Digestive System Goyal Brother Solutions ICSE Class-9 Biology Ch-13. We Provide Solutions of Exercise-13 Digestive System Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Ch-13. All Type exercise question such as name the following, difference between, MCQs, Answer the question. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
ICSE Class 9 Biology Ch-13 Digestive System Goyal Brother Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brother Prakashan |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| Writer | Dr. S.K. Aggarwal |
| Chapter-13 | Digestive System |
| Topics | Solutions of Exercises-13 |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
Ch-13 Digestive System
Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
(Page-135-136)
Questions 1. Name the following parts of a tooth:
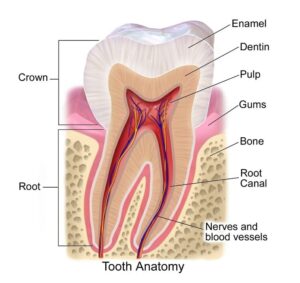
(i) The cavity surrounded by the dentine.– Pulp Cavity.
(ii) The part in level with the gum.– Neck
(iii) The part embedded in sockets of the jaw bone.– Root
(iv) The solid tissue inner to enamel– Dentine
Questions 2. Give technical terms for the following:
(i) Arrangement of teeth in the jaws.– Dentition
(ii) Gap between the incisors and premolars in herbivores.– Diastema
(iii) Part of tooth lying above the gums.– Crown
(iv) Hard, whitish exposed part of a tooth.– Enamel
Questions 3. Write the functions of the following parts
(i) Enamel– As the outer layer of the tooth, enamel serves as a protective barrier against harmful bacteria and acids that can attack the teeth and cause dental problems. It also protects the teeth from the pressure and stress of the teeth’s daily use, including in chewing, biting, and grinding.
(ii) Pulp cavity–The pulp has several important functions, including: Sensory function: Pain from trauma to the dentin and/or pulp, differences in temperature, and pressure are caused by stimulation of the pulp. Formation of dentin: The pulp is responsible for the formation of dentin.
(iii) Cement– The main function of cement is to act as hydraulic binder, which increases the bond between fragmented particles, so it can enable their use in different fields. The resulted material will have different physical and mechanical properties from the initial materials.
Questions 4. Explain the following terms:
(i) Diastema– Diastema is a gap between your teeth. This can happen between any of your teeth. Because of its position, it’s most noticeable when there’s a gap between your upper front teeth.
(ii) Carnassial teeth– Most carnivores have carnassial, or shearing, teeth that function in slicing meat and cutting tough sinews. The carnassials are usually formed by the fourth upper premolar and the first lower molar, working one against the other with a scissorlike action.
(iii) Dentine.– Dentin or dentine is a layer of material that lies immediately underneath the enamel of the tooth. It is one of the four major components of the tooth which comprises: The outer hard enamel. The dentin underneath the enamel. The dental pulp that lies soft and encased within the dentin.
Questions 5. Complete the following statements:
(i) The enzyme present in saliva is ….amylase…………. (amylase/pepsin/lipase)
(ii) Enzyme lipase converts fats into fatty acids and …maltose………….. (sugars/glycerol/maltose)
(iii) Enzyme trypsin is produced in …..duodenum………… region of alimentary canal. (duodenum/stomach/ileum)
Questions 6. Answer the following questions:
(i) What is dentition? Give dental formula of humans.
Ans– the arrangement , type, and number of the teeth in a particular species is dentition. The dental formula for the adult human beings is 2123/2123. There are 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars aand 3 molars in one row.
(ii) Name the different kinds of teeth in mammals and state their functions.
Ans– The four main types of teeth are:
- Incisors – Your incisors are eight teeth in the front center of your mouth (four on both bottom and top). …
- Canines – Your canines are the next teeth that develop in your mouth. …
- Premolars – Premolars are used for tearing and crushing food. …
- Molars – Your molars are your largest teeth.
(iii) Draw labelled diagram to show the internal structure of a tooth.
(iv) Identify the tooth shown below and mention its function in human beings.
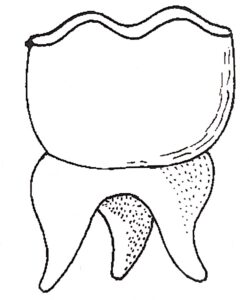
Ans: Teeth shown in figure is Molar teeth. Function of molar teeth is chewing food.
(v) One should not talk while swallowing. Why?
Ans– When there is air in the pharynx, the vocal cords are vibrated and sounds are produced which allows the person to speak. When the person is eating or swallowing, the epiglottis is closed so that the food does not enter the tracheal tube. This is the reason that a person cannot swallow and talk simultaneously.
(vi) Mention the functions of liver.
Ans– Functions of the liver
- Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion.
- Production of certain proteins for blood plasma.
- Production of cholesterol and special proteins to help carry fats through the body.
(vii) Describe the role of the following enzyme in the digestion of food:
(a) Amylase– Amylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. Starch comprises a significant portion of the typical human diet for most nationalities.
(b) Pepsin– Pepsin is a stomach enzyme that serves to digest proteins found in ingested food. Gastric chief cells secrete pepsin as an inactive zymogen called pepsinogen. Parietal cells within the stomach lining secrete hydrochloric acid that lowers the pH of the stomach. A low pH (1.5 to 2) activates pepsin
(c) Lipase.– Lipase is an enzyme the body uses to break down fats in food so they can be absorbed in the intestines. Lipase is produced in the pancreas, mouth, and stomach.
(viii) Which part or organ of the human digestive system is associated with
(a) Ingestion– From the esophagus, food then travels to the stomach, where it breaks down further with the help of the acids and powerful enzymes secreted by the stomach. This semi-digested food then travels down to the small intestine, where secretions from the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas further act on the food particles.
(b) Digestion– A major digestive organ is the stomach. Within its mucosa are millions of embedded gastric glands. Their secretions are vital to the functioning of the organ. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine which is the longest part of the GI tract.
(c) Absorption of food– The small intestine absorbs most of the nutrients in your food, and your circulatory system passes them on to other parts of your body to store or use. Special cells help absorbed nutrients cross the intestinal lining into your bloodstream.
(d) Absorption of water.– The walls of the small intestine absorb water and the digested nutrients into your bloodstream. As peristalsis continues, the waste products of the digestive process move into the large intestine.
Questions 7. How will you test for the presence of following in the various food items?
(i) Starch– To know the presence of starch in any given sample of food, the iodine test can be performed. In this, iodine solution is used. In this, few drops of iodine solution is added to the food sample. If starch is present in a food item, it will turn blue-black colour.
(ii) Sugar– Dissolve the food item in water and take the solution in a test tube and add a few drops of benedict’s solution in it. Heat it for a minute. A red precipitate will be formed at the bottom showing the presence of sugar in the given food item.
(iii) Protein– Proteins can be tested by using the following methods. Take the given food sample and prepare its extract. Add the aqueous copper sulphate to the prepared food extract. A solution that turns violet in colour confirms the presence of protein in the foodstuff.
(iv) Fat– Test if a food item contains fat.
- Take a small quantity of the food item to be tested.
- Wrap the food item in a piece of paper and crush it.
- Straighten the paper.
- Dry the paper by keeping it in sunlight for a while.
- Observe the paper.
- An oily patch on the paper indicates the presence of fats in the tested food item.
Questions 8. Observe the figure given below and answer the following questions:
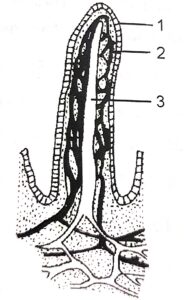
(i) What does the figure represent?
Ans– Single Villus Enlarged
(ii) Label the parts 1-3.
Ans– 1. Epithelium 2. Blood Capillaries 3. Lymphatic Capillary
(iii) Mention the role of structure shown in the figure.
Ans–The structure of the small intestine is designed for absorption of nutrients.
Questions 9. Draw a labelled diagram to show the alimentary canal in humans.
Answer : please refer que-10 figure
Questions 10. Observe the figure given below and answer the following questions:
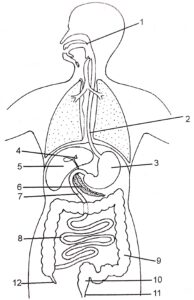
(i) What does this figure show?— Human Digestive System.
(ii) Label the parts marked 1–12.
Ans– 1-mouth 2- esophagus 3- stomach 4- gall bladder 5- liver 6- pancreas 7- appendix 8- small intestine 9- large intestine 10- rectum 11- anus
–: End of Digestive System Goyal Brother Biology Solutions:–
Return to:- ICSE Biology for Class 9 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks



Nice
thanks for positive response