Economic Applications Sem-2 ICSE Specimen Question Paper Solved Class-10. Step by step solutions of ICSE Class-10 specimen model sample Question paper so that student can achieve their goal in next upcoming exam of council . Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
Economic Applications Sem-2 ICSE Specimen Question Paper Solved Class-10
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 10th (X) |
| Subject | Economic Applications |
| Topic | Semester-2 ICSE Specimen Paper Solved |
| Syllabus | on bifurcated syllabus (after reduction) |
| session | 2021-22 |
| Question Type | Descriptive Type (as prescribe by council) |
| Total question | Total- 7 with all parts {Sec-A & B } |
| Max mark | 50 |
Economic Applications Sem-2 Specimen Question Paper Solved for ICSE Class-10
Warning :- before viewing solution view Question Paper
SECTION A
(Attempt all questions)
Economic Applications Sem-2 Specimen Question Paper Solved for ICSE Class-10
Question 1:
Choose the correct answers to the questions from the given options. (Do not copy the question, Write the correct answer only.)
(i) Which of these is the apex bank of the Indian Banking System?
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Central Bank of India
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Canara Bank
Answer : (c) Reserve Bank of India
(ii) SLR stands for:
(a) Statutory Limit Rationing
(b) Standard Liquid Requirement
(c) Statutory Liquidity Ratio
(d) Standard Limit Rationing
Answer : (c) Statutory Liquidity Ratio
(iii) The policy of converting public ownership of an asset to private ownership is ____________.
(a) Nationalisation
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) Privatisation
Answer : (d) Privatization
(iv) Which of these is generally a short term loan?
(a) Cash credit
(b) Home loans
(c) Overdraft
(d) Car loans
Answer : (a) Cash credit
(v) Which of the following is a selective/qualitative method of credit control:
(a) Bank Rate
(b) Cash Credit Ratio
(c) Open Market Operations
(d) Moralsuasion
Answer : (b) Cash Credit Ratio
(vi) Identify the type of taxation shown in the figure below:
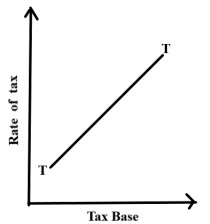
(a) Progressive taxation
(b) Regressive taxation
(c) Proportional taxation
(d) Degressive taxation
Answer : Update soon….
(vii) Study the relationship in the first pair of words and complete the second pair:
Creeping inflation : 2% to 3%
Running inflation : __________
(a) 8% to 9%
(b) 8% to 20%
(c) 3. 3% to 8%
(d) 20% to 40%
Answer : Update soon….
(viii) Study the relationship in the first pair of words and complete the second pair:
Income tax : Direct tax
_____________ : Indirect tax
(a) Property tax
(b) Entertainment tax
(c) House tax
(d) Road tax
Answer : Update soon….
(ix) Which of the following does not belong to the group?
(a) Accepting deposits
(b) Giving loans
(c) Controlling credit
(d) Creating credit
Answer : Update soon….
(x) A compulsory payment by the citizens of the country to the government without any expectation of corresponding benefits for such payments. This defines:
(a) Tax
(b) Subsidy
(c) Discount
(d) Concession
Answer : (a) Tax
SECTION B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Economic Applications Sem-2 Specimen Question Paper Solved for ICSE Class-10
Question 2:
(i) Define money.
(ii) State two advantages of a bank account.
(iii) Mention any three demerits of Public Sector Enterprises.
(iv) What are direct taxes? State two merits of direct taxes.
Answer :
(i) Money : Money is an economic unit that functions as a generally recognized medium of exchange for transactional purposes in an economy. Money provides the service of reducing transaction cost, namely the double coincidence of wants. Money originates in the form of a commodity, having a physical property to be adopted by market participants as a medium of exchange.
(ii) (a) Bank accounts offer convenience. For example, if you have a checking account, you can easily pay by check or through online bill pay.
(b) Bank accounts are safe. Your money will be protected from theft and fires.It’s an easy way to save money.Bank accounts are cheaper.
(iii) Update soon….
(iv) A direct tax is an equitable tax to all the citizens.
Equity: A direct tax is an equitable tax to all the citizens.
Certainty: A direct tax satisfies the strength of certainty.
Question 3:
(i) What is Privatization?
(ii) Differentiate between progressive taxation and proportional taxation.
(iii) Briefly explain how Cash Reserve Ratio can be used to control credit.
(iv) Explain how money acts as a measure of value.
Answer :
(i) The transfer of ownership, property or business from the government to the private sector is termed privatization. The government ceases to be the owner of the entity or business.
(ii) Progressive tax: A tax that takes a larger percentage of income from high-income groups than from low-income groups.
Proportional tax : A tax that takes the same percentage of income from all income groups.
(iii) CRR helps in keeping inflation under control. If there is a threat of high inflation in the economy, RBI increases the CRR, so that banks need to keep more money in reserves, effectively reducing the amount of money that is available with the banks. This curbs excess flow of money in the economy.
(iv) Money acts as a unit of account or money is the measure of exchange value. This means that money is a sort of common denominator, through which the exchange value of all goods and services can be expressed without any difficulty.
Question 4:
(i) Name two instruments of Fiscal Policy.
(ii) Explain why the purchasing power of money falls when price level rises.
(iii) State three reasons why privatization is not always desirable.
(iv) What are Commercial banks? Name one commercial bank in India.
Answer :
(i) Fiscal Policy are : Taxes, Expenditure
(ii) When the price level rises money can buy less goods and services. So we say that its purchasing power has fallen. Conversely, when the price level falls, money can buy more and we can say its purchasing power has gone up. Thus, the value of money changes inversely with the price level.
(iii) Update soon….
(iv) The term commercial bank refers to a financial institution that accepts deposits, offers checking account services, makes various loans, and offers basic financial products like certificates of deposit (CDs) and savings accounts to individuals and small businesses. State Bank of India is the commercial bank.
Question 5:
(i) Give one difference between qualitative and quantitative credit control.
(ii) What is galloping inflation?
(iii) State three differences between a Commercial bank and a Central bank.
(iv) What type of tax is Goods and Services Tax? State two features of this type of tax.
Answer :
(i) Quantitative credit control refers to overall credit in the economy, affecting all sectors of the economy equally and without discrimination. Qualitative credit control refers to selective credit control that focuses on allocation of credit to different sectors of the economy.
(ii) Galloping inflation (also jumping inflation) is one that develops at a rapid pace (dual or triple-digit annual rates), perhaps only for a brief period of time.
(iii)
| Central bank is the apex financial institution of the country that is concerned with formation of monetary policies and the way money should be regulated in the economy | It is a type of financial institution that is concerned with providing banking services to the general public and businesses by facilitating deposit, offering loan facilities |
| Central bank is always having public ownership | Commercial banks can be either public or private in their ownership |
| There is only one central bank in a country | There can be many commercial banks in a country |
(iv) GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It is an Indirect tax which introduced to replacing a host of other Indirect taxes such as value added tax, service tax, purchase tax, excise duty, and so on. GST levied on the supply of certain goods and services in India. It is one tax that is applicable all over India.
Question 6:
(i) Give two reasons as to why a Central Bank is needed.
(ii) Mention two important differences between Public Sector and Private Sector.
(iii) Explain how taxes can bring about equality in income distribution.
(iv) What are term/time deposits? Explain any one type of term deposit.
Answer :
(i)
- To control the supply of money and credit in the economy
- To control the entire banking system of the country
- Have a sound monetary policy to achieve full employment and stability
(ii)
| Public Sector | Private Sector |
|---|---|
| This sector is controlled and managed by the government. | This sector is owned by a private individual. |
| The purpose of the public sector is not just to earn profits. | Activities in the private sector are guided by the motive to earn profits. |
(iii) Updates soon ………
(iv) Updates soon ………
Question 7:
(i) What is bank rate?
(ii) What are current accounts?
(iii) Can inflation lead to economic development? Give a reason for your answer.
(iv) Explain how an increase in sales tax can cause an increase in price.
Answer :
(i) Bank rate is the rate charged by the central bank for lending funds to commercial banks.
(ii) A current account, also known as financial account is a type of deposit account maintained by individuals who carry out significantly higher number of transactions with banks on a regular basis. It is created by the bank on request of the applicant and is made available for frequent or immediate access.
(iii) Updates soon ………
(iv) The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Similarly, the price the seller obtains falls, but by less than the tax.
Return to :- ICSE Class-10 Specimen Paper Semester-2 of 2021-22
thanks
Please share with your ICSE friends