (a) Water (b) Acids explain with suitable examples how the reactivity of the metals could be differentiated.
Answer: Activity series of metals: “Is a series of arrangements of metals in decreasing order of their reactivity.”
i.e. metals at the top are most reactive and least reactive metals are at the bottom of the series. The metal above is more reactive than the lower metal. In other words, K is more reactive than all the metals below it and Na is more reactive than all the metals below it.
Action of metals with water: K, Na, Ca react with cold water.
K: Darts on the water surface and react violently.
Na: Revolves on the water surface and bums.
Ca: Sinks in water, react less violently.
Hence, K > Na > Ca calcium is less reactive than K and Na.
Mg and Al react with boiling water/steam.
Hence, Mg and Al are less reactive than K, Na, and Ca. Zn, Fe, Pb also react with steam and reaction stops soon. Fe when hot reacts with steam
This shows that Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb.
Cu, Hg, Ag, Pt, Au do not react with steam or even when hot is less reactive.
Action of metals with acids: As reactivity decreases from top to bottom in metal activity series.
K and Na react with dil. HC1 and dil. H2SO4 explosively to produce H2↑
2Na + 2HCl ⟶ 2NaCl + H2
Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, and iron react less vigorously with decreasing vigour with dil. H2SO4 or dil. HC1 to produce H2↑
Ca + H2SO ⟶ CaSO4 + H2
Metals below hydrogen do not react with dil. acid and do not displace H2 from it.
Question: 7. A chemical reaction may be ‘reversible’ in nature. State the meaning of the term in italics. Give a reason why a catalyst is used in certain chemical reactions. Give a r balanced equation for the following – (a) A reversible catalytic reaction involving –
1. nitrogen as one of the reactants
2. sulphur dioxide as one of the reactants.
Answer: Reversible reaction: “A chemical reaction is said to be reversible in nature if “products formed react together – to form actual reactants depending on the condition of the reaction.”
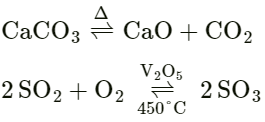
A catalyst is used to make the reaction fast or slow down it. When KClO3 is heated, oxygen is produced but the reaction is very slow. If we add MnO2 to KClO3 and heat the rate of production of oxygen becomes faster.
Balanced chemical equation for a reversible reaction involving,
Nitrogen as one of the reactants
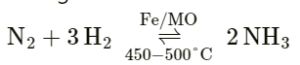
Here iron is used as a catalyst
Balanced chemical equation for a reversible reaction involving,
SO2 as one of the reactants
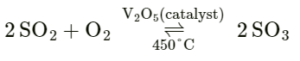
Question: 8. State which type of chemical reactions proceed with –
(a) Evolution of heat energy
(b) Absorption of heat energy.
State in each of the following reactions whether heat is evolved or absorbed
(i) water is added to quicklime
(ii) two neutral gases on passage through an electric arc give nitric oxide
(iii) two neutral gases combine to give – a basic gas.
Answer:
(a) Exothermic reaction
(b) Endothermic reaction
(i) Exothermic reaction, heat is evolved.
CaO + H2O ⟶ Ca(OH)2 + Δ
(ii) Endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed.

(iii) Exothermic reaction, heat is evolved.
![]()
Question: 9. Certain thermal decomposition reactions, result in formation of oxides. Give balanced equations for the thermal decomposition of the following, which result in formation of a metallic oxide:
(a) Limestone
(b) Lead carbonate
(c) Calcium nitrate
(b) Calcium hydroxide
Answer:

Question: 10. State the meaning of the term ‘oxide’. Give a balanced equation for formation of the following oxides –
(a) Sulphur dioxide from a non-metal
(b) Zinc oxide from a metal
(c) Lead oxide from a mixed Oxide.
Answer: Oxides are binary compounds of a metallic or non-metallic element with oxygen.
(a) Sulphur dioxide from a non-metal :
S + O2 ⟶ SO2
(b) Zinc oxide from a metal :
2Zn + O2 ⟶ 2ZnO
(c) Lead oxide from a mixed oxide :
2Pb3O4 →Δ 6PbO + O2
Question: 11. Give two examples each of the following oxides –
(a) Acidic oxides
(b) Basic oxides
(c) Amphoteric oxides
(d) Neutral oxides.
State which of the following oxides i.e. (a) to (d)
(i) React with water to give a base
(ii) React with a base to give salt & water
(iii) React with acids & bases to give salt & water.
Answer: (a) Acidic oxides — SO2 , CO2
(b) Basic oxides — K2O, CaO
(c) Amphoteric oxides — ZnO, PbO
(d) Neutral oxides — NO, CO
(i) React with water to give a base — (b) Basic oxides
(ii) React with a base to give salt & water — (a) Acidic oxides
(iii) React with acids & bases to give salt & water — (c) Amphoteric oxides
Question: 12. Give one example each of –
(a) A peroxide
(b) A mixed oxide
(c) A dioxide.
Answer: Example of-
(a) A peroxide — Na2O2
(b) A mixed oxide — Pb3O4
(c) A dioxide — PbO2
– : End of Chemical Reactions Class-8 Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-8 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.



It’s is very easy for teacher to give answer for their student .
we could not understood your problems please call if any at 8957797189