ML Aggarwal Coordinate Geometry Exe-19.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths APC Understanding Solutions. Solutions of Exe-19.1. This post is the Solutions of ML Aggarwal Chapter 19 – Coordinate Geometry for ICSE Maths Class-9. APC Understanding ML Aggarwal Solutions (APC) Avichal Publication Solutions of Chapter-19 Coordinate Geometry for ICSE Board Class-9. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
ML Aggarwal Coordinate Geometry Exe-19.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Avichal Publishig Company (APC) |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-19 | Coordinate Geometry |
| Writer | ML Aggarwal |
| Book Name | Understanding |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-19.1 Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Exe-19.1 Solutions of ML Aggarwal for ICSE Class-9 Ch-19, Coordinate Geometry
Note:- Before viewing Solutions of Chapter – 19 Coordinate Geometry Class-9 of ML Aggarwal Solutions . Read the Chapter Carefully. Then solve all example given in Exercise-19.1, Exercise-19.2, Exercise-19.3, Exercise-19.4, MCQs, Chapter Test.
Coordinate Geometry Exercise-19.1
ML Aggarwal Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page 448
Question 1. Find the co-ordinates of points whose
(i) abscissa is 3 and ordinate -4.
(ii) abscissa is – 3/2 and ordinate 5.
(iii) whose abscissa is -1(2/3) and ordinate -2 (1/4) .
(iv) whose ordinate is 5 and abscissa is -2
(v) whose abscissa is -2 and lies on x-axis.
(vi) whose ordinate is 3/2 and lies on y-axis.
Answer :
Abscissa is the x-coordinate and ordinate is the y-coordinate of a point.
(i) The coordinate of the point whose abscissa is 3 and ordinate is -4 is (3,-4).
(ii) The coordinate of the point whose abscissa is -3/2 and ordinate is 5 is (-3/2,5).
(iii) The coordinate of the point whose
![]()
(iv) The coordinate of the point whose ordinate is 5 and abscissa is -2 is (-2,5).
(v) The coordinate of the point whose abscissa is -2 and lies on x-axis is (-2,0).
If a point lies on x-axis, its y-coordinate is zero.
(vi) The coordinate of the point whose ordinate is 3/2 and lies on y-axis is (0,3/2).
If a point lies on y-axis, its x-coordinate is zero.
Question 2. In which quadrant or on which axis each of the following points lie?
(-3, 5), (4, -1) (2, 0), (2, 2), (-3, -6)
Answer :
In first quadrant, both x and y coordinate are positive.
In second quadrant, x-coordinate is negative and y-coordinate is positive.
In third quadrant, x-coordinate is negative and y-coordinate is negative.
In fourth quadrant, x-coordinate is positive and y-coordinate is negative.
(-3,5) lies in second quadrant.
(4,-1) lies in fourth quadrant.
(2,0) lies on x-axis. Here y-coordinate is zero.
(2,2) lies in first quadrant.
(-3,-6) lies in third quadrant.
Question 3. Which of the following points lie on
(i) x-axis? (ii) y-axis?
A (0, 2), B (5, 6), C (23, 0), D (0, 23), E (0, -4), F (-6, 0), G (√3,0)
Answer :
A (0, 2), B (5, 6), C (23, 0), D (0, 23), E (0, -4), F (-6, 0), G (√3,0)
(i) If y-coordinate of a point is zero, then the point lies on X-axis.
C(23,0), F(-6,0) and G(√3,0) lies X-axis.
(ii) If x-coordinate of a point is zero, then the point lies on Y-axis.
A(0,2), D(0,23) and E(0,-4) lies Y-axis.
Question 4. Plot the following points on the same graph paper :
A (3, 4), B (-3, 1), C (1, -2), D (-2, -3), E (0, 5), F (5, 0), G (0, -3), H (-3, 0).
Answer :
A (3, 4), B (-3, 1), C (1, -2), D (-2, -3), E (0, 5), F (5, 0), G (0, -3), H (-3, 0).
The points are plotted in the graph below.
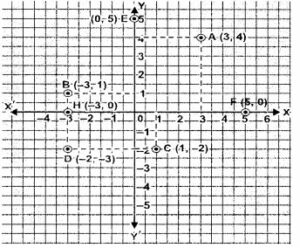
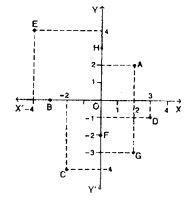
Question 5. Write the co-ordinates of the points A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H shown in the adjacent figure.
Answer :
point A is (2,2).
point B is (-3,0).
point C is (-2,-4).
point D is (3,-1).
point E is (-4,4).
point F is (0,-2).
point G is (2,-3).
point H is (0,3).
Question 6. In which quadrants are the points A, B, C and D of problem 3 located ?
Answer :
Point A (2,2), both x and y coordinate are positive. So it lies in the first quadrant.
Point B(-3,0), y-coordinate is zero. So it lies on X-axis.
Coordinate Geometry Exercise-19.1
ML Aggarwal Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page 449
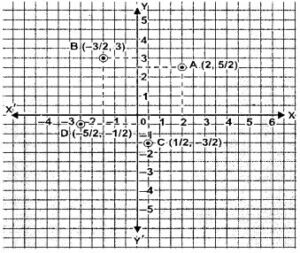
Question 7. Plot the following points on the same graph paper :
A(2, 5/2), B(-3/2, 3), C(1/2, -3/2) and D(-5/2, -1/2).
Answer :
points are A(2, 5/2), B(-3/2, 3), C(1/2, -3/2) and D(-5/2, -1/2).
The points are plotted in the graph below.
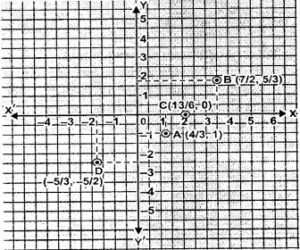
Question 8. Plot the following points on the same graph paper.
A(4/3, -1), B(7/2, 5/3), C(13/6,0), D(-5/3,-5/2).
Answer :
A(4/3, -1), B(7/2, 5/3), C(13/6,0), D(-5/3,-5/2).
The points are plotted in the graph below.
Question 9. Plot the following points and check whether they are collinear or not:
(i) (1,3), (-1,-1) and (-2,-3)
(ii) (1,2), (2,-1) and (-1, 4)
(iii) (0,1), (2, -2) and (2/3 ,0)
Answer :
(i) (1,3), (-1,-1) and (-2,-3)
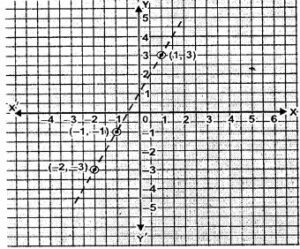
The given points lie on a line. So they are collinear.
(ii) (1,2), (2,-1) and (-1, 4)
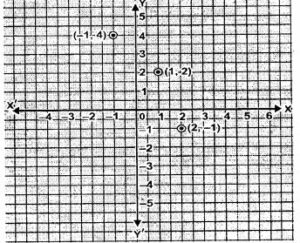
The given points do not lie on a line. So they are not collinear.
(iii) (0,1), (2, -2) and (2/3,0).
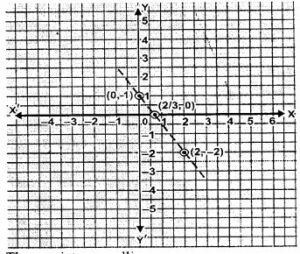
The given points lie on a line.
So they are collinear.
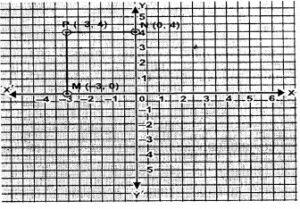
Question 10. Plot the point P(-3, 4). Draw PM and PN perpendiculars to x-axis and y-axis respectively. State the co-ordinates of the points M and N.
Answer :
P(-3,4).
The point is plotted in the graph below.
PM and PN is drawn perpendicular to x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Coordinates of point M are (-3,0) .
Coordinates of point N are (0,4).
Question 11. Plot the points A (1,2), B (-4,2), C (-4, -1) and D (1, -1). What kind of quadrilateral is ABCD ? Also find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
Answer :
A (1,2), B (-4,2), C (-4, -1) and D (1, -1).
The points are plotted in the graph below.
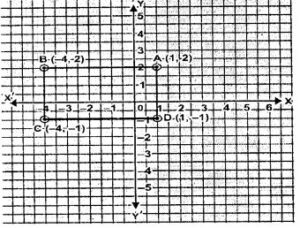
ABCD is a rectangle.
Area of rectangle ABCD = length ×breadth
= AB×AD
= (1-(-4))×(2-(-1))
= 5×3
= 15 sq. units.
Question 12. Plot the points (0,2), (3,0), (0, -2) and (-3,0) on a graph paper. Join these points (in order). Name the figure so obtained and find the area of the figure obtained.
Answer :
(0,2), (3,0), (0,-2) and (-3,0).
The points are plotted in the graph below.
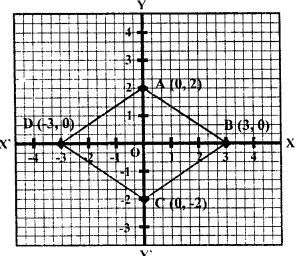
BD and AC are the diagonals of the rhombus.
Area of a rhombus = ½ ×d1×d2
Where d1 and d2 are the length of diagonals.
AC = 4 units [from graph]
BD = 6 units [from graph]
Area of rhombus ABCD = ½ ×BD×AC
= ½ ×6×4
= 12 sq. units.
Hence,
the area is 12 sq. units.
Question 13. Three vertices of a square are A (2,3), B(-3, 3) and C (-3, -2). Plot these points on a graph paper and hence use it to find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex. Also find the area of the square.
Answer :
A (2,3), B (-3, 3) and C (-3, -2).
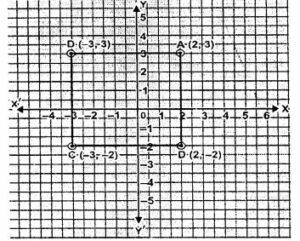
point D are (2, -2).
Here AB = 5 units
Area of the square = side ×side
Area of the square ABCD = AB×AB
= 5×5
= 25 sq. units.
Hence the area of the square is 25 sq. units.
Question 14. Write the co-ordinates of the vertices of a rectangle which is 6 units long and 4 units wide if the rectangle is in the first quadrant, its longer side lies on the x-axis and one vertex is at the origin.
Answer :
Longer side lies on x -axis and one vertex is at origin.
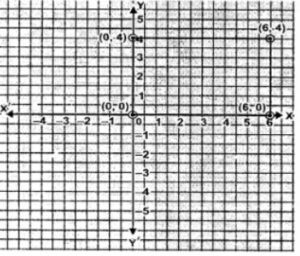
Coordinates of the rectangle are A (0,0), B (6,0), C (6,4) and D (0,4).
Question 15. In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a rectangle with length 6 units and breadth 3 units. If O is the mid-point of AB, find the coordinates of A, B, C and D.
Answer :
A rectangle which is 6 unit long and 4 units wide and this rectangle is in the third quadrant.
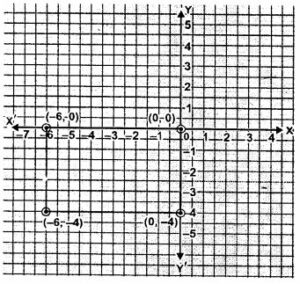
Coordinates of the rectangle are A(0,0), B(-6,0), C(-6,-4) and D(0,-4).
Question 16. The adjoining figure shows an equilateral triangle OAB with each side = 2a units. Find the coordinates of the vertices.
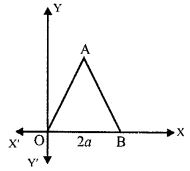
Answer :
Equilateral triangle OAB.
OA = OB = AB = 2a units.
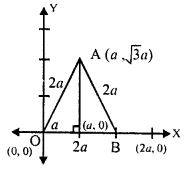
AD = √(AO2-DO2)
= √((2a)2-a2)
= √(4a2-a2)
= √(3a2)
= √3 a
Co-ordinates of O are (0,0).
Co-ordinates of A are (a, √3 a)
Co-ordinates of B are (2a,0).
Question 17. In the given figure, APQR is equilateral. If the coordinates of the points Q and R are (0, 2) and (0, -2) respectively, find the coordinates of the point P.
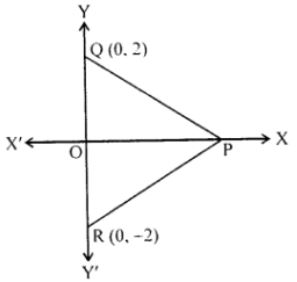
Answer :
In PQR is an equilateral triangle in which Q(0,2) and R(0,-2).
Let (x,0) be the coordinates of P.
PQ = PR = QR = 2+2 = 4
OQ = 2
In POQ,
PQ2 = OP2+OQ2
⇒ 42 = OP2+22
⇒ OP2 = 42-22
⇒ OP2 = 16-4
⇒ OP2 = 12
⇒ OP = √(4×3) = 2√3
Hence,
the coordinates of P are (2√3,0).
— : End of ML Aggarwal Coordinate Geometry Exe-19.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarawal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class-9
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends