Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-3. We Provide Step by Step Solutions to Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 8th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-3 | Elements, Compounds and Mixtures |
| Unit-1 | Elements, Compounds and Mixtures |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
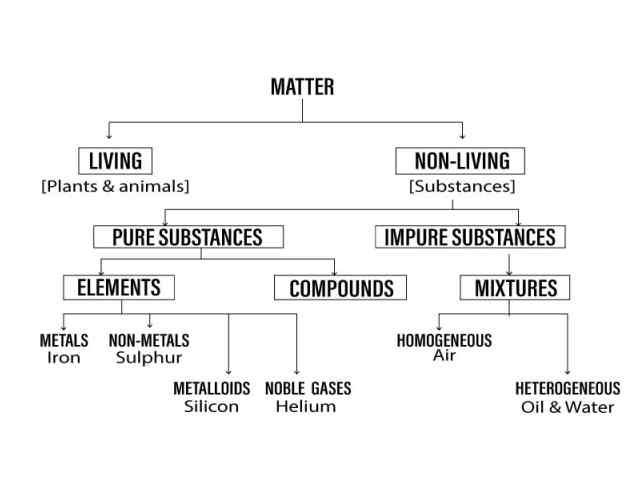
Question: 1. Represent with the help of a simple chart how matter is classified into pure or impure substances & further into elements, compounds & mixtures, with elements further segmented.
Answer:
Question: 2. Define the terms elements, compounds & mixtures with a view to show their basic difference.
Answer 2: Element:
- Element is a pure substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms.
- An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simple substances by any physical or chemical change.
- Elements are represented by symbols.
- For examples Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Iron(Fe), Gold (Au), etc.
Compound:
- Compounds are chemical substances, formed by the combination of two or more elements that are chemically bound together in a fixed ratio.
- Compounds are represented by a chemical formula like NaCl (Sodium chloride), CO (Carbon monoxide), etc.
Mixture:
- A mixture consists of molecules of two or more substances in any proportion such that they do not undergo any chemical change.
- The mixture is of two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture.
- For example Air, Tap water, Muddy water, etc.
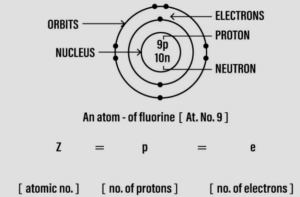
Question: 3.‘An atom is the basic unit of an element’. Draw a diagram of an atom – divisible as seen today.
Answer 3: ‘An atom is the basic unit of an element’.
Question: 4. ‘The modern periodic table consists of elements arranged according to their increasing atomic numbers’. With reference to elements with atomic numbers 1 to 20 only in the periodic table – differentiate them into – metallic elements, metalloids, non-metals & noble gases.
Answer 4: Names and symbols of metal, non-metals, metalloids, and noble – gases out of 1st 20 elements.
| Metal | Symbol | Non-metal | Symbol |
| Lithium | Li | Hydrogen | H |
| Beryllium | Be | Carbon | C |
| Sodium | Na | Nitrogen | N |
| Magnesium | Mg | Oxygen | O |
| Aluminium | Al | Fluorine | F |
| Potassium | K | Phosphorus | P |
| Calcium | Ca | Sulphur | S |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Metalloids | Symbol | Noble gas | Symbol |
| Boron | B | Helium | He |
| Silicon | Si | Neon | Ne |
| Argon | Ar |
Question: 5. Elements are broadly classified into metals & non-metals, six general differences in physical properties of metals & non-metals, two metals & two non-metals which contradict with the general physical properties – giving reasons, one difference in property between metalloids & noble gases.
Answer 5: Metallic elements :
(a) Have lustre – i.e. shine.
(b) Are malleable – i.e. can be beaten into sheets.
(c) Are ductile – i.e. can be drawn into wires.
(d) Are good conductors – of heat and electricity.
(e) have high – melting and boiling points.
(f) Have a high – density.
(g) Contain – one type of atoms – monoatomic
Non-metallic Elements :
(a) Do no have lustre.
(b) Are non-malleable – i.e. cannot be beaten into sheets.
(c) Are non-ductile – i.e. cannot be drawn into wires.
(d) Are poor conductors – of heat and electricity.
(e) Have low – melting and boiling points.
(f) How low – density.
(g) Contain – monoatomic or diatomic atoms.
Two metals which contradict properties :
- Mercury — is liquid at room temperature whereas metals are mostly solid.
- Zinc — is NON-MALLEABLE and NON-DUCTILE contradicts metal which is MALLEABLE and DUCTILE.
Two Non-metals are :
- Iodine — is lustrous contradicts non-metals have no lustre.
- Graphite — is a good conductor of electricity whereas non – metals are poor conductor of electricity.
Question: 6. With reference to elements – define the term ‘molecule’. Give two examples each of a monoatomic, diatomic & polyatomic molecule.
Answer 6: Atoms of the same element or different elements combine to form a molecule. It is the smallest particle of a substance which can normally exist independently & can retain, the physical & chemical properties of the substance.
Examples : Monoatomic molecule — Sodium [Na] and Magnesium [Mg]
Diatomic molecule — Hydrogen [H2] and Oxygen [O2]
Polyatomic molecule — Ozone [O3] and Tetra phosphorous [P4]
Question: 7. Define the term ‘compound’. In the compound carbon dioxide – the elements carbon & oxygen are combined in a fixed ratio. Explain.
Answer 7: A compound is a pure substance made up of two or more different elements [atoms] combined chemically in a fixed proportion.
(a) Contains – two or more kinds of atoms, e.g. compound – carbon dioxide [CO2].
(b) It can be broken down – into two or simpler substances – by chemical means.
(c) Properties of compounds – differ from those of their elements, e.g. CO2 contains elements – Carbon [C] is combustible and Oxygen [O] is a supporter of combustion – but carbon dioxide is non-combustible and non-supporter of combustion.
Question: 8. State five different characteristics of compounds. Give three differences between elements & compounds with relevant examples.
Answer 8: Five characteristics of compounds are:
(i) Components in a compound are in a definite proportion.
(ii) Particles in a compound are of one kind
(iii) Compounds have a definite set of properties
(iv) Elements in the compound do not retain their original properties.
(v) Components in a compound can be separated by chemical means only.
Three differences between elements & compounds are:
| S. No. |
Elements | Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Elements contain one kind of atoms only. E.g., Carbon [C], Oxygen [O] |
Compounds contain two or more kinds of atoms. E.g., Carbon dioxide [CO2] |
| 2. | Elements cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by physical or chemical means | Compounds can be broken down into two or more simpler substances by chemical means. |
| 3. | Elements have their own set of properties E.g., elements Carbon [C] is combustible and oxygen [O] supports combustion. |
Properties of compounds differ from those of their elements E.g., CO2 contains carbon and oxygen where carbon [C] is combustible and oxygen [O] supports combustion but carbon dioxide is non-combustible and non-supporter of combustion. |
Question: 9. Explain the term ‘mixture’. Differentiate between homogenous & heterogenous mixtures. State why brass is considered as a homogenous mixture while a mixture of iron & sulphur – heterogenous. Give an example of two liquids which form (a) homogenous (b) heterogenous – mixtures.
Answer 4: A mixture is made up of two or more substances — elements or compounds or both — mechanically mixed together in any proportion.
Difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures:
| Homogeneous mixtures | Heterogeneous mixtures |
|---|---|
| Constituents – uniformly mixed | Constituents – not uniformly mixed |
| Properties & composition – same throughout the mixture | Properties & composition vary throughout the mixture |
Brass is considered as a homogeneous mixture:
- The constituents are uniformly mixed and
- Properties and composition are same throughout the mixture.
A mixture of iron & sulphur is considered a heterogeneous mixture:
- The constituents are not uniformly mixed and
- Properties and composition vary throughout the mixture.
(a) Two liquids forming homogeneous mixture : Alcohol and Water
(b) Two liquids forming heterogeneous mixture : Oil and Water
Question: 10. Compare the properties of iron [II] sulphide with iron – sulphur mixture, considering iron [II] sulphide as a compound & particles of iron & sulphur mixed together as an example of a mixture.
Answer 10:
| Compound [iron [II] sulphide] | Mixture [particles of iron & sulphur] |
|---|---|
| present in a fixed proportion. | present in a varying proportion |
| always homogeneous | homogeneous or heterogeneous |
| components do not retain their original properties | components retain their original properties |
| components can be separated by chemical means | components can be separated by physical means |
Question: 11. State one method to separate the following mixtures –
(a) Two solid mixtures one of which – directly changes into vapour on heating.
(b) Two solid mixtures one of which – dissolves in a – particular solvent and other does not
(c) A solid-liquid mixture containing – an insoluble solid in the liquid component
(d) A solid-liquid mixture containing – a soluble solid in the liquid component
(e) A liquid-liquid mixture containing – two immiscible ”’ liquids having different densities
(f) A liquid-liquid mixture containing – two miscible liquids having different boiling points.
(g) A liquid-gas mixture containing – a gas dissolved in a liquid component.
(h) A gas-gas mixture containing – two gases with different densities.
(i) A mixture of different solid constituents – in a liquid constituent.
Answer 11: (a) Two solid mixtures one of which – directly changes into vapour on heating — Sublimation
(b) Two solid mixtures one of which — dissolves in a particular solvent and other does not — Solvent extraction
(c) A solid-liquid mixture containing – an insoluble solid in the liquid component — Filtration
(d) solid-liquid mixture containing – a soluble solid in liquid component — Evaporation
(e) A liquid-liquid mixture containing – two immiscible liquids having different densities — Separating Funnel
(f) liquid-liquid mixture containing – two miscible liquids having different boiling points — Fractional Distillation
(g) A liquid-gas mixture containing – a gas dissolved in a liquid component — Boiling the liquid gas mixture
(h) gas-gas mixture containing – two gases with different densities — Diffusion
(i) A mixture of different solid constituents – in a liquid constituent — Chromatography
Question 12. Explain with diagrams the process used to – separate the following substances from the given mixtures.
(a) Ammonium chloride from a mixture of – ammonium chloride & potassium chloride.
(b) Iron from a mixture of – iron & copper
(c) Sulphur from a mixture of – sulphur & copper.
(d) Potassium nitrate from a mixture of – potassium nitrate & potassium chlorate.
(e) Lead carbonate [insoluble] from a mixture of – lead carbonate & water.
(f) Lead nitrate [soluble] from a mixture of – lead nitrate & water Le. lead nitrate solution.
(g) Carbon tetrachloride from a mixture of – carbon tetrachloride [heavier component] & water.
(h) Benzene from a mixture of – benezene [b.p. 80°C] & toluene [b.p. 110°C].
(i) Different dyes – in their liquid constituent ink.
Answer: (a) By sublimation : Ammonium Chloride from a mixture of ammonium chloride & potassium chloride

Here A is Ammonium Chloride and B is Potassium Chloride.
(b) By magnetic separation : By bringing a magnet near the mixture iron pieces can be separated which will cling to the magnet.
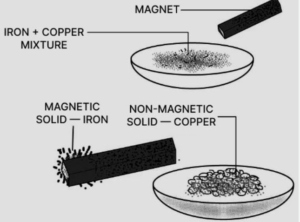
Here A is Iron and B is Copper.
(c) By solvent extraction : Mixture of copper and sulphur is added to the beaker containing solvent carbon disulphide and stirred well. Sulphur dissolves. Put this mixture on filter paper in the funnel. Copper remains on filter paper and sulphur passes into the beaker as filtrate. Sulphur separates as carbon disulphide evaporates.
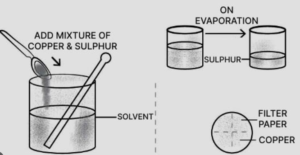
Here A is for Copper and B is Sulphur.
(d) Potassium nitrate:
KNO3 is more-soluble than potassium chlorate KClO3. On heating to get saturated solution and on cooling the saturated solution less soluble (KClO3) crystallize out. More soluble KNO3 is filtered out from hot saturated solution and is recrystallized from hot water and dried.
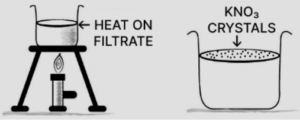

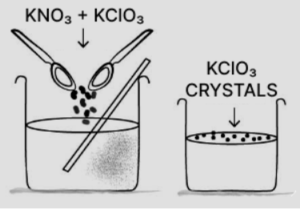
(e) Evaporation :
Lead carbonate can be separated by evaporation. On evaporation, water evaporates leaving behind solid lead carbonate which has higher M.P.
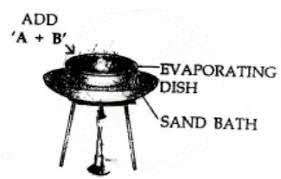
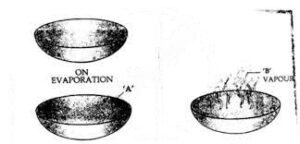
(f) Lead nitrate:
Lead nitrate is separated from soluble lead nitrate solution by crystallization.
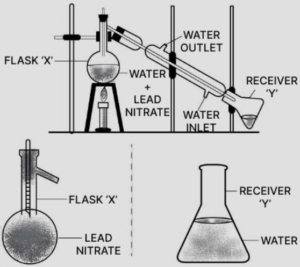
(g)By spearing:
By spearing funnel, heavier CCl4 carbon tetrachloride form the lower layer is separated when tap is opened and collected in the flask. Water the lighter top layer remains in the funnel.

(h) By fractional distillation, miscible low boiling point benzene (B.P. 80°C) evaporates on heating the mixture and condenses in and collects in flask ‘Y’ where as higher boiling pt. Toluene (B.P. 110°C) remains in flask ‘X’ after condensation.

(i) By chromatography :
Different dyes [solid constituents i.e. A, B, C, D] in ink which is the liquid constituent. By placing the ink spot containing different solid constituents [dyes] on the filter paper.

– : End of Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Class-8 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3 :–
Return to – Dalal New Simplified Chemistry ICSE Class-8 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.