Different Forms of Energy ICSE Class 10 Physics Notes. In this articles you would learn about Mechanical Potential and Kinetic Energy. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Physics.
Different Forms of Energy ICSE Class 10 Physics Notes
Point to be Discuss |
| Potential Energy |
| Forms of Potential Energy |
| Gravitational Potential Energy |
| Kinetic Energy |
| Expression for Kinetic energy |
| Relation between Kinetic Energy and Momentum |
| Work Energy Theorem |
| Forms of Kinetic Energy |
| Conversion of Mechanical Energy |
| Different Forms of energy |
| Conversion of Forms of Energy |
| Numericals |
Mechanical Energy
Mechanical energy refers to the energy possessed by an object due to its motion (kinetic energy) or its position (potential energy). It’s essentially the energy an object has that can be used to do work,
Potential Energy
Potential energy is a type of energy that is stored in an object due to its position relative to other objects
Forms of Potential Energy
Potential energy exists in several forms, including gravitational, elastic, electric, chemical, and nuclear
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. It’s the energy stored in an object when it’s lifted against gravity, ready to be released as kinetic energy when the object is allowed to fall. The amount of gravitational potential energy an object has depends on its mass and its height above a reference point
U = mgh
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass.
Expression for Kinetic energy
v² = u² + 2 a s
F = ma
W = ma * s.
s = (v² – u²) / 2a.
Substituting s = (v² – u²) / 2a into W = ma * s,
we get: W = ma * (v² – u²) / 2a.
Simplifying: The ‘a’ in the numerator and denominator cancel out:
W = m * (v² – u²) / 2.
Assuming Initial Velocity (u) = 0:
W = mv² / 2.
final kinetic energy: KE = mv² / 2.
Final Formula: Therefore,: KE = 1/2 * mv².
Relation between Kinetic Energy and Momentum
Start with the kinetic energy formula: KE = 1/2 * m * v².
Rearrange the momentum formula: v = p / m.
Substitute the velocity into the kinetic energy : KE = 1/2 * m * (p/m)².
Simplify the equation: KE = 1/2 * m * (p²/m²) = p²/2m
Work Energy Theorem
The work-energy theorem states that the work done by the net force acting on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. Mathematically, this is expressed as W = ΔKE, where W represents the total work done, and ΔKE represents the change in the object’s kinetic energy
The principle of work and kinetic energy (also known as the work-energy theorem) states that the work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle
Expression for Work Energy Theorem
F = ma,
KE = 1/2mv^2,
Relating Displacement to Velocity and Acceleration:
Using equation v^2 = u^2 + 2as
Substitute F = ma into the work equation (W = Fd)
W = mad = m (a) ((v^2 – u^2) / 2a)
= (1/2)mv^2 – (1/2)mu^2.
Forms of Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy, the energy of motion, can manifest in several forms, including translational, rotational, and vibrational,
Different between kinetic energy and potential energy
| Sr.no | Kinetic Energy | Potential Energy |
| 1. | Kinetic energy is the kind of energy present in a body due to the property of its motion | Potential Energy is the type of energy present in a body due to the property of its state |
| 2. | It can be easily transferred from one body to another | It is transferable into kinetic only |
| 3. | The determining factors for kinetic energy are Speed or velocity and mass | Here, the determining factors are Height/ distance and mass |
| 4. | Flowing water is one of the examples of kinetic energy | Water present at the top of a hill is an example of potential energy |
| 5. | It is relative with respect to nature | It is non-relative with respect to nature |
Conversion of Mechanical Energy
Potential energy and kinetic energy are constantly converting back and forth. Potential energy, which is energy stored due to an object’s position or state, transforms into kinetic energy, the energy of motion, when a force acts upon it, causing it to move. Conversely, kinetic energy can transform back into potential energy as an object slows down or changes its position,
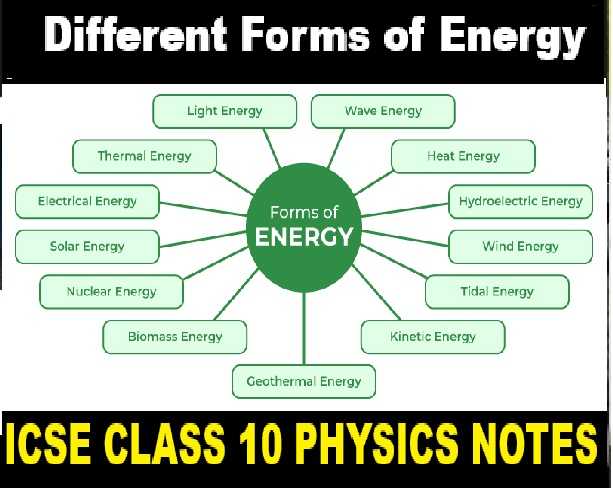
Different Forms of Energy
Energy exists in various forms, including kinetic, potential, thermal, light, sound, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and radiant energy
Conversion of Forms of Energy
Car Engine:The chemical energy stored in gasoline is converted into mechanical energy, which is used to move the car.
Human Body: The chemical energy from food is converted into mechanical energy for movement and other bodily functions.
Battery: Chemical reactions within a battery convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
Light Bulb: Electrical energy is converted into light and heat.
Speaker: Electrical energy is converted into sound energy.
Electric Motor: Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
Solar Panels: Solar energy (light) is converted into electrical energy by solar panels.
Plants: Plants convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
Wind Turbines: Wind energy (kinetic) is converted into mechanical energy, which can be used to generate electricity.
Hydroelectric Dams: Potential energy of stored water is converted into kinetic energy as it flows down, and then into electrical energy.
Geothermal Energy: Heat energy from the Earth is converted into electrical energy.
–: End of Different Forms of Energy ICSE Class 10 Physics Notes about Mechanical Potential and Kinetic Energy :–
Please share with your friends if helpful
Return to :
- Concise Selina Physics Solutions for ICSE Class 10.
- Goyal Brothers Prakashan Physics Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks