Elements and Compounds Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-1 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Unit-1 Elements and Compounds Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-2. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -2 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Elements and Compounds Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-1
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 6th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-2 | Elements, Compounds and Mixtures |
| Unit-1 | Elements & Compounds |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Elements and Compounds Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-1
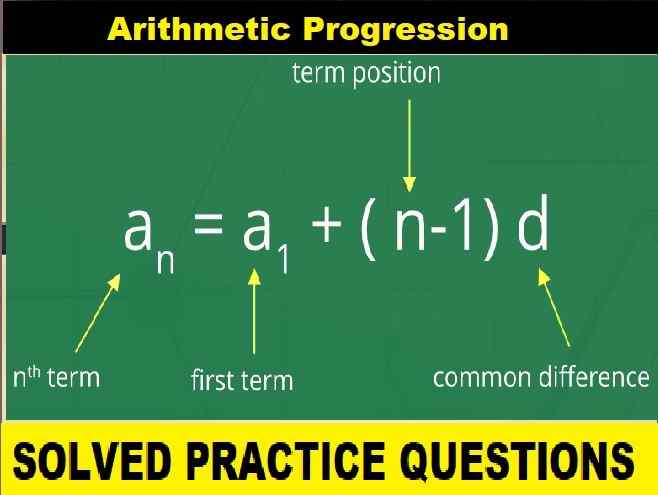
Question: 1. Classify substances into pure & impure substances in the form of a chart or tabulation.
Answer: Pure & impure substances in the form of a chart or tabulation:
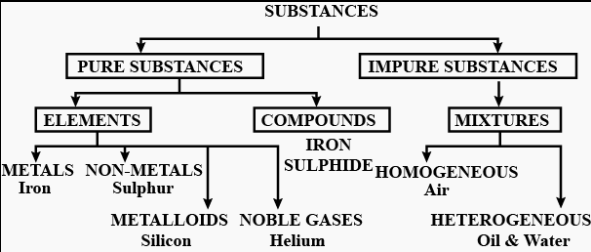
Question: 2. Differentiate between the terms – elements, compounds & mixtures.
Answer: Differentiate between the terms – elements, compounds & mixtures:
Element is the simplest pure substances in which all the atoms are exactly the same. It can be classified into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Example – Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen [1 Mark]Compounds –
It is a combination of two or more elements. It is a pure substance.
Example – Water, Carbon dioxide [1 Mark]Mixtures –
A mixture consists of two or more substances which are not combined chemically. The substances combined in a mixture are in any ratio. Examples: sand and salt, flour and husk. [1 Mark]
Question: 3. The important physical properties of substances are colour, odour, nature, density & solubility in water. Name –
a] two coloured gases [with their colours]
b] a gas with a pungent, choking odour which is lighter than air
c] a poisonous gas almost as heavy as air.
Answer: The important physical properties of substances are colour, odour, nature, density & solubility in water. Name –
(c) Carbon monoxide
Question: 4. Complete the statement – an element is a pure substance made up or [identical/different] atoms.
Answer: An element is a pure substance made up of atoms.
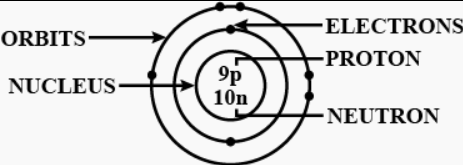
Question: 5 Draw a labelled diagram of an atom including its nucleus, orbits & their contents.
Answer: Draw a labelled diagram of an atom including its nucleus, orbits & their contents:
Question: 6. Elements are classified into – Metals – Non-metals – Metalloids – Noble gases.
State which of A, B, C, D is a –
i] Metallic element
ii] Non-metallic
iii] Metalloid
iv] Noble gas
Answer:
A: Is non-malleable, non-ductile & a poor conductor of electricity ….Non-metallic element…
B: Has luster, is malleable and ductile & a good conductor of heat ….Metallic element…
C: Is unreactive and inert and present in traces in air ….Noble gas…..
D: Shows properties of both metals and non-metals ….Metalloid….
Question: 7. An atom of an element is denoted by a ‘symbol’. Explain the meaning of the term ‘symbol’.
State a reason for representing the following elements by their symbols.
a] Hydrogen by ‘H’
b] Helium by ‘He’
c] Copper by ‘Cu’
Answer: S The short form or abbreviated name of the element (or radicals) The reason for representing the following elements by their symbols are as follow :
(a) Hydrogen by ‘H’ – First letter of the name of the element
(b) Helium by ‘He’ – First two letters of the name of Noble gases
(c) Copper by ‘Cu’ – Deriving symbols from their Latin names
Question: 8. Match the metallic elements – with their correct symbols:
| Metallic elements | Symbols |
| 1. Potassium | (a) Ca |
| 2. Sodium | (b) Zn |
| 3. Calcium | (c) Pb |
| 4. Magnesium | (d) Hg |
| 5. Zinc | (e) Cu |
| 6. Aluminum | (f) Au |
| 7. Iron | (g) K |
| 8. Lead | (h) Fe |
| 9. Copper | (i) Al |
| 10. Mercury | (j) Na |
| 11. Silver | (k) Mg |
| 12. Platinum | (l) Pt |
| 13. Gold | (m) Ag |
Answer:
| Metallic elements | Symbols |
| 1. Potassium | (a) K |
| 2. Sodium | (b) Na |
| 3. Calcium | (c) Ca |
| 4. Magnesium | (d) Mg |
| 5. Zinc | (e) Zn |
| 6. Aluminum | (f) Al |
| 7. Iron | (g) Fe |
| 8. Lead | (h) Pb |
| 9. Copper | (i) Cu |
| 10. Mercury | (j) Hg |
| 11. Silver | (k) Ag |
| 12. Platinum | (l) Pt |
| 13. Gold | (m) Au |
Question: 9. Match the non-metallic elements – with their correct symbols:
| Non-metallic elements | Symbols |
| 1. Carbon | (a) O |
| 2. Chlorine | (b) I |
| 3. Oxygen | (c) Si |
| 4. Phosphorus | (d) C |
| 5. Hydrogen | (e) Cl |
| 6. Nitrogen | (f) P |
| 7. Iodine | (g) F |
| 8. Bromine | (h) H |
| 9. Fluorine | (i) S |
| 10. Silicon | (j) Br |
| 11. Sulphur | (k) N |
Answer:
| Non-metallic elements | Symbols |
| 1. Carbon | (a) C |
| 2. Chlorine | (b) Cl |
| 3. Oxygen | (c) O |
| 4. Phosphorus | (d) P |
| 5. Hydrogen | (e) H |
| 6. Nitrogen | (f) N |
| 7. Iodine | (g) I |
| 8. Bromine | (h) Br |
| 9. Fluorine | (i) F |
| 10. Silicon | (j) Si |
| 11. Sulphur | (k) S |
Question: 10. Match the noble gases – with their correct symbols:
| Noble gases | Symbols |
| 1. Helium | (a) Ar |
| 2. Neon | (b) Xe |
| 3. Argon | (c) Rn |
| 4. Krypton | (d) He |
| 5. Xenon | (e) Kr |
| 6. Radon | (f) Ne |
Answer:
| Noble gases | Symbols |
| 1. Helium | (a) He |
| 2. Neon | (b) Ne |
| 3. Argon | (c) Ar |
| 4. Krypton | (d) Kr |
| 5. Xenon | (e) Xe |
| 6. Radon | (f) Rn |
Question: 11. Give a reason why elements are tabulated in a table called the ‘Periodic table’.
Answer: Give a reason why elements are tabulated in a table called the ‘Periodic table’:
- or arranging all the elements In a systematic and simple manner, the arrangement of elements was done In the form of a table called
- In this, elements are arranged in Increasing order of their atomic numbers.
- Elements in the Periodic Table are arranged in Horizontal rows called and vertical columns called
- . Metallic elements are placed on the , non-metallic on the and noble gases on the of the Periodic table.
Question: 12. Give the names and symbols of the first twenty elements of the periodic table. Differentiate them into metals, non-metals, metalloids & noble gases.
Answer:
| Metals | Metalloids | Non-Metals | Noble Gases |
| Lithium-Li | Boron-B | Carbon-C | Helium-He |
| Beryllium-Be | Silicon-Si | Nitrogen-N | Neon-Ne |
| Sodium-Na | Oxygen-O | Argon-Ar | |
| Magnesium-Mg | Fluorine-F | ||
| Aluminium-Al | Phosphorus-P | ||
| Potassium-K | Sulphur-S | ||
| Calcium-Ca | Chlorine-Cl | ||
| Scandium-Sc | |||
| Titanium-Ti |
Question: 13. Explain the term – molecules. Give three examples of atoms of the same elements forming a molecule. State the atomicity of the same.
Answer: Atoms of the same element or different elements combine to form a molecule. Atoms of the same element forming a molecule
- Atomicity is the number of atoms present in one molecule of the element.
Question: 14. Give one example of –
a] a triatomic molecule
b] a polyatomic molecule
Answer: Give examples of:-
a] Triatomic molecules: A triatomic molecule is made up of three atoms. Ozone (O3,), a form of oxygen, is a triatomic molecule. The atomicity of triatomic molecules is 3.
b] Polyatomic molecules: A polyatomic molecule is made up of more than three atoms. Phosphorus (P) as P4 and sulphur (S) as S8 occur in nature as polyatomic molecules. Their atomicities are 4 and 8, respectively.
Question: 15. Explain the term – compounds. Give the example of a compound containing –
a] hydrogen & oxygen
b] carbon & oxygen
c] nitrogen & oxygen
d] calcium & oxygen
Answer: A compound is a pure substance made up of two or more different elements combined chemically in a fixed proportion. Example of Atoms of different elements forming a compound:
Question: 16. State two characteristics of water which prove that it is a – compound.
Answer: State two characteristics of water which prove that it is a – compound:
Question: 17. Explain the term ‘chemical formula’. State what a chemical formula denotes.
Answer: The chemical formula is a representation of a substance either element or compound by means of symbols.
Question: 18. Give the symbols and the number of atoms of each element present in –
a] sodium chloride
b] water
c] carbon dioxide
d] zinc chloride
Answer: (a) Sodium chloride 1 atom of sodium and 1 atom of chlorine are present.
Question: 19. For writing a chemical formula – ‘symbols’ & combining capacity of an element with hydrogen i.e. ‘valency’ should be known. Explain the term – combining capacity of an element i.e. valency.
Answer: For writing a chemical formula – ‘symbols’ and combining capacity of an element with hydrogen i.e. ‘valency’ should be known. Explain the term – combining the capacity of an element i.e. valency.
The combining power of an element especially as measured by the number of hydrogen atoms can combine or displace with the element.
Question: 20. State what are radicals. Give the names of the radicals –
a] NO3
b] OH
c] SO4
d] CO3
Answer: A radical is an atom or group of atom of same or different elements that behaves in the manner of positive or negative ions.
Question: 21. Match the symbols of – metallic elements – with their correct combining power or capacity.
a] K
b] Zn
c] Al
d] Na
e] Ca
Combining power or capacity – A: 3; B: 2; C: 1. [positive valencies]
Answer:
Question: 22. Match the symbols of – non-metallic elements – with their correct combining power or capacity.
a] O
b] S
c] Cl
Combining power or capacity – A: 3; B: 2; C: 1. [negative valencies]
Answer: (a) O — Valency-2 (B)
(b) S — Valency-2 (B)
(c) Cl — Valency-1 (C)
Question: 23. Match the symbols of -radicals – with their correct combining power or capacity [valency].
a] OH
b] SO4
c] NO3
d] CO3
Combining power or capacity – A: 3; B: 2; C: 1. [negative valencies]
Answer:
Question: 24. Write the formula of the compound formed – given symbols & combining power or capacity [valency] or each element in the compound.
a] K1+ Cl1-
b] Na1+ Cl1-
c] Ca2+ NO31-
Answer:

Question: 25. Match the formulas of the following – gases – with their correct names:
| Gases | Name |
| 1. H2 | (a) Ammonia |
| 2. N2 | (b) Nitrogen dioxide |
| 3. O2 | (c) Oxygen |
| 4. Cl2 | (d) Hydrogen |
| 5. HCI | (e) Nitrogen |
| 6. NH3 | (f) Chlorine |
| 7. CO | (g) Carbon monoxide |
| 8. CO2 | (h) Sulphur dioxide |
| 9. SO2 | (i) Nitrogen monoxide |
| 10. NO | (j) Carbon dioxide |
| 11. NO2 | (k) Hydrogen chloride |
Answer:
| Gases | Name |
| 1. H2 | (a) Hydrogen |
| 2. N2 | (b) Nitrogen |
| 3. O2 | (c) Oxygen |
| 4. Cl2 | (d) Chlorine |
| 5. HCI | (e) Hydrogen chloride |
| 6. NH3 | (f) Ammonia |
| 7. CO | (g) Carbon monoxide |
| 8. CO2 | (h) Carbon dioxide |
| 9. SO2 | (i) Sulphur dioxide |
| 10. NO | (j) Nitrogen monoxide |
| 11. NO2 | (k) Nitrogen dioxide |
Question: 26. Match the formulas of the following – acids – with their correct names:
| Acids | Name |
| 1. HCl | (a) Carbonic acid |
| 2. HNO3 | (b) Sulphuric acid |
| 3. H2SO4 | (c) Hydrochloric acid |
| 4. H2CO3 | (d) Nitric acid |
Answer:
| Acids | Name |
| 1. HCl | (a) Hydrochloric acid |
| 2. HNO3 | (b) Nitric acid |
| 3. H2SO4 | (c) Sulphuric acid |
| 4. H2CO3 | (d) Carbonic acid |
Question: 27. Match the formula of the following – bases – with their correct names:
| Bases | Name |
| 1. NaOH | (a) Potassium hydroxide |
| 2. KOH | (b) Zinc hydroxide |
| 3. Ca(OH)2 | (c) Calcium hydroxide |
| 4. Zn(OH)2 | (d) Sodium hydroxide |
Answer:
| Bases | Name |
| 1. NaOH | (a) Sodium hydroxide |
| 2. KOH | (b) Potassium hydroxide |
| 3. Ca(OH)2 | (c) Calcium hydroxide |
| 4. Zn(OH)2 | (d) Zinc hydroxide |
Question: 28. Complete the statements with the correct words:
a] Acids – are chemicals which are ….sour…. in teste & derived from plants & …minerals….
b] Bases – are chemicals which are hydroxides [or oxides] of …metals… eg. sodium hydroxide.
c] Salts – are chemicals formed on reaction of a base with an ….acid… giving salt & water.
Question: 29. In the chemical word equation :- Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
a] State the reactants & products of the above reaction. What does the arrow indicate.
b] The molecular equation is : Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 [g]. State what [g] represents.
Answer: (a) The chemical equation for Zinc + Sulphuric acid giving Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen is as follows:
– : End of Elements and Compounds Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-1 :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.