Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
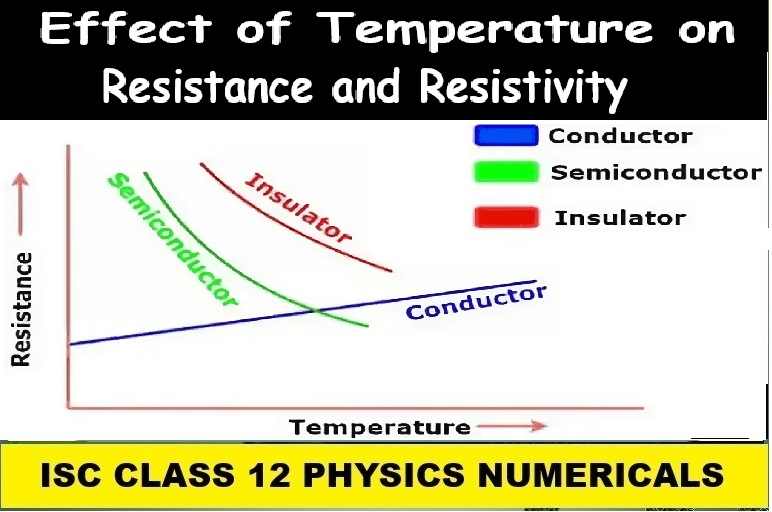
Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-5 | Electric Resistance and Ohm’s Law |
| Topics | Numericals on Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Numericals on Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity
Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law
Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity:– In most conductors, increasing the temperature leads to a higher resistance and resistivity. This is because increased temperature causes atoms to vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move through the material and reducing conductivity. The relationship between temperature and resistivity is generally linear, with a positive temperature coefficient of resistance
Que-17. The resistance of a silver wire at 0°C is 1.25 Ω. Up to what temperature it must be heated so that its resistance is doubled? The temperature coefficient of resistance of silver is 0.00375°C¯¹. Will the temperature be the same for all conductors of silver?
Ans-17 Given Rt = 2Ro
According to formula
Rt = Ro(1 + 2t)
=> 2R0 = Ro(1 + 2t)
=> 2-1 = 0.00375 t
=> t = 1/0.00375 = 267°C
Que-18. The resistance of the coil used in a platinum-resistance thermometer at 0°C is 3.00 Ω and at 100°C is 3.75 Ω. Its resistance at an unknown temperature is measured 3.15 Ω. Calculate the unknown temperature.
Ans-18 Ro = 3.00 Ω R100 = 3.75 Ω Rt = 3.15 Ω t = ?
R100 = Ro(1 + 100α)
=> 3.75 = 3.00 (1 + 100α)
=> 1 + 100α = 3.75 / 3.00 = 1.25
=> 100α = 1.25 – 1 = 0.25
=> α = 0.0025 °C¯¹
again, Rt = Ro(1 + αt)
=> 3.15 = 3 (1 + 0.0025 t)
=> 3.15/3 – 1 = 0.0025 t
=> 1.05 – 1 = 0.0025 t
=> t = 0.05 / 0.0025 = 20°C
Que-19. The resistance of a carbon filament at 0°C is 104 Ω. What should be the resistance of an iron filament which should be connected in series with the carbon filament so that the resistance of the combined filament does not change with temperature? The temperature coefficient of resistance of iron is α = + 0.0052°C¯¹ and of carbon is – 0.0003°C¯¹.
Ans-19 effect will be multiplied when increase in resistance are equal with temp and opposite and their sum is zero
i.e. Ro α t (copper) = Ro α t (carbon) = 0
=> Ro x 0.0052 x t + 104 (-0.0003) t = 0
=> Ro = 104 x 0.0003 / 0.0052 = 6 Ω
Que-20. A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
Ans-20 Rt = Ro(1 + αt)
=> 4.8 = 3.0 (1 + α x 150)
=> 4.8/3 = 1 + α x 150
=> 1.6 – 1 = 150 α
=> α = 0.6 / 150
=> α = 4 x 10^-3 °C¯¹
— : End of Effect of Temperature on Resistance and Resistivity Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Ch-5 Electric Resistance and Ohms Law solutions. :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends