Hydrogen Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-7, Hydrogen Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-7. We Provide Step by Step Solutions to Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
Hydrogen Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-7
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-7 | Hydrogen |
| Unit-1 | Hydrogen |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Hydrogen Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-7
Question: 1. State how hydrogen occurs in the free state. Name three compounds containing hydrogen in the combined state.
Answer: In Free state:
- In traces : Hydrogen occurs in minute traces in the earth’s crust, atmosphere & in volcanic gases
- In & around the sun : Hydrogen occurs in the interior of the sun which consists mainly of hydrogen, which is converted to energy released as heat & light.
The compounds containing hydrogen are: ammonia (NH3), hydrochloric acid (HCl), water(H2O)
Question: 2. Starting from zinc how would you obtain hydrogen using-
(a) Steam
(b) A dilute acid
(c) An alkali
[Give balanced equations for each & name the product formed in each case other than hydrogen]. Name a metal which will not react with the reactants above to give hydrogen.
Answer: (a) Steam : Zn reacts with steam to form zinc oxide and liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + H2O ⟶ ZnO + H2 ↑
Lead (Pb) will not react with steam to give hydrogen.
(b) A dilute acid : Zn reacts with dil. sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2 ↑
Copper (Cu) will not react with dilute acid to give hydrogen.
(c) An alkali : Zn reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium zincate and liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2NaOH ⟶ Na2ZnO2 + H2 ↑
Silver (Hg) will not react with alkali to give hydrogen.
Question: 3. ‘Hydrogen is obtained by electrolysis of acidified water’. Answer the following pertaining to the preparation of hydrogen by electrolysis,
(a) The meaning of the term ‘electrolysis’ and ‘electrolyte’,
(b) Name the electrode –
1. through which the current enters the electrolyte.
2. at which hydrogen is liberated.
Answer: (a) Electrolysis — It is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound [electrolyte] in the fused [molten] or solution state by passage of an electric current resulting in the dissociation of the chemical compound into ions which are discharged as neutral atoms at the respective electrodes.
Electrolyte — A chemical compound which in the molten or solution state can conduct electric current & undergo chemical decomposition due to flow of current.
(b) The electrodes are:
1. Anode
2. Cathode
Question: 4. In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc & dilute hydro choloric acid – state a reason for
(a) Addition of traces of copper [II] sulphate to the reaction medium
(b) Collecting the hydrogen by downward displacement of water and not air & collecting it after all the air in the apparatus is allowed to escape
(c) Having the end of the thistle funnel dip below the level of the acid in the flask.
Answer: (a) Addition of traces of copper [II] sulphate to the reaction medium enhances the speed of the reaction.
(b) Hydrogen forms a highly explosive mixture with air. Hence, it is not collected by the downward displacement of air and collected only after all the air in the apparatus is allowed to escape. As it is almost insoluble in water, so it is collected by downward displacement of water.
(c) The lower end of the thistle funnel should dip below the level of the acid in the flask, otherwise hydrogen gas produced will escape through thistle funnel.
Question: 5. In the industrial method of preparation of hydrogen by the Bosch process – give
(a) Balanced equations for the first two main steps in the production of hydrogen
(b) The reason for use of addition of a promoter to the catalyst in the final step
(c) The name of the solution which absorbs the unreacted carbon monoxide.
Answer: (a) Balanced equations for first two main steps of Bosch process:
Step I — Production of water gas

Step II — Reduction of steam to hydrogen by carbon monoxide
![]()
(b) Promoter increases the efficiency of the catalyst.
(c) Ammoniacal cuprous chloride solution [CuCl].
Question: 6. State the following pertaining to the physical properties of hydrogen :
(a) Colour & odour
(b) Solubility in water
(c) Effect on moist blue litmus paper.
Answer:
(a) Colour & odour — colourless and odourless
(b) Solubility in water — Very slightly soluble in water
(c) Effect on moist blue litmus paper — neutral to litmus
Question: 7. Draw neat labelled diagrams for two different experiments to prove that – hydrogen is lighter than air.
Answer: Hydrogen is lighter than air:
- To show that H2 is lighter than air :
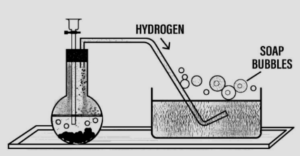
- Air from jar B being heavier runs down in jar A and H2 runs to jar B as it is lighter than air and burns with ‘pop’ sound in jar B if a burning splinter is brought there.
Question: 8. Starting from hydrogen gas how would you obtain
(a) A neutral liquid
(b) A basic gas
(c) A metal by reduction of its heated oxide.
[The metal formed is above iron in the activity series]
Answer:(a) Hydrogen burns quietly in oxygen with a pale blue flame and water is formed.
2H2 + O2 ⟶ 2H2O
(b) Three volumes of hydrogen, reacts with one volume of nitrogen to form ammonia which is a basic gas.
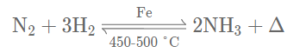
(c) Hydrogen reduces oxides of less active metals e.g. zinc to form the reduced metal & water.
ZnO + H2 ⟶ Zn + H2O
Question: 9. Using a burning candle and a jar of hydrogen – how would you prove experimentally that (a) Hydrogen is a combustible gas (b) Hydrogen does not support combustion.
Answer: Experiment : Take a jar filled with hydrogen with inverted mouth downwards and introduce a burning candle near the mouth of jar.
Observation : The gas burns at the mouth of the jar while the burning candle is extinguished when pushed inside the jar.
Conclusion :
- Hydrogen is combustible & hence burns at the mouth of the jar.
- It does not support combustion and extinguishes a burning candle when pushed inside.

Question: 10. State a reason why, when hydrogen is passed over heated copper oxide, the resultant product formed, differs in colour from the original reactant.
Answer: As hydrogen is a strong reducing agent hence it reduces heated copper (II) oxide to copper. Therefore, the original black copper (II) oxide changes to reddish brown copper.
![]()
Question: 11. With reference to the uses of hydrogen, give reasons for the following :
(a) Hydrogen is not used in air balloons
(b) A mixture of hydrogen & oxygen on burning, find application in welding & cutting metals
(c) Reaction of hydrogen with nitrogen under specific conditions finds industrial utility.
Answer: (a) Hydrogen is lighter than air but it is a highly combustible gas. It forms an explosive mixture with air (due to the oxygen present in it). Hence, it is not used in air balloons.
(b) A mixture of hydrogen & oxygen on burning produces heat [temperatures upto 2800°C]. Such high temperature flames are used for welding & cutting metals.
(c) Hydrogen combines with nitrogen at 450°C and in the presence of catalyst iron to give ammonia. Ammonia is used in the manufacture of urea, fertilizers, nitric acid, explosives, etc.
Question: 12. Give a test to differentiate between two gas jars – one containing pure hydrogen and the other hydrogen-air mixture.
Answer: When a burning splinter is brought near the mouth of the gas jar containing pure hydrogen, it burns quietly with a pale blue flame whereas the other jar containing hydrogen-air mixture burns with a pop sound.
Question: 13. With reference to oxidation & reduction reaction – complete the statement given by filling in the blanks with only the words (a) Addition (b) Removal.
‘Oxidation is a chemical reaction involving __addition__ of oxygen to a substance or __removal__ of hydrogen from a substance. Reduction on the other hand involves __addition__ of hydrogen to a substance or __removal__ of oxygen from a substance.
Question: 14. With reference to the equation :
Cl2 + H2S → 2HCl + S
pertaining to a redox reaction – select the correct answer in each case –
(a) Chlorine is __reduced__ (oxidised/reduced) to HCl.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide is __oxidised__ (oxidised/reduced) to sulphur since the reaction involves __removal__ (addition/removal) of hydrogen.
(c) Chlorine acts as an __oxidising__ (oxidising/reducing) agent.
– : End of Hydrogen Class-8 Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Class-8 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.



THANKS BRO. SO MUCH I WAS FINDING THE ANSWERS FOR LIKE HOURS.
thanks for response